![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What kind of arthritis is degenerative? |
Osteoarthritis
|
|
|
What kind of arthritis is inflammatory? Which of these is seropositive?
|
RA: seropositive |
|
|
What are some kinds of crystal deposition disease/
|
CPPD
Gout |
|
|
What are some of the radiological signs of OA?
|
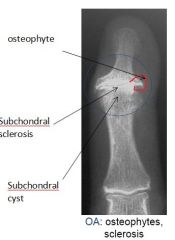
Joint space narrowing
Osteophyte Subchondral sclerosis Subchondral cyst |
|
|
What are some of the radiological signs of inflammatory arthritis?
|
Juxta articular osteopenia
Joint space narrowing Erosions Alignment abnormalities |
|
|
What is the common pathway for conditions causing inflammatory arthritis?
|
Synovitis
Marrow edema Erosion Deformities |
|
|
What is osteopenia?
|
Loss of bone density
In normal bone xray, you can see the cortex on either side. In osteopenia, you see a blurring of the layers |
|
|
What are the ABCS or arthritis?
|
A: alignment
B: bone C: cartilage S: soft tissues |
|
|
What does a film of reactive arthritis look like?
|
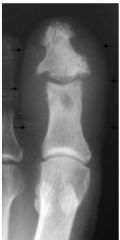
"Sausage digit"
Fusiform swelling of an entire digit |
|
|
What does a film of gout look like?
|
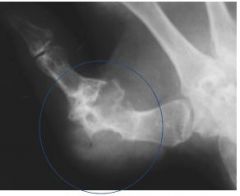
Non-marginal erosions
Asymmetrical soft tissue swelling (tophi) which is just a collection of urate crystals |
|
|
What is a heberden's node? Where is it found?
|
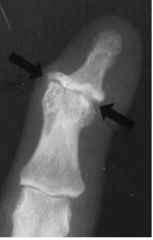
It's a narrowing of the DIP
OA |
|
|
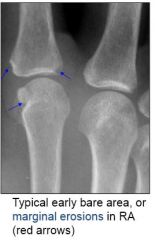
What are the features of RA on plainfilms?
|
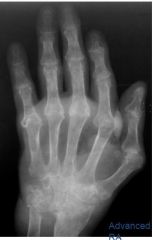
Bare areas, erosions
Uniform joint space narrowing Absence of osteophytes Symmetric Periarticular, diffuse osteopenia Periarticular swelling Subluxations |
|
|
What is a condition that can cause abnormal alignment of the hands without erosions?
|
SLE
|
|
|
Where does psoriatic arthritis target?
|
DIP symmetrically |
|
|
What are the features of psoriatic arthritis?
|
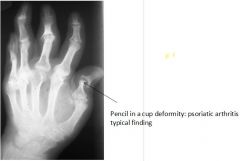
Marginal erosions
Fluffy periositis near involved joints Fusiform soft tissue swelling (sausage digit) PRESERVED MINERALIZATION Sometimes, pencil in a cup! |
|
|
Where does reactive arthritis target?
|
Pauciarticular joints in feet more commonly than hands
SI joints |
|
|
What are the features of reactive arthritis?
|
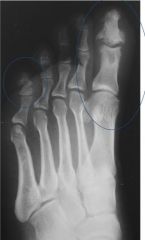
Similar to psoriatic, but more commonly attacks the feet
Fluffy periositis SI joins |
|
|
What are the signs of ankylosing spondylitis on plainfilms?
|
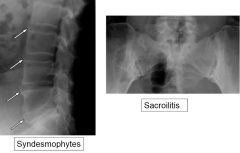
Sacroilitis and Syndesmophytes
|
|
|
Where does ankylosing spondylitis attack?
|
SI joints |
|
|
What are the features of ankylosing spondylitis?
|
Symmetrical SI joint erosions, fusion |
|
|
What crystals are deposited in gout? CPPD? HADD?
|
Gout: monosodium urate |
|
|
Where are the target sites for gout?
|
Great toe MCP
Other asymmetric, pauciartiular sites |
|
|
What are the features of gout on plainfilms?
|
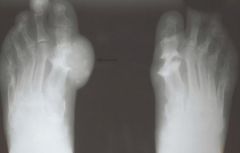
Bone changes late in course
Bizarre, non-marginal erosions TOPHI Bone mineralization is preserved |
|
|
What are some of the malignant tumors of the musculoskeletal system?
|
Malignant: osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, Ewing's ssarcoma |
|
|
What are characteristics of nonaggresive MSK tumors?
|
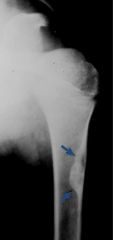
Well defined margins with native bone
No (or mature) periosteal reactions |
|
|
What are characteristics of nonaggresive MSK lesions?
|
Poorly defined margins
Periosteal reaction |
|
|
What are the characteristics of an osteosarcoma?
|
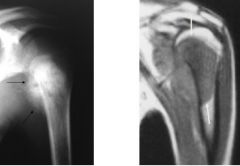
Calcified soft tissue mass
|
|
|
What are the features of a chondrosarcoma?
|
Calcified matrix of cartilage
|
|
|
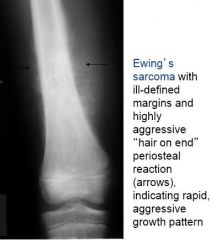
What are the features of Ewing's Sarcoma?
|
Ill-defined margins, permeating bone
Hair on end, sunburst periosteal reaction Large soft tissue expasion |
|
|
Who gets a simple bone cyst?
|
Kids
|
|
|
What is the most common location for a simple bone cyst?
|
Proximal humerus
|
|
|
What are the features of a simple bone cyst?
|
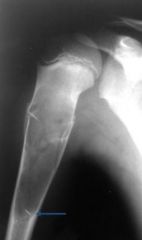
Central lesion
Mildy expansile Sharp margins No periosteal reaction Blue arrow is a fallen fragment, which is a fracture htat has happened through a cyst (pathognomonic) |
|
|
What are the features of a nonossifying fibroma?
|
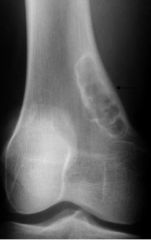
Eccentrically located
Well defined sclerotic margins with ridges |
|
|
What are the features of fibrous dysplasia?
|
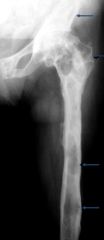
Greyish, homogenous (ground glass) appearance
|
|
|
Where is fibrous dysplasia commonly found?
|
Proximal femur, pelvis
|
|
|
What are the feagures of Paget's disease?
|
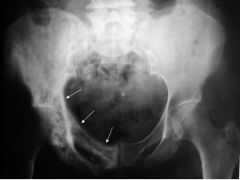
A triad!
-Bone expansion -Trabecular thickening -Cortical thickening |
|
|
What are the features of an osteoid osteoma?
|
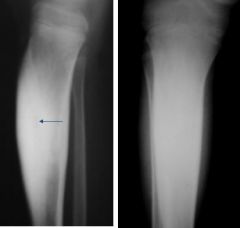
Small, benign
Sclerotic reactive bone |
|
|
What kind of a person gets an osteoid osteoma?
|
Kids, young adults
M>F |
|
|
What kinds of medications does an osteoid osteoma respond to? Why?
|
NSAIDS (asprin)
It produces prostaglandins |
|
|
If someone comes in with a cervical spine fracture, what views should you order?
|
Lateral (most important) |
|
|
What is a hangman's fracture?
|
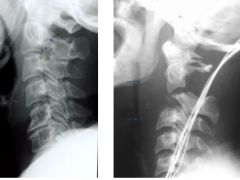
A fracture of the posterior process of C2
|
|
|
What is a Jefferson fracture? What causes this?
|
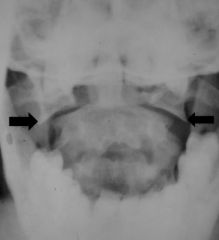
C1 ring fracture with lateral displacement of fragments
Caused by diving into shallow water |
|
|
What kind of fracture is caused by hyperextension? Why is it so crucial?
|
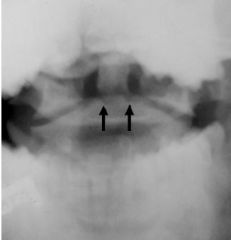
Odontoid
YOU CAN'T MISS THIS. THEY WILL BE PARALYZED IF YOU LET THEM LEAVE! |
|
|
What is the most common kind of shoulder dislocation?
|
Anterior
|
|
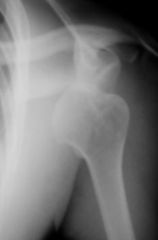
What has happened here?
|
Anterior shoulder dislocation
|
|
|
What direction to hips dislocate?
|
Posterior
|
|
|
What kinds of joints can you see effusions with on plainfilms?
|
Elbows |
|
|
What is a common location for a fracture on the radius?
|
Head |
|
|
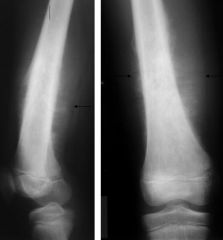
What is the characteristic sign of a radial head fracture?
|
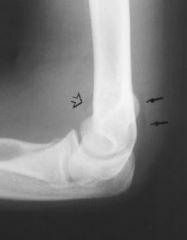
The fat pad sign!
|
|
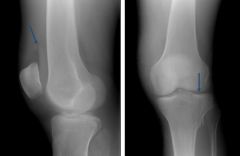
If you see this in the knee, what should you think? What is it?
|
It's lipohemarthrosis: fat from the marrow getting into the joint space
You should always think fracture here |
|
|
What are signs of child abuse on films?
|
Posterior rib fractures |
|
|
What kind of imaging is best for the soft structures of the knee?
|
MRI
|
|
|
Generally, what is the source for osteomyelitis in adults? Kids?
|
Adults: contiguous |
|
|
What are the features of renal osteodystrophy?
|
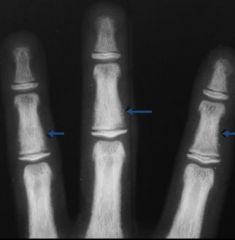
Hyperparathyroidism --> bone resorption
Osteoporosis Osteosclerosis Fuzzy margins of bone |
|
|
What's the best imaging modality for osteonecrosis?
|
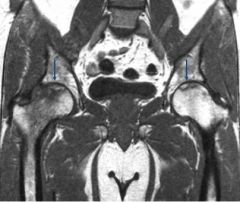
MRI
This may be the most disturbing MRI I've ever seen. |
|
|
What are features of sickle cell disease in the MSK?
|
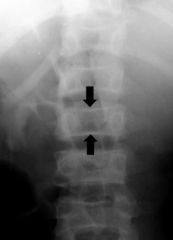
Osteonecrosis
H-shaped depressionin the vertebral bodies |

