![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Metabolism |
All of the chemical reactions inside a cell |
|
|
|
Exergonic Reactions |
Reactions that are spontaneous and release energy |
|
|
|
Endergonic Reactions |
Require energy to proceed |
|
|
|
Anabolism |
Endergonic pathways converting simple molecular building blocks into more complex |
|
|
|
Catabolism |
Exergonic pathways that break down complex molecules into simpler ones |
|
|
|
Oxidation Reaction |
Reactions that remove electrons from donor molecules leaving them oxidized |
|
|
|
Reduction Reaction |
Adding electrons to acceptor molecules leaving them reduced |
|
|
|
Redox Reactions |
Pairing an oxidation reaction with a reduction reaction |
Oxidation-reduction Reactions |
|
|
ATP |
Adenosine Triphosphate |
Energy Currency |
|
|
ADP |
Adenosine Diphosphate |
When the 3rd phosphate falls off of ATP |
|
|
NAD |
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide |
|
|
|
Nicotine Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate |
NADH |
|
|
|
Catalyst |
Speeds up chemical reaction. Reusable. |
|
|
|
Enzymes |
Proteins serve as a catalyst for biochemical reactions in a cell. |
|
|
|
Activation Energy |
Energy needed to form or break chemical bonds and convert reactants to products |
|
|
|
Substrates |
The chemical reactants than enzymes bind |
|
|
|
Catalase |
Enzymes that break down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen |
2 H2O2 -> H2O + O2 |
|
|
True or False: The new lagging DNA strand is synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction only |
True |
|
|
|
Capnophiles |
Require high carbon dioxide conditions to grow |
|
|
|
What enzyme catalyzes: H2O2 + 2H+ -> 2 H2O |
Peroxidase |
|
|
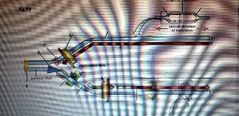
Label 1-6 |
1. DNA Polymerase III 2. Single Strand Binding Protein 3. Helicase 4. Topoisomerase/Gyrase 5. DNA Ligase 6. DNA Polymerase III |
|
|
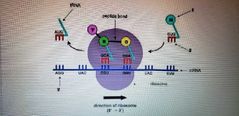
Label 1-3 |
1. Amino Acid 2. Start Codon 3. Anticodon |
|
|
|
TDT; Thermal Death Time |
Time during which all cells in a culture are killed |
|
|
|
TDP; Thermal Death Point |
The lowest temperature which all cells in a culture are killed in 10 minutes |
|
|
|
DRT; Decimal Reduction Time |
Time (minutes) to kill 90% of a population at a given temperature |
|
|
|
Glycolysis |
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C₆H₁₂O₆, into pyruvate, CH₃COCOO⁻ + H⁺. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules ATP and NADH. Glycolysis is a sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions |
|
|
|
Steps of Calvin Benson Cycle |
1. Carbon Fixation - CO2 binds to RuBP sugar with help from Rubisco 2. Reduction Phase - 3-PGA is converted into G3P 3. Carbohydrate Formation - G3P turned into carbohydrates (sugars) 4. Regeneration Phase - G3P+ATP used to make RuBP |
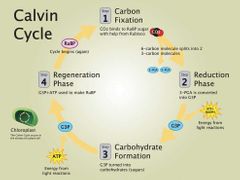
|
|
|
Prion |
Will not denatured in an autoclave. |
|
|
|
List protein from most resistant |
- Prions - Endospore of Bacteria - Mycobacterium |
|
|
|
Phenotype |
Expression of the genes |
|
|
|
Genotype |
Genes of an organism |
|
|
|
3D structure of DNA Discovered in 1950 by |
- James Watson - Maurice Wilkins - Rosalyn Franklin - Cricket |
|
|
|
Lac Inducible Operon |
Catabolic (Breaks Apart) |
|
|
|
Tryptophan Operon Repressible |
Anabolic (Binds, shuts off replicant) |
|
|
|
Process of Translation |
1. Translation come together 2. tRNA pairs with start codon 3. Second codon of RNA pairs with tRNA 4. Ribosome moves the mRNA until second tRNA is in P site 5. Second amino acid joins in peptide bond, first tRNA released from E site 6. Ribosome continues along mRNA until reaching a stop codon. Polypeptide is released 7. The last tRNA is released, the ribosome comes apart, and poly peptide forms a new protein |
|
|
|
Process of Transcription |
1. RNA polymerase binds to promoter. 2. RNA is synthesized 3. Synthesis site moves along DNA 4. Transcription reaches terminator 5. RNA and RNA polymerase are released |
|
|
|
Thioglycolate Tube Culture |
Reducing medium which oxygen diffuses from the tube opening. |
|

