![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
4 types of Biological Molecules |
Fats/Lipids, carbs, proteins, nucleic acids (DNA & RNA) |
|
|
|
Chromosome |
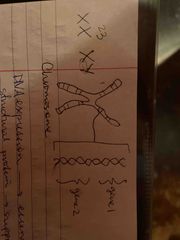
Comprised of DNA and proteins (DNA double helix wound to make chromosomes)
23 distinct PAIRS, each chromosome is 1 long DNA molecule |
Looks like an “X” |
|
|
What takes place in the nucleolus? |
Ribosome synthesis |
|
|
|
Chromatin |
Made up of protein histones |
|
|
|
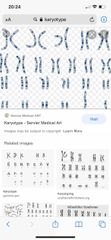
Human karyotype |
See all 23 pairs of chromosomes and what they look like |
|
|
|
Gene |
Units of heredity Genes being expressed in the cytoplasm |
|
|
|
Human genome |
1. All genetic material in the cells (complete set of chromosomes and junk!) 2. Present in every cell in the body (in nucleus) 3. Very large: 3billion bp, >6.5feet of DNA, ~35,000 genes 4. Genes comprise only ~1% of human genome 5. Humans are 99.9% genetically similar (differ by only 3billion bp) 6. Sequence of base pairs determines which trait is expressed |
|
|
|
Types of proteins |
DNA expression- essentially protein production Structural proteins- support us like collagen Hormonal protein- hormone (ex: insulin) Respiratory proteins- transports oxygen (hemoglobin) Enzymes- molecules that increase rate of reaction |
|
|
|
Chargaff’s Rule |
1:1 ratio between adenine and thymine as well as cytosine and guanine (universal rule for all species) |
|
|
|
Who elucidated structure of DNA? |
Watson and Crick (1953) |
|
|
|
Who discovered nuclein in WBC? |
Miescher |
|
|
|
Who discovered 3 parts of nucleotide? What are the parts? |
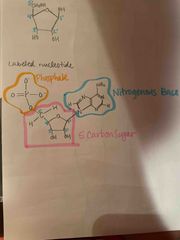
Levine (1919) 1. Phosphate group 2. Deoxyribose sugar (5 carbons) 3. Nitrogenous base |
|
|
|
Alleles |
Alternate versions of genes |
|
|
|
Genotype |
Genetic makeup of an organism (Dictates the phenotype) |
|
|
|
Phenotype |
Outward appearance (red hair color) |
|
|
|
Diploid |
Genetic information of higher organisms is carried in duplicate (2N) |
|
|
|
Heterozygous |
2 copies of a gene could code different information for the same gene (Aa) |
|
|
|
Homozygous |
2 identical copies of the same gene |
|
|
|
Genetic locus |
Specific location where each gene is coded for on a chromatid |
|

