![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Bacterium (Singular) Bacteria (Plural) |
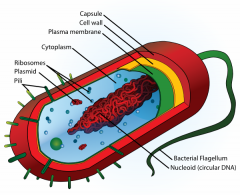
unicellular microorganisms that have cell walls but lack organelles and an organized nucleus
|
|
|
Eubacteria |
1). All bacteria except archaea 2). Unicellular 3). Prokaryotic 4). Cell wall usually contains peptidoglycan 5). Various shapes 6). Binary Fission 7). Energy Sources vary: inorganic, organic, and photosynthesis |
|
|
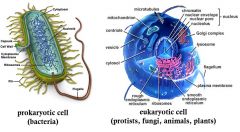
Prokaryotic cells
|
Lack Nuclei or membrane bound organelles |
|
|
Peptidoglycan
|
1). Also known as murein,
2). A polymer composed of polysaccharide and peptide chains, 3). Consisting of sugars and amino acids, 4). Forms a mesh-like layer outside the plasma membrane of most bacteria 5). Forms cell wall |
|
|
Binary Fission |
Reproduces asexually by dividing two identical cells |
|
|
Archaeon (Singular)
Archaea (Plural) |
1). Archaebacteria 2). Unicellular 3). Prokaryotic 4). Binary Fission 5). May have cell wall; if so, no peptidoglycan 6). Broad habitats 7). Some extremophiles such as; *Extreme halophiles *Hyperthermophiles |
|
|
Extremophiles
|
An organism that thrives in extreme/ harsh environments
|
|
|
Extreme halophiles
|
Organisms that live in extremely salty environments
|
|
|
Hyperthermophiles
|
An organism that thrives in extremely hot environments
|
|
|
Alga (Singular) Algae (Plural) |
1). Eukaryotic 2). Unicellular or multicellular 3). Cell wall made of cellulose 4). Reproduce sexually or asexually 5). No binary fission 6). Energy from photosynthesis 7). Produce oxygen (O2) 8). Usually found in aquatic environments and soil |
|
|
Eukaryotic Cells
|
Any organism whose cells contain a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
|
|
|
Cellulose
|
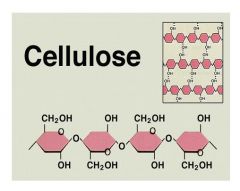
1). An insoluble substance
2). Main component of plant cell walls 3). A polysaccharide consisting of chains of glucose monomers. |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
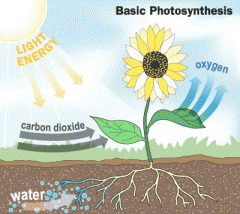
A process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities.
|
|
|
Ekaryotic Cells VS. Prokaryotic Cells |
|
|
|
Fungus (Singular) Fungi (Plural) |
1). Eukaryotic Cells 2). Yeast 3). Molds 4). Cell wall made of chitin 5). Reproduces sexually or asexually 6). Non- motile/ not mobile 7). Energy from organic matter 8). Mushrooms ( not MOs) |
|
|
Yeast |
1). Consisting of single oval cells that reproduce by budding
2). Capable of converting sugar into alcohol and carbon dioxide. |
|
|
Molds |
Grows in the form of multicellular filaments called hyphae
|
|
|
Chitin
|
A fibrous substance consisting of polysaccharides |
|
|
Hyphae
|
Each of the branching filaments that make up the mycelium (tangled hyphae) of a fungus
|
|
|
Protozoan (Singular) Protozoa (Plural) |
1). "Little animals" 2). Eukaryotic 3). Unicellular 4). No cell wall 5). Usually motile using flagella, cilia, or pseudopods 6). Engulfers 7). Reproduces sexually and asexually 8). Energy source is organic matter 9). Found in aquatic environments or in animals |
|
|
Flagellum (Singular)
Flagella (Plural) |
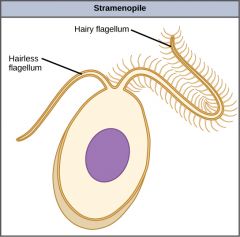
A slender threadlike structure microscopic whiplike appendage that enables many MOs to swim
|
|
|
Cilium ( Singular) |
1). A short, microscopic, hairlike vibrating structure.
2). Occur in large numbers on the surface of certain cells 3). Causing currents in the surrounding fluid, or propulsion 4). Like an eyelash, or a delicate hairlike structure that resembles one |
|
|
Pseudopodium (Singular) |
1). A temporary foot- like extension of a unicellular organism
2). Used for moving |
|
|
Engulfers
|
Ingest organic matter and other MOs |
|
|
Viruses |
1). Not eukaryotic or prokaryotic 2). Acellular infectious agent 3). Contains DNA or RNA (not both) 4). Capsid (a protein shell) 5). Sub-microscopic (too small for microscope) 6). Obligate intracellular parasites 7). Host specific |
|
|
Acellular |
Not consisting of, divided into, or containing cells
|
|
|
Obligate Intracellular Parasites
|
1). Must invade a host cell in order to replicate 2). Hijackers |
|
|
Host Specific |
A plant virus will only infect plants and a human virus will only infect humans |

