![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Group A streptococcus
lab characteristics pathogenesis |
Streptococcus Pyogenes
gram positive cocci in chains beta hemolytic (clear) inhibited by Bacitracin, PYR + Pathogenesis: Hyaluronic acid capsule--non-immunogenic; inhibits phagocytic uptake M-protein-antiphagocytic Toxins: (lysins) Streptolysin O--immunogenic (rheumatic fever) Streptolysin S--nonimmunogenic streptokinase--breaks fibrin, helps spreading streptococcal DNAse--liquifies pus, extension of lesion Hyaluronidase--hydrolyses the ground substances of the connective tissues (spread of cellulitis) Exotoxins A-C (pyrogenic or erythrogenic exotoxins) |
|
|
Group A streptococcus
diseases treatment |
Suppurative Strep Pyogenes Infections:
1. Pharyngitis 2. Scarlet fever--blanching "sandpaper rash", strawberry tongue, nausea/vomiting 3. Pyoderma/Impetigo--pus producing skin infection (honey crusted lesions) 4. Erysipelas--"slapped cheek (does not blanch, no raised corners) 5. Necrotizing faciiatis (cellulitis--blanches, flat) Non-suppurative 1. Rheumatic fever--sequelae to pharyngitis w/ group A strep--antibodies to heart tissue (~19 days) fever,joint inflammation, carditis, erythema nodosum 2. Acute glomerulonephritis (M12 serotype)--sequelae to pharyngitis or cutaneous --immune complexes bound to glomeruli/pulmonary edema and hypertension, dark urine treatment: beta-lactam antibiotics or erythromycin |
|
|
Group B streptococcus
labs diseases treatment |
Streptococcus Agalactiae
gram positive cocci in chains beta hemolytic (same as group A) Bacitracin Resistant! hydrolyze hippurate, cAMP test positive found in vagina(15-20%)-- newborn infected during birth --causes neonatal septicemia and meningitis treatment: Ampicillin w/ cefotaxime or gentamicin |
|
|
Streptoccus pneumoniae
laboratory characteristics |
"pneumococcus"
Alpha hemolytic (partial--green) Inhibited by optochin gram positive lancet shaped diplococci lysed in bile (unlike Streptococcus Viridans) |
|
|
Streptoccus pneumoniae
Pathogenesis |
IgA--helps colonization
Techoic Acids--attachment Polysaccharide capsule--inhibits phagocytosis (via alternative complement path-antibody independent) Quellung reaction positive Pneumolysin O--damages respiratory epithelium--"rusty sputum"-RBC's & WBC's Peptidoglycan/techoic acids-- highly inflammatory in CNS |
|
|
Streptococcus Pneumonia
Diseases Treatment |
Bacterial Pneumonia--most common bacterial cause (shaking chill, high fever, lobar consolidation w/ blood tinged "rusty" sputum)
Adult meningitis (most common cause) CSF high WBC, low glucose Otitis Media & Sinusitis(kids) most common cause Treatment: Penicillin G (resistant strains--Vancomycin +/- Rifampin) prevention--vaccine(23 serotypes of capsule) |
|
|
Viridans Streptococci
labs & reservoir |
S. Salivarius
S. Mutans S. Sanguis Alpha Hemolytic Optochin resistant(unlike S.Pneumonia) Also-not bile soluble Reservoir: human oropharynx (normal flora) |
|
|
Viridans Streptococci
pathogenesis diseases treatment |
Pathogenesis:
Dextran(biofilm) mediated adherence onto tooth enemal or damaged heart valve/hole Diseases: dental caries infective endocarditis Treatment: Penicillin G w/ aminoglycoside for endocarditis (PCN prophylaxis if damaged valves) |
|
|
Enterococcus Feacalis
|
= Streptococcus Feacalis (group D)
Gamma hemolytic (no hemolysis) Gram positive cocci in chains Catalase negative Bile esculing + (black)allows survival in bowel/gall bladder Reservoir: human colon, urethra, genital tract Diseases: urinary/biliary infections, subacute infective endocarditis, infections after GI/GU procedures Tx: Vancomycin IV, most strains have some drug resistance |
|
|
Staphylococcus Aureus
labs & distiguishing characteristics reservoir |
Catalase positive (unlike strep)
Beta-hemolytic gram positive cocci clusters coagulase positive (unlike S. epidermis & saphrophyticus) Salt tolerant, ferments mannitol Reservoir: normal flora on nasal mucosa & skin |
|
|
Staphylococcus Aureus
virulence factors |
Protein A
TSST-1 (toxic shock syndrome) Enterotoxins-milk/eggs(fast 2-6 hr-food poisoning) Exfolitins (SSS) Alpha-toxin (cytolysin) osteomyolitis protein A--inhibits phagocytosis--binds Fc portion of antibody Coagulases--spread |
|
|
predisposing factors for staph infections
|
surgery--break in the skin
neutropenia cystic fibrosis IV drug abuse--more S.Aureus on the skin than epidermidis Chronic Granulamatous disease--staph are catalase + |
|
|
Staphylococcus Aureus
diseases treatment |
infective endocarditis in IV drug users
abcesses toxic shock syndrome gastroenteritis (food poisoning from preformed exotoxin--fast onset 2-6hrs- vomiting, diarrhea, nausea) suppurative lesions (impetigo) pneumonia--productive w/ fast onset--high rate of necrosis/fatality (nosocomial, ventilator, post influenza, IV drug user, CF, CGD ) Treatment: Methicillin (resistant to PCN) MRSA-use Vancomycin & fusidic acid |
|
|
Staphylococcus Epidermidis
labs diseases |
Coagulase negative!
No hemolysis suspectible to Novobiosin (unlike Staph. Saphrolyticus) Disease: Catheter & prostetic devise, shunts Endocarditis in IV drug users (along w/ Staph Aureus) |
|
|
Staphylococcus Saprophyticus
|
Coagulase negative
no hemolysis Novobiocin resistant! (differentiats from S.Epiderm) UTI's in sexually active young females |
|
|
Bacillus Anthracis
|
large gram + rods--boxcar like
Capsule is polypeptide (poly D glutamate)--immunogenic & anti-phagocytic Aerobic & spore forming Pathogenesis: Anthrax toxin-3 protein components (capsule +) 1. protective antigen (B component)--mediates the entry of LF or EF into eukaryotic cell 2. lethal factor--kills cells 3. edema factor--is an adenylate cyclase reservoir: animal skins, soil--inhalation of spores cutaneous or pulmonary (life-threatening pneumonia w/ mediastinal hemorrhagic lymphadenitis) treatment: Ciprofloxacin or Doxycycline (vaccine also available) |
|
|
Bacillus Cereus
|
gram + rod, spore former (spores are not killed by boiling), aerobic
Food poisoning: food held warm-not hot (fried rice) Toxins: Emetic toxin-fast (1-6 hrs) Diarrheal toxin-meats & sauces (18 hrs--increases cAMP watery diarrhea) |
|
|
Listeria
labs & characteristics reservoir |
small gram +, non-spore forming rod
beta-hemolytic (partial-green) facultative intracellular tumbling motility cold growth Reservoir: animal GI/GU tracts, unpasteurized milk, plants & soil cold growth: deli meats, soft cheese, coleslaw foodborne--transmits across placenta or by contact during delivery |
|
|
Listeria
pathogenesis diseases |
Pathogenesis:
listeriolysin O (beta-hemolysin dumps lysosomal contents into phagosome--"jets" by actin filament formation to next cell) Diseases: immuno-immaturity--risk for serious infection (babies) Listeriosis--peaks in summer healthy pt's--mild diarrhea pregnant--septicemia Neonatal: early-in utero-granulomatosis infanseptice late-2-3 wks after birth-fecal exposure-meningitis w/ septicemia Immunocompromised: Septicemia & meningitis (renal transplant pt's & cancer pt's) Treatment: Ampicillin (w/ gentamicin for IC pt's) |
|
|
Corynebacterium Diphteriae
labs |
gray/black colonies of club-shaped gram + rods (telluride medium-V or L shape arrangements), non-spore forming, non-motile, aerobic
Granules (volutin) produced on Loeffler's coagulated serum medium stain metachromatically |
|
|
describe the culture of Streptococcus Pyogenes (group A strep)
|
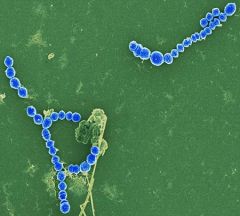
gram + cocci in chains
|
|
|
streptococcus pyogenes
|

identify bacteria
|
|
|
corynebacterium diphteriae
|

identify bacteria
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of corynebacterium diptheria
disease & tx |
non-invasive, colonizes epithelium (resp. drops)
Diphteria toxin: (Elek test) inhibits protein synthesis by adding ADP ribose to EF-2 Causes: dirty gray pseudomembrane on oropharynx /larynx/trachea-can obstruct heart & nerve damage Disease: Diphteria sore throat w/ pseudomembrane, bull neck, myocarditis, recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy & lower limb polyneuritis Treatment: Erythromycin & antitoxin (vaccine-part of DTP, DTaP or Td) |
|
|
Actinomyces Israelii
characteristics |
ANAEROBIC bacteria
gram + rods/branching filaments not acid fast sulfur granules and a beaded appearance |
|
|
Actinomyces Israelii
disease & tx |
Actinomycosis
reservoir: endogenous-gums & vag very invasive-Rib destruction, Cutaneous sinuses, cavitation, spreads to pleura and chest wall (draining abscesses w/ sulfur granules) "lumpy jaw"-dental trauma or poor hygiene thoracic-aspiration w/ contagious spread abdomen/pelvis-surgery/trauma CNS-solitary abscess treatment: Ampicillin or Penicillin G and surgical drainage |
|
|
Nocardia Asteroides
characteristics & reservoir |
Aerobic
Partially Acid-Fast gram + filaments breaking into rods reservoir: soil & dust immunosupression & cancer predispose to pulmonary infection |
|
|
Nocardia Asteroides
disease & tx |
Nocardiosis
cavitary bronchopulmonary--cough fever, dyspnea--may spread to brain via blood cutaneous nocardiosis starts w/ trauma-cellulitis w/ swelling-draining abscess w/ granules (mycetoma) treatment: Sulfanamides or TMP/SMX looks similar to actinomyces but tx totally different-no PCN |
|
|
nocardia asteroides
|

caused by a gram+ aerobic, partially acid fast bacteria
|
|
|
Group B strep (S. Agalactiae)
|

gram + bacitracin resistant (P disk), hippurate utilized, cAMP test positve
|

