![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the layers of the Dermis |
Reticular layer (top) Papillary later |
|
|
What is a DVT |
A blood clot in a deep vein in the body |
|
|
Symptoms of a DVT |
Pain Swelling Warm skin Redness |
|
|
What is an aneurism |
A localised abnormal beak spot in a blood vessel |
|
|
Symptoms of an aneurism |
Similar to a stroke |
|
|
Name the 4 layers of the epidermis |
This is the top layer of skin Striatum corneum (top) Striatum granulosum Striatum spirosum Striatum basale |
|
|
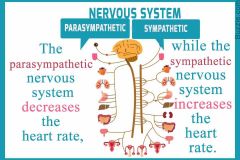
How does the autonomic nervous system affect the heartrate |
The autonomic nervous system sends a signal to the adrenal glands to release adrenaline which increases heartrate |
|
|
Symptoms of a stroke |
Facial drop Dizziness Trouble walking Trouble seeing Spurred speech Confusion Numbness or weakness |
|
|
TBI (traumatic brain injury symptoms) |
Loss or change in consciousness Seizure Unequal dilation of pupils Clear fluid from eyes and ears Nausea and vomiting Slurred speech Leg weakness Balance problems Headache Dizziness |
|
|
Name parts of peripheral nervous system |
Nerves and ganglia outside brain and spinal cord |
|
|
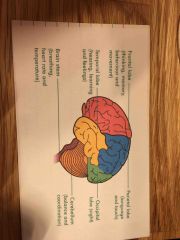
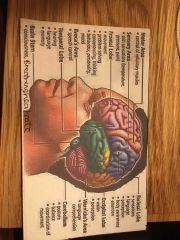
Central nervous system |
Brain and spinal cord |
|
|
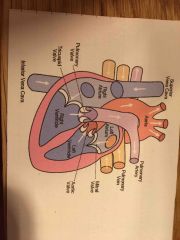
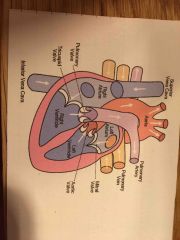
Main function of the heart and cardiovascular system |
To provide cells with oxygen by exchanging gas in lungs and pumping blood around body |
|
|
What is Homeostasis |
Ability of body to maintain a relatively stable internal condition despite the changing environment |
|
|
Blood reaches the lungs via the pulmonary vein and it is deoxygenated. It leaves the lungs oxygenated via the pulmonary artery |
Vein and artery switch |
|
|
What is systole and diastole in blood pressure? |
Systole is the heart when it is pumping Diastole is the heart measure when it is relaxing |
|
|
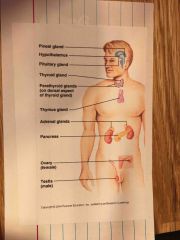
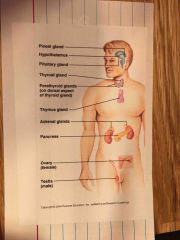
Link of endocrine and central nervous system |
Hypothalmus link between central nervous system and endocrine system it controls pituitary gland and other endocrine glands eg fight or flight adrenal gland |
|
|
Cause if Hepatitis C and how it’s contracted |
Virus that can infect and damage the liver Can contract if come into contact with blood of infected person |
|
|
Cause if Hepatitis C and how it’s contracted |
Virus that can infect and damage the liver Can contract if come into contact with blood of infected person |
|
|
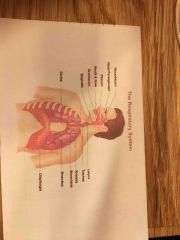
Where is the pharynx located |
Behind the nose and mouth which connects the esophagus |
|
|
What does the diaphragm do |
Separates, heart lungs and digestive system and produces lung inflation and deflation |
|
|
Knee jerk reflex |
A way of checking the central nervous system without a scan as it is an automatic reflex at spinal cord level |
|
|
Hepatitis A symptoms and contracted by |
Viral liver infection Uncommon in England widespread in Africa and India |
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Symptoms of UTI |
Burning feeling when weeing Frequent need to wee Pain pressure in back Feeling tired and shaky Cloudy bloody pee Fever and chills |
|
|
Larynx what do they do |
Vocal cords produce voice when you have laryngitis u cannot speak properly |
|
|
Larynx what do they do |
Vocal cords produce voice when you have laryngitis u cannot speak properly |
|
|
Describe role of epiglottis |
Flap which prevents food from entering larynx and trachea |
|
|
What is cause of cystic fibrosis |
Excessive sticky mucous clogs lungs liver pancreas and intestines
Lower oxygen level in body |
|
|
What is pneumonia |
Infection of the lungs caused by bacteria |
|
|
Early symptoms of diabetes |
Going to the toilet Thirsty Fatigue Weight loss Genital itching Slow wound healing Blurred vision Extreme hunger |
|
|
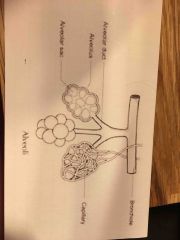
Bronchus |
Extension of windpipe shuttles air in and out of lungs |
|
|
What is the bronchole |
Minute branches of which the bronchus divides |
|
|
Aveoli |
Tiny air sacs which allow rapid gas exchange in lungs |
|
|
Hepatitis B how is it contracted |
Blood and body fluid Unprotected sex Tattoo needles Vaccines |
|
|
Role of trachea |
Cartilaginous tube also called windpipe |
|
|
Things which help reduce diabetes symptoms |
Lose weight Exercise Drink water Follow plant based diet Stress less Don’t smoke |
|
|
Role of autonomic nervous system |
Unconcious function digestion heart rate etc |
|
|
Symptoms of multiple sclerosis |
Visual problems Tingling and numbness Pain and spasms Weakness and fatigue Balance problems Dizziness Bladder issues Sexual dysfunction Cognitive problems |
|
|
What is cardiac arhythmia |
Heart rate to fast or slow |
|
|
What is brachycardia? |
Slow heart rate |
|
|
What’s tachycardia? |
Fast heart rate |
|
|
Symptoms of irregular flutter or fibrillation heart rate |
Chest pain fluttering sensation shortness of breath symptoms like panic attack |
|
|
What’s angina |
A chest pain caused by reduced blood to heart muscles |
|
|
Symptoms of angina |
Dizziness fatigue pain swearing worse with over exertion |
|
|
Purpose of respiration |
Exchange of gassed to provide cells in body with oxygen |
|
|
Respiration controlled by which part of brain |
Medulla oblongata |
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What’s Cheyenne’s stroke breathing |
Abnormal breathing deep and fast can cause breathing to stop (apnea) periodic breathing common in congestive heart failure and sleep apnea |
|
|
Name where main pulse points in body are? |
Wrist Behind ear Groin Behind knee Top of foot Temple area |
|
|
Name the 4 main integumentary system components |
Skin Sweat gland Hair Nails |
|
|
Name the three types of burn and the layers they cross |
First degree mild Second degree effects epidermis and dermis Third gone through dermis to deeper layer (subcutaneous) |
|
|
What’s a pulmonary embolism |
Blockage of artery because of embolism (like blood clot) which has moved from elsewhere in body via blood stream |
|
|
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism |
Coughing up blood Shortness of breath |
|
|
Role of heart valves |
To prevent backflip and allow chambers to fill |
|
|
What is the main role of the endocrine system |
Maintenance of internal environment control of storage and utilisation of energy Regulation of growth and development Body’s response to environmental stimuli |
|
|
Name the two types of bronchitis |
Acute- result of cold Chronic- damage to cilia in bronchial tree from repeated infection |
|
|
Bronchitis symptoms |
Yellow sputum wheezing Long term sinusitis |
|
|
What is the pulse |
Measurement of heart rate |
|
|
What’s the heart rate? |
Speed of heart beat |
|
|
Blood pressure |
How much pressure being used to pump |
|
|
What’s the function of the skin? |
Protects deeper tissue from Mechanical damage, bumps Chemical damage- acid alkaline Bacterial damage Ultraviolet light Thermal damage Dedication drying out |
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Which side of the body is the liver located? |
Right side |
|
|
What is the approximate size and weight of the liver? |
3 pounds and size of football |
|
|
The liver is divided Into two lobes the right and left which one is Smaller? |
Left due to heart |
|
|
There are two smaller lines of the liver what are they? |
The caudate and the quadrite |
|
|
What does the liver manufacture food into? |
Chemicals |
|
|
The body refined nutrients and drugs why? |
So they can be absorbed by the body |

