![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pathogenicity
|
the ability to cause disease
|
|
|
Virulence
|
Virulence : the extent or degree of pathogenicity
~100 bacteria cause significant disease in humans |
|
|
The Establishment of Disease
|
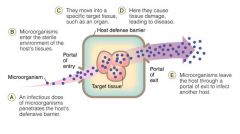
1. Portal of Entry (correct portal / multiple portals)
2. Dose (sufficient number / virulence factors) 3. Adhere (adhesions) 4. Tissue penetration / invasion 5. Resist Host Defenses 6. Toxins |
|
|
2. Effect of Number (Dose) : ID50 Experiment
|
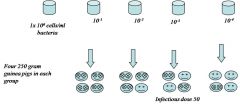
|
|
|
Relationship between Portal and Dose
|
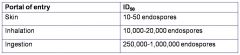
|
|
|
3. Adherence
|
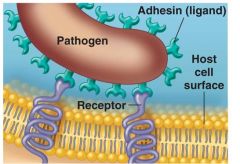
Adhesions / ligands on pathogen bind specifically* to receptors on host cells
|
|
|
4. Penetration/Invasion in host cell
|
invasins cause cell membrane to ruffel
|
|
|
5. Resist Host Defenses (enzymes)
|
Coagulase= coagulate blood (avoid bacteriocidal substances and antibodies)
bacteria coat themselves with fibrinogen fibrin (soluble) ——> fibrinogen (insoluble) Ex: Staphylococcus and Streptocccus IgA proteases= destroy IgA antibodies Ex: Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis |
|
|
Toxin
|
Substances that contribute to pathogenicity
|
|
|
Toxemia
|
Presence of toxin the host's blood
|
|
|
Toxoid
|
Inactivated toxin used in a vaccine
|
|
|
Antitoxin
|
Antibodies against a specific toxin
|
|
|
Exotoxin verses Endotoxin
|
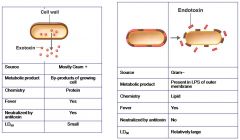
|
|
|
A-B Toxins
|
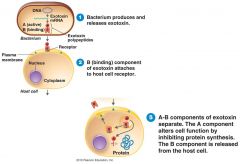
|
|
|
Membrane-disrupting toxins
|
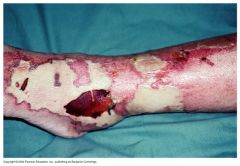
Lyse host’s cells by:
form protein channels in the plasma membrane disrupting phospholipid bilayer Streptococcus pyogenes (enterotoxin A) necrotizing fascitus or flesh eating disease |
|
|
Endotoxins Fever and Septic Shock
|
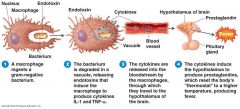
Macrophages also release TNF-alpha (Tumor necrosis factor)
septic shock inflammatory mediator clotting, organ failure and circulatory collapse (No antitoxin stimulation - No toxoids available - No Immunity) |
|
|
kinases
|
dissolves blood clots
|
|
|
hyaluronidase
|
spreading factor dissolves tissues
gan gragrene- clostridium perfringenes |
|
|
collagenase
|
breaks down protein collagen
|
|
|
Staphylococcus aureus TSST-1
|
toxic shock syndrome result of superantigen- intense immune response
fever, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, shock, death |

