![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
132 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What color is and uninoculated TSIA |
Red |
|
|
What color is an uninoculated LIA? |
Purple |
|
|
Yellow clearings around a colony on a blood agar plate indicates what type of hemolysis? |
beta hemolysis |
|
|
What shape are coliforms? |
coliforms are rod shaped |
|
|
Are coliforms Gram + or Gram -? |
Coliforms are Gram - |
|
|
What are some examples of simple stains? |
crystal violet, safrainin, methylene blue |
|
|
Are coliforms lactose fermentors? |
yes, but there are exceptions |
|
|
Do coliforms form spores? |
No |
|
|
What does a positive oxidase test tell you? |
That the organism is + for cytochrome C; the + test result will appear blue |
|
|
What is the reason for streaking on a TSA plate? (3) |
Isolate pure colonies Check colony morphology Check for contamination |
|
|
What media is used to determine if there is amylase activity? |
Starch agar |
|
|
Which types of media and methods allow for growth of anaerobic organisms? (3) |
TSA plates in anaerobic jars TSA deeps thioglycolate media |
|
|
What does TTC do? |
TTC is used as alternative electron acceptor to O2 |
|
|
What is MRS selective media selective for and what type of pH tolerance? |
MRS plates select for Lactobacillis and low pH |
|
|
What is an example of a negative staining procedure? |
capsule staining |
|
|
What color are Salmonella colonies when grown on BGA plates? |
Salmonella colonies are red when grown on BGA plates |
|
|
What color is P. vulgaris on BGA plates? |
P. vulgaris is yellow on BGA plates (this is also true of stuff that isn't salmonella) |
|
|
What does the capsule do? (2) |
Prevents phagocytosis assists in adhesion
|
|
|
What is serving as the inoculum in the yogurt fermentation lab? |
yogurt |
|
|
What is serving as the inoculum in the cabbage fermentation? |
The bacteria already present on the cabbage is the inoculum |
|
|
What is the purpose of iodine in the Gram stain procedure? |
Iodine acts as the mordant (it fixes the stain) |
|
|
What is the purpose of alcohol (ethanol) in the Gram stain procedure? |
Alcohol removes excess dye |
|
|
Does a Gram - cell have a thinner or thicker petidoglycan cell wall in comparison to a Gram + cells? |
Gram - cells have a thinner peptidoglycan wall compared to a Gram + cell |
|
|
Is B. megaterium Gram - or Gram + |
B. megaterium is Gram + |
|
|
In the ethanol rinse step in Gram staining, why should you not rinse for too long of a time with ethanol? |
because the ethanol will remove stain from Gram + cells if left on too long |
|
|
Under what conditions did we ferment the sauerkraut? What was the purpose of these conditions? |
The sauerkraut was fermented under anaerobic conditions; this was done because the bacteria this lab was selecting for ferment under anaerobic conditions |
|
|
Lactic acid is the result of fermentation of...? |
Simple sugars |
|
|
What is the purpose of the Durham tube? |
It tests if gas is present |
|
|
What are some methods that you can use to sterilize your culture/media? |
Autoclave Flame Alcohol |
|
|
What bio safety level has low individual risk and low community risk? |
level 1 |
|
|
Which of the two types of microscopy used in this laboratory would one use to view a stained bacterial slide? |
Bright field microscopy |
|
|
If the digits on a P1000 micropipettor read: 027, What is the volume expressed? |
270µm |
|
|
What are TSA plates used for? |
To grow colonies |
|
|
What are TSA slants used for? |
To grow more bacteria and for long term storage |
|
|
What are TSB used for? |
TSB is used to grow pure colonies |
|
|
How are Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) plates selective and how are they differential? |
EMB plates are selective for Gram - bacteria EMB plates are differential for lactose fermentors |
|
|
Why does the Presence - Absence broth turn yellow in the presence of coliforms? |
If coliforms are present, the P-A broth turns yellow. This is because the coliforms ferment lactose and produce an acidic byproduct. The acid causes the Bromcresol Purple to change color. |
|
|
What do lactose fermentors look like on EMB plates? |
Lactose fermentors on EMB plates are colonies with a dark center; or green with a metalic sheen (E. coli/bacteria that produce a lot of acid) |
|
|
What do non-lactose fermentors on EMB plates look like? |
Non-lactose fermentors on EMB plates have pink colonies |
|
|
What was the purpose of incubating the spinach sample in the lactose broth? |
This was the pre-enrichment step; this increased the number of Salmonella; lactose fermentors die off when the pH gets too low and Salmonella is left behind |
|
|
What was the purpose of the TGBG broth in the salmonella lab? |
The TGBG broth was part of the selective enrichment phase. The tetrathionate, bile salts and brilliant green kill off the stuff that isn't Salmonella |
|
|
How does Salmonella appear on BGA (brilliant green agar) plates? |
Salmonella appears red on BGA plates |
|
|
Why are Salmonella colonies red on BGA plates? |
BGA plates contain lactose and sucrose with a phenol red indicator. Salmonella cannot ferment either lactose or sucrose so salmonella colonies are red on BGA plates |
|
|
What was the purpose of the selective plating on BGA plates in the salmonella lab? |
The selective plating on BGA plates isolate salmonella cultures |
|

What flagella arrangement is this? |
Monotrichous |
|

What flagella arrangement is this? |
Lophotrichous |
|

What flagella arrangement is this? |
Amphitrichous |
|
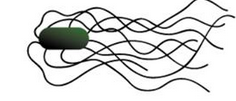
What flagella arrangement is this? |
Peritricious |
|
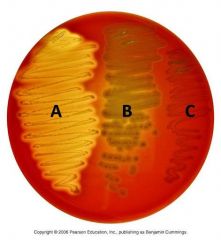
What type of hemolysis is represented by A? |
Beta hemolysis. The hemoglobin is completely destroyed by the exotoxin protein, hemolysin. |
|
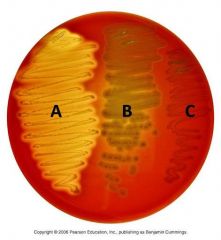
What type of hemolysis is represented by B? |
Alpha hemolysis. The incomplete lysis of red blood cells. Generally caused by preoxides produced by the bacterium |
|
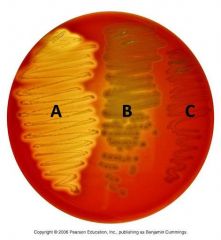
What type of hemolysis is represented by C? |
Gamma hemolysis. The colonies do not change color. |
|
|
What are the eye holes of a microscope called? |
Ocular objectives |
|
|
What are the different magnification lenses on a microscope called? |
Objectives |
|
|
What does the Presence-Absence broth tell you? |
Just whether or not coliforms are present. The P-A broth does not tell you about the level of coliform contamination. |
|
|
What is the purpose of the mineral oil overlay in the Hugh-Leifson media? |
The oil layer prevents oxygen from reaching the microbe |
|
|
What does CFU stand for? |
Colony forming units |
|
|
What does TBGB do? |
It allows for the proliferation of S. typhimurium It inhibits the growth on competing non-salmonella organisms |
|
|
You innoculate a BGA plate from a food sample enriched in TBGB broth and observe a yellow color change. What does this indicate? |
The microbe is not salmonella The microbe ferments lactose or sucrose |
|
|
How does TTC agar work? |
TTC tests for motility. Organisms that are motile spread out from the source of inoculation and organisms that are not motile stay in the inoculation lane. The TTC acts as an electron acceptor in place of oxygen and causes a colored precipitate to form. |
|
|
What to amylases break down? |
Starch |
|
|
What do hydrolases break down? |
Chemical bonds; they add water |
|
|
What is the bacterial extracellular capsule composed of? |
polysaccharides |
|
|
What are the two ways to determine if a bacteria is motile or not? |
A wet mount on phase contrast TTC media |
|
|
What is the main benefit of an uninoculated control? |
The uninoculated control tells if there is contamination is present. It can also show what a negative result should look like. |
|
|
What enzyme aids in transporting electrons to O2 in aerobic organisms? |
Cytochrome-C oxidase |
|
|
What is broken down in beta hemolysis? |
hemoglobin |
|
|
What is the main purpose of the LIA slant test? |
Lysine metabolism; the LIA is used for differentiating organisms based on their ability to decarboxylate or deaminate lysine |
|
|
When are micropipettors most precise? |
Micropipettors are most precise towards their upper range |
|
|
How many µL in 1 mL? |
There are 1000 µL in 1 mL |
|
|
What is bright field microscopy used for? |
Inanimate objects and stained cells |
|
|
What is phase contrast microscopy used for? |
Live and unstained bacteria |
|
|
What does 1 division on a stage micrometer equal always? |
1 division on a stage micrometer = 10 µm always |
|
|
How do you calculated the calibration constant? |
stage divisions/ocular divisions X 10 µm = calibration constant |
|
|
Can you use the calibration constant for different magnification levels? |
No, the calibration constant is only valid for a specific magnification level |
|
|
What is the equation for determining the number of cells after preforming a serial dilution? |
#cells/mL = (total cells counted/number of squares counted) x dilution factor x 1x10^4 (constant) |
|
|
What do ST plates select for? |
ST plates have sucrose and select for S. thermophiles |
|
|
What do tomato juice (TJ) plates select for? |
TJ plates are acidic and select for acidophiles; can select for lactobacillus or Leuconostoc sp. |
|
|
What does the indole part of the IMViC test? |
The "I" part of the IMViC tests if tryptophan is metabolized by tryptophanase |
|
|
What does the indole test look like if the test is positive? |
The solution turns red when the Kovac's reagent is added |
|
|
What does the Methyl Red test in the IMViC determine? |
The methyl red tests the pH of the fermentation products. |
|
|
What does a positive methyl red test look like? |
The solution turns red; this means there are acidic products |
|

What does this methyl red result indicate? |
The products of glucose fermentation are acidic |
|

What does this methyl red result indicate? |
The products of glucose fermentation are neutral - alkali |
|
|
What is the purpose of the Voges-Proskauer (VP) test? |
The Vogues-Proskauer test determines whether or not 2,3 butane diol is formed |
|

What does this VP result indicate? |
A red (+) VP result means that the neutral 2,3 butane diol is present and butylene glycol fermentation occurs |
|

What does this VP result indicate? |
A clear/yellow (-) VP result means that 2,3 butane diol is not present |
|
|
What does the phenol red broth contain? |
The phenol red broth contains peptone, a Durham tube, a sugar and a phenol red indicator |
|
|
What does the phenol red broth test for? |
Sugar and protein metabolism |
|

What does this phenol red broth test result show? |
The bacteria is not able to ferment the sugar but is able to metabolize the protein. The pH is raised. |
|

What does this phenol red broth test result show? |
The bacteria is able to ferment the sugar and the pH is lowered. Gas is also produced. |
|
|
What does the in Citrate portion of the IMViC test determine? |
The in Citrate test determines is the bacteria can use ammonia as the sole nitrogen source and citrate as the sole carbon source |
|

What does this Citrate result mean? |
The blue Citrate tube means that growth has occurred (+) and that the bacteria can use citrate as the sole carbon source and ammonia as the sole nitrogen source |
|
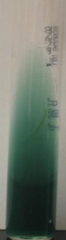
What does this Citrate result mean? |
The green Citrate tube means that growth has not occurred (-) and that the bacteria cannot use citrate and ammonia as the sole carbon and nitrogen sources |
|
|
What is the purpose of the Hugh-Leifson glucose oxidation/fermentation test? |
The Hugh-Leifson test determines between aerobic oxidation and anaerobic fermentation |
|

What does this Hugh-Leifson glucose oxidation/ fermentation test indicate? |
The bacteria ferments and oxidizes glucose (+) |
|

What does this Hugh-Leifson glucose oxidation/ fermentation test indicate? |
The bacteria is only able to oxidize glucose |
|

Is this bacteria motile or not motile? |
this bacteria is not motile |
|

What does this TTC test result show? |
The bacteria is motile |
|
|
What is the big limitation of using TTC? |
You can only use it with bacteria that are capable of aerobic respiration |
|
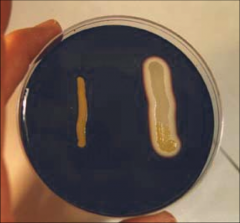
What does this result determine right side bacteria grown on starch agar? |
The bacteria on the right side is capable of amylase exoenzyme production as evidenced by the color change. |
|
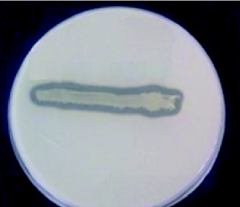
What does this growth pattern on casein agar indicate? |
The clearing pattern surrounding the bacteria growing on casein agar indicates that this bacteria is capable of producing the caseinase exoenzyme |
|
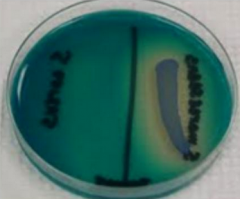
What does this growth pattern on DNase agar indicate? |
The clearing zone surrounding the bacteria growing on DNase agar indicates that this bacteria produced the exoenzyme DNase |
|
|
What do the MacConkey MUG agar plates test for? |
Lactase production |
|
|
How is does the MacConkey MUG agar plate show if lactase is present or not? |
In bacteria that produce the lactase exoenzyme, the sugar derivatives are visible under UV light. They fluoresce. |
|
|
What is in TSIA? |
Glucose, sucrose, lactose and a pH indicator |
|
|
What is in LIA? |
Dextrose, a pH indicator and lysine |
|
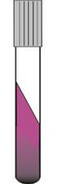
What does this LIA result indicate? |
The purple slant and black butt indicates - lysine deamination, + lysine decarboxylation |
|
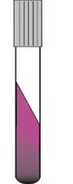
What is this LIA result indicative of? |
The purple slant and black butt LIA result is indicative of salmonella |
|

What does this LIA result indicate? |
The red slant and yellow butt indicates + lysine deamination and - lyside decarboxylation |
|

What is this LIA result indicative of? |
The red slant and yellow butt LIA result is indicative of P. vulgaris |
|

What type of microbial growth is this? |
Strict aerobe |
|
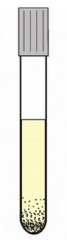
What type of microbial growth is this? |
Strict anaerobe |
|

What type of microbial growth is this? |
facultative aerobe |
|

What type of microbial growth is this? |
microaerophilic aerobe |
|
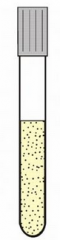
What type of microbial growth is this? |
Aerotolerant anaerobe |
|
|
What color will the LIA slant turn if lysine deamination occurs? |
Red |
|
|
What color will the LIA butt turn is lysine decarboxylation occurs? |
Yellow |
|

What does a Red/Red TSIA result indicate? |
A red slant and red butt on a TSIA indicates that no fermentation has occurred. |
|

What does a yellow/yellow + gas TSIA result indicate? |
A yellow slant and a yellow butt of a TSIA indicates that sugar fermentation has occurred with gas production |
|

What does a red/yellow TSIA result indicate? |
A red slant and yellow butt TSIA indicates that glucose fermentation has occurred |
|

What does a red/black TSIA result indicate? |
A red slant and black butt TSIA indicates that glucose fermentation has occurred and H2S precipitate has formed |
|
|
What does a yellow TSIA indicate? |
Acid production |
|
|
What does a red TSIA indicate? |
Alkaline production |
|
|
What does the catalase test test for? |
The presence of catalase |
|
|
What does a positive catalase test look like? |

Bubbles form |
|
|
What does catalase do? |
Catalase degrades hydrogen peroxide |
|
|
What doe MSA plates select for? |
MSA plates select for Streptococcus mitis, S. salivarius and Enterococcus spp. |
|
|
What do MSA plates inhibit the growth of? |
MSA plates inhibit the growth of Gram + organisms (via the crystal violet stain) |
|
|
How do you compare antibiotic efficiency? |
The size of the clearing zone surrounding the antibiotic is proportional to the efficiency of the antibiotic |
|
|
Define enteric bacteria |
Enteric bacteria are gram -, non-sporulating rods, facultative anaerobes that live in the digestive tracts of animals |
|
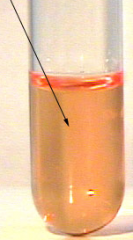
What does this urea broth test indicate? |
This is a negative urea broth test. It indicates that the microbe is not able to produce the exoenzyme urease. |
|

What does this urea broth test result indicate? |
This is a positive urea broth test result. A positive result indicates that the exoenzyme urease is produced. The pink indicates an alkaline environment. |

