![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the first and last thing that you should do in lab? |
Wash your hands with antibacterial soap |
|
|
What is used to disinfect the tables? |
isopropanol
|
|
|
What is a growth medium? |
Contains nutrients to support microbial growth |
|
|
Compare nutrient agar (NA) and Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA), withrespect to composition and which type of organism is favored for growth. |
Nutrient Agar Composition: pH of 6.8; contains nutrients Favored growth: bacteria SDA –Sabouraud Dextrose Agar Composition: pH of 5.8; higher dextrose context of 4% Favored growth: fungal growth |
|
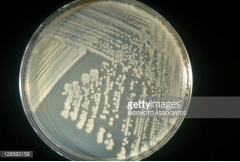
What kind of growth is this? What growth medium? |
Bacterial Growth - Nutrient Agar |
|
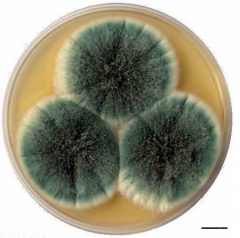
What kind of growth is this? What kind of medium? |
Fungal Growth - SDA - Sabouraud Dextrose Agar |
|
|
Describe howto practice ‘aseptic technique’ and explain why it is important to achieveaseptic technique in the microbiology lab. |
Disinfection: bench tops disinfected with isopropanol Sterilization: Inoculating tools aresterilized by incineration Importance: To ensure safety, prevent the spread of infection,minimize risks and ensure that our experiments are safely executed |
|
|
What is "aseptic technique"? |
A method designed to prevent contamination from microorganisms. |
|
|
Difference between Light and Electron microscopes |
Light: uses visible light as a source of illumination Electron: uses an electron beam for illumination; magnetsfocus the beam |
|
|
Difference between Simple and Compound Microscope |
Simple:(magnifying glass); only one lens Magnifies up to~300x Compound:(Jansen); multiple lens1. Magnifies up to1000x |
|
|
Difference between TEM and SEM |
TEM –Transmission Electron Microscope Up to 1 million x Studies cellinterior SEM –Scanning Electron Microscope 3-D views ofobjects in great detail |
|
|
Advantages and Disadvantages of Light microscope |
Advantage: Can beused to view living specimen Disadvantage:lower magnification potential |
|
|
Advantages and Disadvantages of Electron Microscope |
Advantages: canmagnify up to 1 million x, studying inside the well and give a 3-d view Disadvantages:cannot view living specimen |
|
|
Total Magnification = |
Total Magnification = ocular lens x objective lens |
|
|
Care steps for microscope (3 things) |
Use Lens paper toclean Low power: coarseand fine adjustment to focus High power oroil: fine adjustment ONLY |
|
|
Storage steps for microscope |
Allow bulb tocool before moving Place back toscanning objective lens, coil cord, and carry with two hands |
|
|
What are the 6 I's of Media Inoculation? |
Inoculation, Incubation, Isolation, Inspection, Information Gathering, Identification |
|
|
Inoculation |
Sample is transferred to the growth medium- providesample nutrients and space; may be solid or liquid Tools: sterile swabs, inoculating loop, inoculatingneedle |
|
|
Incubation |
Allow microbes to grow at optimum temperature (20-40C; 68-104 F) Cell #’s rapidly increase Tools: incubator or at room temperature |
|
|
Isolation |
Form individual colonies leading to a pure culture Tools: Streak plate technique |
|
|
Inspection |
Look at microbe for micro and macro characteristics 1. Micro –shape, arrangement, stain results.. 2. Macro –colony morphology, color, smell, consistency |
|
|
Information Gathering |
Perform additional tests |
|
|
Identification |
Use inspection and info to identify species |
|
|
Colony |
contains a single type of bacteria |
|
|
pure culture |
a single species present in medium |
|
|
What is a broth used for? What is the proper way to innoculate? |
a. used to grow large numbers quickly i. Use sterile loop to transfer sample from brothculture into sterile broth. |
|
|
What is a plate used for? What is the proper way to innoculate? |
a. used for isolating and determining colony morphology i. Perform the streak technique as demonstrated byinstructor. ii. Be sure to sterilize the loop between each successivesection. |
|
|
What is a slant used for? What is the proper way to innoculate? |
a. same use as plate, but conserves material and space i. Use sterile loop to obtain sample from broth culture. ii. Position loop at base of slant surface; zig-zagupward over surface. |
|
|
What is a deep tube used for? What is the proper way to innoculate? |
a. may be solid or semi-solid; used to determine O2requirements, motility i. Use sterile needle to obtain sample from brothculture. ii. Perform stab by inserting needle into center of deepand extending downward almost to the bottom. iii. Withdraw needle up through same pathway |
|
|
Distinguishbetween a pure culture and a mixed/contaminated culture. |
A pureculture is one in which only one kind of microbial species is found whereas inmixed culture two or more microbial species formed colonies. |
|
|
Difference between Negative and Positive (Direct) stain |
Negative Stain Acidic stain (-)adheres to glass slide (+) Clear area (cell)contrasts with opaque background Positive (Direct)stain Basic stain (+)adheres to bacterial cell wall (-) |
|
|
Negative stain dyes |
Colors: Nigrosin,Congo Red, India ink |
|
|
Positive stain dyes |
Colors: Crystalviolet, safranin, methylene blue, malachite green, others |
|
|
What advantage does a negative stain have over apositive stain? |
you are able toview the cells without risk of them being damaged or distorted as they might bewith a positive stain |
|
|
What is thepurpose of heat fixation when preparing a smear? |
Will cause the bacteria to adhere to the slide and not be rinsed off as easily during the staining process |
|
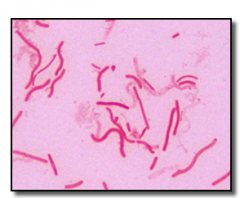
Is this a positive or negative stain? |
positive |
|
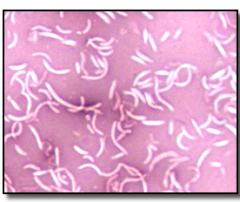
Is this a positive or negative stain |
negative |
|
|
What is the difference between true motility and Brownian movement? |
True motility achieved by rotation of flagella Brownianmovement motion due to collision with molecules of surroundmedium flagella are too thin to be seen with the compoundlight microscope |
|
|
What are the 3 lab procedures where bacterial motility can be determined? |
a. Flagella Stain b. Semi-solid Media c. Handing DropProcedure |
|
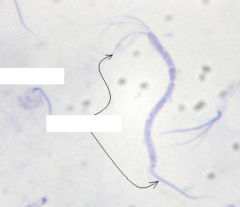
What is this? |
Spirillum volutans Morphology: amphitrichous flagella |
|
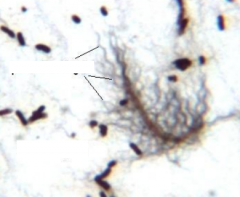
|
Proteus vulgaris Morphology: Peritrichous flagella |
|
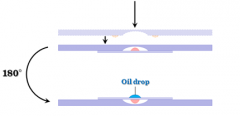
What is this? What does it do? |
Hanging drop procedure? Used to determine motility |
|
|
What are culture characteristics?
|
i. Unique growth pattern of a particular bacterialspecies exhibited on different forms of media such as broth deep and plate ii. Used to help distinguish between types of bacteriaand to identify species iii. Must be combined with other characteristics(staining, biochemical) to completely identify bacterial species |
|
|
What is motility agar? |
Like agar deep but less agar Motile: growth spread through semi-solid agar Non-motile: growth only along stab line; no spreading |
|
|
What characteristics can a broth tube identify? |
Turbid, Sediment, Pellicle, Ring or Flocculent |
|
|
Describe the following: Turbid: Sediment: Pellicle: Ring: Flocculent: |
Turbid: cloudy Sediment: collection at bottom Pellicle: film on surface Ring: ring around perimeter of surface Flocculent: flakes or small masses throughout |
|
|
What characteristics can agar deep tubes identify? |
Obligate aerobe Surfacegrowth (needs oxygen) Facultative anaerobe Growththroughout but most on surface |
|
|
Kingdom of Yeasts and molds |
Fungi |
|
|
Properties of Yeasts |
Single-celled Oval shape Reproduce by budding (asexually) |
|
|
Properties of Molds |
Multi-cellular Consists of filamentous hyphae Reproduce by forming spores |
|
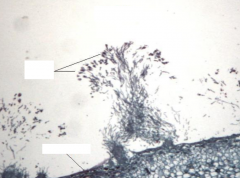
Identify and list properties |
Penicillium Mold Produced penicillin Has conidia – always asexual |
|
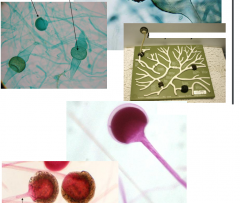
Identify and list properties |
Rhizopus i. Mold ii. Has sporangiospores enclosed within sporangia iii. Has zygospores Sexual – on zygospores Asexual – on hyphae |
|
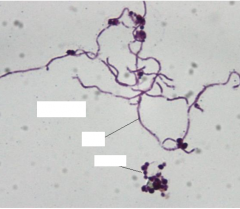
Identify and list properties |
Candidaalbicans Yeast with hyphae Dimorphic Budding - asexual |
|
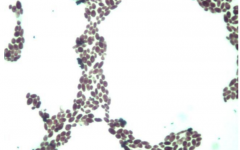
Identify and list properties |
Saccharomyces Yeast Used in bread and beer making (baker’s yeast) Budding – asexual |

