![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
biochemical tests can tell 3 things
|
1) type of energy used
2) substrates utilized 3) enzymes broken down |
|
|
selective media
|
suppresses growth of some bacteria but encourages growth of others
|
|
|
differential media
|
distinguishes specific characteristics between organisms
certain species can be identified because they look different |
|
|
energy metabolism (2 types)
|
respiration and fermentation
|
|
|
three steps to obtain energy through respiration
|
1. glycolysis 2. TCA cycle 3. electron transport chain
|
|
|
fermentation
|
partial breakdown of organic molecules.
|
|
|
produces of fermentation
|
alcohol, acids, hydrogen, carbon dioxide, atp
|
|
|
key ingredient for respiration
|
oxygen
|
|
|
shape of streptococcus
|
gram positive cocci; facultative anaerobe
|
|
|
requirements of cultivation of streptococcus
|
blood agar
|
|
|
important human pathogens of streptococcus
|
s. pyogenes; s. agalactiae; s. pneumoniae
|
|
|
Hemolysis
|
the destruction of red blood cells
|
|
|
means of detection of hemolysis
|
blood agar and candle-in-jar method to reduce oxygen levels. (streptococci are anaerobic organisms)
|
|
|
beta hemolysis
|
complete destruction of red blood cells
|
|
|
example of beta hemolysis
|
streptococcus pyogenes
|
|
|
alpha hemolysis
|
partial destruction of red blood cells
|
|
|
example of alpha hemolysis
|
streptococcus pneumoniae
|
|
|
Gamma hemolysis
|
no destruction of red blood cells
|
|
|
example of gamma hemolysis
|
streptococcus lactis
|
|
|
shape of staphylococcus
|
gram postiive cocci; salt tolerant.
|
|
|
3 main species of staphylococcus
|
staph. aureus
staph. epidermidis staph. saprophyticus. |
|
|
MSA-what it stands for and differential/selective
|
mannitol salt agar; selective and differential
|
|
|
what MSA requires
|
mannitol (carbs), 7% NaCl (salt), and pH indicator
|
|
|
selective factor of MSA
|
only bacteria that grows in salty conditions thrive
|
|
|
differential factor of MSA
|
staph. aureus turns from yellow to red because of acid produced
|
|
|
red bacteria in MSA
|
staph. aureus
|
|
|
shape of enterics
|
gram negative, non spore-forming rod shaped
|
|
|
MacConkey Agar contents
|
-bile salt and crystal violet
-neutral red dye -lactose |
|
|
role of bile slat and crystal violet in MacConkey Agar
|
inhibits growth of gram-positive bacteria and non-enteric bacteria
|
|
|
role of neutral red dye in MacConkey Agar
|
indicates the pH
|
|
|
role of lactose in MacConkey Agar
|
carbohydrates for lactose fermentation
|
|
|
selective factor of MacConkey Agar
|
only gram-negative will grow from the bile salt and crystal violets
|
|
|
differential factor of MacConkey Agar
|
if enterics form lactose-pink color
if enterics don't form lactose-no change in color |
|
|
a pink colored bacteria in MacConkey Agar
|
lactose-fermenting enteric present
|
|
|
TSI test
|
Triple Sugar Iron
|
|
|
contents of TSI
|
carbohydrates, peptone, beef extract, yeast extract, sodium thiosulfate, phenol red
|
|
|
SIM test
|
Sulfur reduction, Indole production, Motility
|
|
|
formation of black precipitate in SIM test
|
positive in sulfur reduction
|
|
|
red after 5 drops of kovac's reagent in SIM test
|
positive in indole production
|
|
|
spread from point of inoculation in SIM test
|
positive in motility
|
|
|
MRVP
|
methyl red-vogues proskauer
|
|
|
methyl red test
|
if red after adding methyl red reagent, mixed acid fermentation. none if yellow.
|
|
|
red in methyl red test
|
mixed acid fermentation
|
|
|
yellow in methyl red test
|
no mixed acid fermentation
|
|
|
vogues proskauer test
|
if red after adding vogues proskauer reagent, fermenting bacteria utilize butylene glycopathogen
|
|
|
red in vogues proskauer test
|
fermenting bacteria utilize butylene glycopathogen
|
|
|
coopper in vogues proskauer test
|
fermenting bacteria don't utilize butylene glycopathogen
|
|
|
Citrate utilization
|
determines if bacteria uses citrate as sole carbon source
|
|
|
contents of citrate utilization
|
bromthymol blue dye
|
|
|
blue in citrate utilization
|
high pH
|
|
|
green in citrate utilization
|
low pH
|
|
|
shape of bacilllus
|
gram-positive, spore forming rods
|
|
|
starch hydrolysis
|
whether or not starch is hydrolyzed by bacillus
|
|
|
enzymes used to hydrolyze starch
|
amylase and glucosidase
|
|
|
contents of starch plate
|
beef extract, starch, agar
|
|
|
blue/black starch plate after iodine addition
|
starch hydrolyzed
|
|
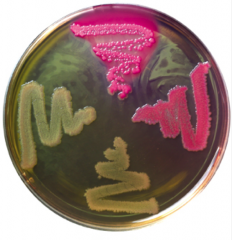
|
MacConkey agar
|
|

|
uses up oxygen so facultative aerobes can grow; used with blood agar for hemolysis testing.
|
|
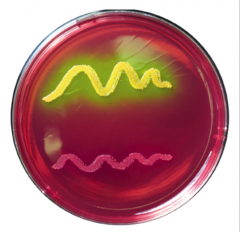
|
mannitol salt agar
yellow-staph. aureus pink-other staph |
|

|
sulfur reduction in SIM
|
|

|
motility in SIM
|
|

|
indole production in SIM
|
|

|
if blue, citrate utilized; if growth, citrate utilized; if neither, not utilized.
|
|

|
upper-no hydrolyzing enzymes
lower-hydrolyzed |
|
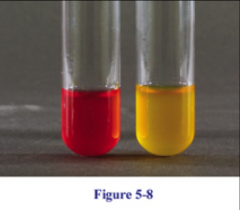
|
MRVP (MR)
acid fermentation-red no acid fermentation-yellow |
|
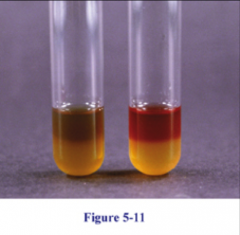
|
MRVP (VP)
butyln glycol pathway used-red not used-copper/no color |
|

|
TSI
yellow-glucose/lactose/sucrose fermentation+acid accumulation (enteric) red with yellow butt-glucose fermentation with acid production (enteric) other red slants-no fermentation, not enteric black -sulfur reduction cracks-gas production |
|
|
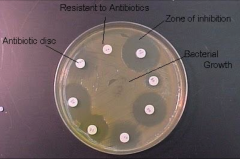
kirby bauer antibiotic susceptibility
|

