![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mitosis |
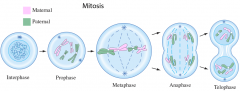
The way body cells divide to create identical cells that are clones (also called copying division). |
|
|
Meiosis |
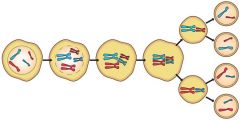
The way sex cells divide to create new cells that are NOT the same as the original cell. |
|
|
Chromosome |

Thread-like structure in cells that carry genetic information. |
|
|
Centrosome |

The area that forms around the centrioles. |
|
|
Centrioles |

The "T"-like shape that forms in centrosomes and what the spindle fibers are connected to. |
|
|
Nuclear membrane |
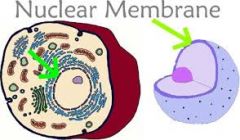
The area that protects the nucleus. |
|
|
Spindle Fibers |
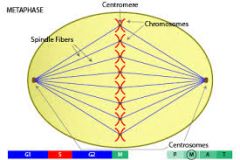
They form a protein structure that divides the genetic material in the cell. |
|
|
Interphase |
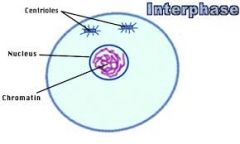
This is the phase of the cell cycle in which a typical cell spends most of its life. During this phase, the cell copies its DNA in preparation for mitosis. Starts with one cell. |
|
|
Prophase |
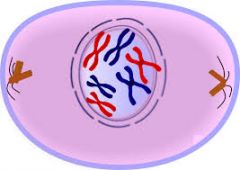
The phase of the cell cycle when chromosomes become visible and the nucleolus and nuclear membrane starts to disappears. Chromosomes pair up. |
|
|
Metaphase |
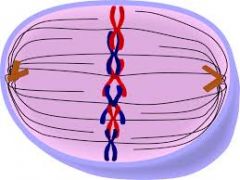
This is the third phase of mitosis. In this phase, the chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell in the spindle fibers. |
|
|
Anaphase |
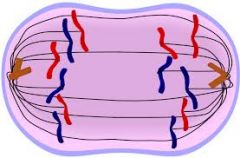
This is the fourth stage of mitosis. In this phase, the duplicated genetic material get seperated ( chromosomes are pulled apart). |
|
|
Telophase |
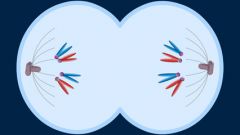
The phase when chromosome sets assemble at the end of each pole as nuclear membrane starts to reform around them. |
|
|
CytoKinesis |
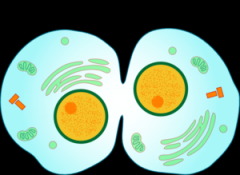
This is the physical process of cell division, which divides the cytoplasm of the parental cell into 2 daughter cells. |

