![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Microscope |
An instrument to magnify the image of an object |
|
|
Compound Microscope |

|
|
|
Basic Types of Compound Micrscopes |
1). Bright- Field 2). Dark- Field 3). Phase Contrast 4). Fluorescence |
|
|
Bright- Field Microscope |
1). Cells absorb or scatter light 2). Contrast between specimens and background 3). 2 sets of lens; Ocular and objective 4). Parfocal |
|
|
Parfocal |
Once focused with one lense, the microscope can keep focus when switching to other lens |
|
|
Magnification |
1).The degree to which the viewed object is enlarged 2). The process of making the object appear larger |
|
|
Total Magnification |
(objective lens magnification) X (ocular lens magnification) |
|
|
Resolution |
The ability of a lens to distinguish 2 adjacent objects as separate and instinct entities |
|
|
Resolving Power |
1). Minimum distance between 2 distinguishable objects 2). Smaller resolving distance makes greater resolution |
|
|
Oil Immersion |
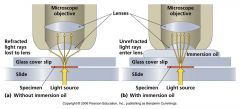
1). A technique used to increase the resolving power of a microscope
2). Immersing both the objective lens and the specimen in a transparent oil |
|
|
Contrast |
Difference in visual properties to make an object distinguishable from others or background |
|
|
What color are bacterial cells? |
Transparent/ Clear |
|
|
How to raise contrast to see bacterial cells |
1). Staining 2). Dark- field microscope 3). Phase Microscope 4). Fluorescent microscope |
|
|
Staining |
1). Dyes used to increase a cells contrast so they can be more easily seen |
|
|
Staining Techniques |
1). Simple staining 2). Differential Staining |
|
|
Simple Staining |
1). Apply one dye to cell or background 2). Make cell visible |
|
|
Differential Staining |
1). Applying at least two stains 2). Distinguish different parts of the cell |
|
|
Cell |
Smallest fundamental unit of all cellular organisms |
|
|
Four Key subcellular structures |
1). Plasma membrane 2). Cytoplasm 3). Nucleus/ Nucleoid 4). Ribosomes |
|
|
Plasma membrane
|
1). A semipermeable barrier 2). Separates the inside of the cell from the outside 3). AKA cytoplasmic membrane and cell membrane |
|
|
Cytoplasm
|
1). Substances and structures dissolved or suspended here 2). The fluid portion of a cell, bounded by the |
|
|
Nucleus/ Nucleoid
|
1). a membrane- enclosed structure in eukaryotic cells that contains the cells DNA genome |
|
|
Ribosomes
|
Protien- synthesizing factory |
|
|
Genome
|
An organism's full complement of genes |
|
|
Macromolecules |
A polymer that occurs naturally in living organisms.
|
|
|
Polymer
|
A substance that has a molecular structure consisting chiefly or entirely of a large number of similar units bonded together
|
|
|
Examples of macromolecules |
1). Nucleic acid 2). Polysaccharides 3). Lipids 4). Proteins
|
|
|
Metabolism |
1). All biochemical reactions in a cell, both anabolic and catabolic 2). Carbon and energy source for cells |
|
|
Anabolic |
The phase of metabolism in which complex molecules are formed from simpler ones.
|
|
|
Catabolic |
The breaking down in living organisms of more complex substances into simpler ones
|

