![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Cells
|
The most basic unit of life
|
|
|
|
Diffusion
|
Through membrane, Works
for small molecules like gas |
|
|
|
Osmosis
|
diffusion of water through the
membrane |
|
|
|
Phagocytosis
|
cell eating
|
|
|
|
Peptidoglycan
|
a complex polysaccharride found in the cell walls of bacteria
|
|
|
|
Mycolic Acid
|
cord factor in atypical cell wall, pathogenicity, basis for acid-fast stain.
|
|
|
|
Nucleoid
|
dense area that contains DNA coiled around a protein
|
|
|
|
Inclusion Bodies
|
allow the cell to store nutrients and macromolecules. some are used for identification of bacteria
|
|
|
|
endospores (prokaryotes)
|
highly durable cells with thick walls. can go dormant. very hard to kill
|
|
|
|
hyphea
|
long, filamentous shape in molds
|
|
|
|
saprobes/saprophytes
|
fungi that live off of dead organic matter
|
|
|
|
trophozoite
|
protozoa in their motile feeding stage
|
|
|
|
cyst
|
protozoa enter a dormant resting stage when conditions are unfavorable for growth & feeding
|
|
|
|
conjugation
|
to reproduce sexually
|
|
|
|
naked virus
|
non-enveloped virus.
|
|
|
|
enveloped virus
|
forms envelope from budding out of host cell membranes and taking some of the membrane with it.
|
|
|
|
which microbes are eukaryotes?
|
Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals
|
|
|
|
which microbes are prokaryotes?
|
Bacteria & Archaea
|
|
|
|
what are yeasts considered? (prokaryotic/eukaryotic)
|
eukaryotic
|
|
|
|
what are chlamydia considered? (prokaryotic/eukaryotic)
|
prokaryotic
|
|
|
|
what are mycoplasma considered? (prokaryotic/eukaryotic)
|
prokaryotic
|
|
|
|
cytoplasm (eukaryotes)
|
substance inside of plasma membrane and outside of nucleus.
|
|
|
|
cytosol (eukaryotes)
|
liquid or fluid portion of the cell, also contains structural support in the form of the cytoskeleton.
|
|
|
|
nucleus (eukaryotes)
|
command and control center of the cell
|
|
|
|
nuclear envelope (eukaryotes)
|
double membrane that surrounds the nuclear surface
|
|
|
|
ribosomes (eukaryotes)
|
"read" RNA and translate them into proteins.
|
|
|
|
endoplasmic reticulum (eukaryotes)
|
extensive system of internal membranes made by folding the plasma membrane
|
|
|
|
rough ER (eukaryotes)
|
used for protein synthesis, embedded ribosomes.
|
|
|
|
Smooth ER (eukaryotes)
|
aids in manufacture of carbohydrates and lipids.
|
|
|
|
Golgi complex (eukaryotes)
|
-Modify molecules
-Packages molecules in vacuoles -Distribute the molecules to the end destination |
|
|
|
lysosomes (eukaryotes)
|
the stomach of the cell. digests proteins, carbs, and fats.
|
|
|
|
lysosomes play a role in what?
|
decomposition
|
|
|
|
lysosomes are found in what cells?
|
animal cells
|
|
|
|
what is the acidic environment that degrades lysosomes?
|
pH of 5
|
|
|
|
peroxisomes are responsible for what process after death?
|
autolysis
|
|
|
|
how is decomposition different from putrefaction?
|
putrefaction involves microbes
|
|
|
|
peroxisomes (eukaryotes)
|
small organelles that contain oxidases and catalase, functions in fatty acid oxidation.
|
|
|
|
mitochondria (eukaryotes)
|
cellular powerhouses, sites for chemical reactions, makes ATP for the cell to use.
|
|
|
|
mitochondria break the _________ bonds in sugars
|
covalent
|
|
|
|
chloroplasts are only found in _________ & many __________ cells.
|
plant & many protist cells
|
|
|
|
central vacuoles are only found in what kind of cells?
|
plant cells
|
|
|
|
centrioles are only found in ___________ cells.
|
animal cells
|
|
|
|
fimbriae
|
hair-like appendages usually covering the surface of cell. helps with adherence to surfaces and other cells
|
|
|
|
flagella
|
long filamentous appendage that propels the bacterium. Allows bacteria to move toward or away from some stimulus.
|
|
|
|
monotrichous
|
single flagellum at one end
|
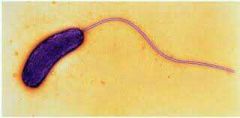
|
|
|
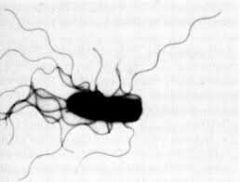
Lophotrichous
|
small bunches of flagellum arising from one end of cell
|
|
|
|
Amphitrichous
|
Flagella at both ends of cell
|
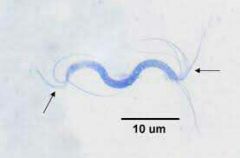
|
|
|
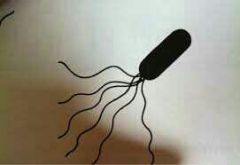
Peritrichous
|
Flagella dispersed over surface of cell; slowest.
|
|
|
|
Atrichous
|
No flagella
|
|
|
|
Pili
|
longer than fimbriae, only a few per cell. They allow cells to pass DNA from one cell to another.
|
|
|
|
bacteria cells secrete ___________ on their surface in either a capsule or a sticky slime layer |
glycocalyx
|
|
|
|
function of glycocalyx
|
facilitates attachment to surfaces, aids in formation of biofilms, protects bacterium from drying out and from phagocytosis.
|
|
|
|
bacteria cell wall
|
semi-rigid, composed of peptidoglycan.
Maintains cell shape and keeps cell from rupturing when water pressure inside is greater than outside |
|
|
|
why is the cell wall a good target for antimicrobial agents?
|
because eukayotic cells do not have peptidoglycan in their cell walls
|
|
|
|
gram positive cell walls
|
-THICK peptidoglycan layer.
-one cell membrane -stain purple using gram stain. -teichtoic acids. |
|
|
|
gram negative
|
-THIN peptidoglycan layer
-two cell membranes (inner and outer) -lipopolysaccharides in outer membrane -stain pink using gram stain |
|
|
|
chloroplasts are unique to ____________
|
plants
|
|
|
|
chloroplasts contain a pigment called ______________
|
chlorophyll
|
|
|
|
chlorophyll is responsible for...
|
gathering energy from light during photosynthesis.
|
|
|
|
eukaryotic cells that are NOT plants, but still contain chloroplast...
|
some protozoa and algae
|
|
|
|
functions of the center vacuole in plant cells...
|
stores water, ions, nutrients and wastes.
regulates turgor pressure through osmosis. |
|
|
|
Diplococci
|
cells remain in pairs
|
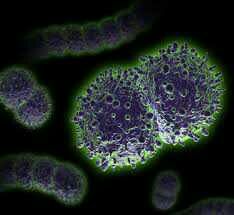
|
|
|
streptococci
|
cells remain attached in chains
|
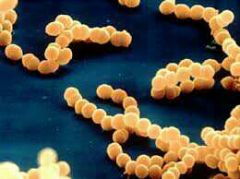
|
|
|
Tetrads
|
four cells in one plane (flat)
|
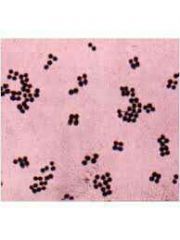
|
|
|
sarcinae
|
eight cells in two planes (cube-shaped)
|

|
|
|
staphylococci
|
many cells in many planes
|
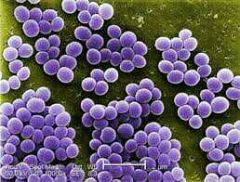
|
|
|
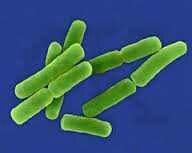
diplobacilli
|
cells remain in pairs after replication
|
|
|
|
streptobacilli
|
cells remain in chains after replication
|
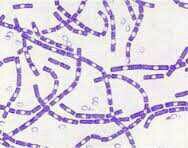
|
|
|
palisades
|
partially fused to the mother cell after replication.
|
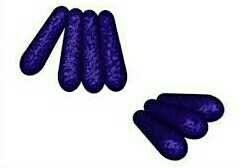
|
|
|
coccobacillus
|
intermediate shape between cocci and bacillus
|
|
|
|
the phospholipid bilayer of a eukaryotic cell is the _____________
|
plasma membrane
|
|
|
|
the three shapes of bacteria
|
1. cocci
2.bacillus 3. spiral |
|
|
|
cocci is a _________ shape
|
spherical
|
|
|
|
bacillus is a _______ shape.
|
rod
|
|
|
|
vibrios
|
curved rods
|
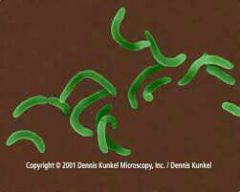
|
|
|
spirichetes
|
helical and flexible
|
|
|
|
spirilla
|
helical, corkscrew shapes
|
|
|
|
atypical cell walls
|
Lack typical cell wall structure.
|
|
|
|
What cellular structure is stained in a Gram Stain?
|
gram positive and gram negative cell walls
|
|
|
|
What cellular structure is stained in the acid-fast stain?
|
atypical cell walls
|
|
|
|
what bacteria are stained using the acid-fast stain?
|
mycobacterium and nocardia
|
|
|
|
why are mycoplasma unique?
|
they have no cell walls, no peptidoglycan not affected by penicillin
|
|
|
|
rickettsia are transmitted through ___________ and are what kind of parasite?
|
-arthropods
-obligate intracellular parasite |
|
|
|
Coxiella burnetii, which causes _________, is transmitted by ________&________ and forms ___________.
|
-Q Fever
- contaminated raw milk & aerosols - spores |
|
|
|
chlamydia causes _____ in the US and ________ in 3rd world countries.
|
-STDs
-blindness |
|
|
|
coxiella burnetii is NOT transmitted by _______________.
|
insects
|
|
|
|
fungi reproduce asexually using ______________ &_____________(spore names), budding and mitosis.
|
1. Conidia
2. sporangiospores |
|
|
|
what are the three fungal sexual spores?
|
1. zygospores
2. ascospores 3. basidospores |
|
|
|
viruses contain EITHER ______ or _______
|
DNA or RNA
(living cells contain both) |
|

