![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cytology
|
-The scientific study of cells for the purpose of diagosing disease
-Involves the microscopic exam of cells obtained from: *tissue surfaces *body cavities *body excretions *body secretions |
|
|
Body excretions
|
- is the removal of material from living thing
-tears,feces, urine, CO2, sweat -this is passive in nature it has to happen |
|
|
Body secretion
|
-is the movement of material from one point to another
-enzymes, hormones, or saliva -removes important materials that can be metabolized and used by our bodies |
|
|
Hystopathology
|
-study of tissue
-use a mycrotome |
|
|
Microtome
|
-an instrument for cutting extremely thin sections of material for examination under a microscope
|
|
|
Pros and cons of cytology
|
-Advantages: quick preparations, good cell detail (depending on the leasion), relatively cheap
-Disadvantages: small sample size, may not have any exfoliated cells, cant rule out disease based on negative sample |
|
|
Cytology sampling methods
|
-fine needle aspirate
-impression smear or touch prep -scrape prep -swab -fluid prep |
|
|
Fine needle aspiration
|
-done on animal while leasion is still on animal
-called an insitu (natural environment) -22-25 gage needle and 12 cc syringe (small animal) -20 gage needle and 12 cc syringe (large animal) -insert needle in center of leasion pull back on plunger and redirect 3 or more times -pull needle out of leasion and take needle off the pull back on plunger and put needle back on and put specimine on a slide |
|
|
Squash prep
|
-put specimin on slide and take another slide and squish it and slide the slides to make a monolayer of cells
-if specimine is wet do the prep like a blood smear |
|
|
Technical problems w/ FNA (fine needle aspiration)
|
- blood contamination- improper equipment , too large needle or too much suction
-dammage to cells- too much suction or too much force expelling sample (use 12cc syringe) -non representative sample - not redirecting the needle in the mass |
|
|
Impression smear/ Touch prep
|
-leasion that has been removed
-cut tumor/leasion in half if big cut more sections -blot if 2 moist dont rub or drag -take cut surface and press down on slide and repeate -lable slide: Name animal, owner, date and what kind of smear |
|
|
Technical problems w/ impression smear
|
-Very dense tissue will make poor sample - few cells exfoliate if tissue is too fibrous or bony
-Damage to cells by smearing the tissue - proper touch technique should be used -Preps that are too thick - blot the tissue b4 touching slide, make several touches |
|
|
Scrape prep
|
-Hard boney leasions/tumors
-use a scalple and scrape the tumor/leasion -spred sample on a slide in a thin layer |
|
|
Problems w/ scrape preping
|
-some cell damage occurs
-scraping may contaminate the sample w/ blood |
|
|
Swab Samples
|
-use clean swab dry or a bit wet
-insert swab to desired level -press cotton tip against wall and gently rotate -withdraw swab -roll swab gently onto slide -EX. ear smear |
|
|
technical problems w/ swab slide
|
-swab too wet -cells don't stick to swab , slide dries to slow
-swab too dry- cells don't come off -cells damage - roll swab on side, don't drag ! |
|
|
Fluid Samples
|
-Cytology is preformed on various body fluids
-effusions: body fluids that have increased in volume -transudate: capillary filtrate or fluid -exudate: inflammatory condition w/ increased fluid |
|
|
Effusions
|
-body fluids that have increased in volume
|
|
|
Transudate
|
-capillary filtrate or fluid
*clear,colorless, low protein *low cellularity, low specific gravity *eg. ascities (fluid in the abdomen) |
|
|
Exudate
|
-inflammatory condition w/ increased fluid
*color, increased protein * increased cells, increased specific gravity * Ex. Pus |
|
|
Fluid prep
|
-depends on the vicosity (thickness) of the fluid
-in most cases the technique used is a variation of a blood smear: : fluid is very thick, can do a squash prep : fluid is similar to blood, use standard technique : fluid is thin, smear but don't make fethered edge, stop and let flow over its self this concentrates the cells on the smear : very thin fluid may also be centrifuged and the sediment examined- like a urine sample |
|
|
vet cytology microscopy
|
-on low power look for area of uniform, intact cells w/ good staining
-mono-layer -look for sheets of cells and other diagnostic structures (bacteria, fungi) -move to oil to look at cell detail |
|
|
Types of cells
|
-inflammatory
-non-inflammatory |
|
|
Hyperplasia
|
-an abnormal increase in # of normal cells in normal arrangement in an organ or tissue
-Chronic irritation -Altered cellular signaling (homone imblanance) -may be associated w/ inflammatory cells -cells may appear more immature, but otherwise resemble normal cells -have a constant N:C ratio |
|
|
Neoplasia
|
-An increase in cell # that is not dependant on stimulus (don't have to have irritation)
-abnormal new growth of tissue in which the multiplication of cells is uncontrolled. -if this forms a distinct mass it is a tumor. -tumors may be benign or malignant -Usually larger cells -varying sizes and shapes (pleomorphic) -Variable N:C ration (nuclear size: cytoplasm present) |
|
|
Benign
|
-Non-spreading
|
|
|
Malignant
|
Spreading
|
|
|
Inflammatory leasions
|
-characterized by WBC's
|
|
|
-Acute inflammation
|
-Inflammatory leasions w/ Neutrophills:
|
|
|
Inflammatory leasion w/ macrophages:
|
-Tissue moncytes, more chronic inflammation (large w/vaccuoles)
|
|
|
Inflammatory leasion w/ Eosinophils
|
-parasitic or allergic reaction or in eosinophillic granulomas of cats
|
|
|
Eosinophilic granuloma (Rodent Ulcers)
|
-auto amune system disease
- will see eocinophills -Take slide impression right on their leasion |
|
|
Urticaria
|
-Hives
-Wheals = hives |
|
|
Types of neoplasia
|
-carcinomas (squamous cell carcinoma)
-sarcomas (osteosarcoma) -roundcell tumors (mass cell tumor) |
|
|
Carcinomas
|
-common
-originate from epithelium, more suface tumors -usually in clusters or sheets Sarcomas |
|
|
Sarcomas
|
-connective tissue,origin,deeper location
-don't exfoliate well, usually need scrape |
|
|
Round cell tumors
|
-characteristically round in shape
-exfoliated as individual cells -serious, very aggressive |
|
|
Cycles of Estrous
|
-Proestrous
-estrus -metestrus -diestrus or anestrus |
|
|
Proestrus
|
-When dog bleeds
-active phase immediately preceedin estrus -smear contains RBC's -Epitheial cells -Too early to breed |
|
|
Estrus
|
-No RBC
-characterized by cornified epithelial cells -Loose neucles |
|
|
Metestrus
|
-Epithelial cell numbers drop
-neutrophil numbers rise -uterus is rebsorbing lining |
|
|
Anestrus/ Diestrus
|
-few cells
-quiescent phase -epithelial cells may be cornified or non-cornified -may see an occasional neutrophill |
|
|
Canine vaginal cytology
|
-can pin point what stage of estrus is in primarly in dogs and rats
-speculum put in vagina -clean long swab in vagina wall till reaches cervix -roll motion on slide and diff quick stain it |
|
|
Histology
|
-processing is used on tissue samples excised from the body
-the normal architecture or pattern of the tissue is seen, rather than just looking at exfoliated cells -it is more time consuming and costly than cytology |
|
|
Monera
|
-are undifferentiated unicellular organisms that do not form specialized tissues or organ systems
:prokaryotic :Eukaryotic |
|
|
Prokaryotic
|
-bacteria
-dont have neuclar membrane |
|
|
Eukaryotic
|
-algae, fungi, protozoa
-have neuclear membrane |
|
|
Unit of measure
|
-micrometer=micron=u=10 to the negitive 6 meter (Small)
-Nanometer=nm-10 to the negitive 9 meter (very small) -Angstrom= Å= 10 to the negitive 10 meter (very very small) -most bacteria we will study are between :0.5 u to 1.0u in width : 2.0u to 5.0u in length ** can not see bacteria on scanning in urine** |
|
|
shape of bacteria
|
-coccus= spherical
-Bacillus= Bacilli rods or cylinders -spiral or spirochetes= loose sprials or tight spirals or comma (gul) shape -Pleomorphic= range from cocci to rods (various size/shape) |
|
|
arrangement of cocci
|
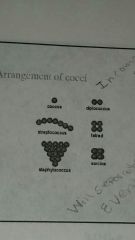
|
|
|
Arrangements of Bacilli
|
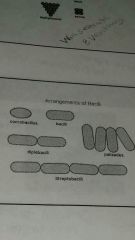
|
|
|
Spriochete Forms
|

|
|
|
Capsule:
|
-Protects against phagocytosis
-helps with attachment -prevets drying and nutrient loss -produces pathogenicity *Makes cell more pathogenic |
|
|
Cell wall
|
-gives rigidity
-layers produce the gram stain reaction |
|
|
Gram positive
|
-Purple
|
|
|
Gram Negative
|
Pink
|
|
|
Pili
|
For attachment NOT movement
|
|
|
Flagella types
|

|
|
|
Endospores
|
-Intracellular bodies that have a low rate of metabolism
-their location in the cell can help w/ the identification of the organism : central : subterminal : terminal |
|
|
Nutrition of bacteria
|
-carbohydrate
-protein -lipids -water -inorganic ions -trace elements |
|
|
Fastidious
|
Organisms that have strict growth requirements
|
|
|
Mesophiles
|
-Grow between 20-40 degrees C
-most pathogens are here |
|
|
Thermophiles
|
-grow at higher than 40 degrees C
|
|
|
Psychrophiles
|
-Grow at lower than 20 degrees C
|
|
|
ObligateAerobe
|
-Requires oxygen to survive
|
|
|
Obligate Anaerobe
|
-Grows only in the absence of O2 (killed or inhibited by O2)
|
|
|
Facultative Anaerobe
|
-can survive in the absence of O2 but growth is limited
|
|
|
Microaerophilic
|
-Grows best at levels of O2 less than contained in air
|
|
|
Capnophilic
|
Requires high CO2
|
|
|
pH
|
-most pathogenic bacteria grow best in a neutral pH such as 6.6 - 7.5
|
|
|
Hypertonic
|
draws water out of the cell
|
|
|
Isotonic
|
releases water as well as lets it in
|
|
|
Hypotonic
|
Draws water in to the cell
|

