![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
96 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
______, or ________ charged, dyes used to stain bacteria are attracted to negatively charged cell components and stain the cell making it readily visible. |
Basic or positively charged. |
|
|
______, or _______ charged, stains are attracted to the glass slide surface leaving the bacterial in stained in a stained background. |
Acid or negatively charged stains. |
|
|
True or false: The process of fixing and staining usually kills the cell. |
True. |
|
|
________ stains use a single basic dye to increase contrast between the cell and the background. |
Simple stains. |
|
|
_________ stains are acidic dyes which color the background only and not the cell. |
Negative stains. |
|
|
_________ stains use a combination of dyes to distinguish between cells with different chemical properties. |
Differential stains. |
|
|
True or false: When creating a smear “more is better.” |
False. More is not better. The smear should be barely cloudy. If this mirror is too thick, you won’t be able to see individual cells. Solid clumps will not stain properly. |
|
|
Methylene Blue is a ______ dye, meaning it will stain what? |
Basic dye. It is positively charged and is attracted to the negatively charged cell structures. Therefore, it will stain all the cells blue. |
|
|
Nigrosin is a(n) _______ dye. It will color what? |
Nigrosin is an acidic dye and stains the background (the glass slide) and not the cells. |
|
|
What is the purpose of staining? |
To visualize cells. Bacterial cells have the same refractive index as water which makes them almost invisible when viewed under a bright field microscope. In order to increase the contrast between the cell and the background a variety of techniques can be used, usually staining! |
|
|
What is the difference between a simple stain and a differential stain? |
A simple stain uses a single basic die to increase contrast between the cell and the background. A differential stain uses a combination of dies to distinguish between cells with different chemical properties. |
|
|
What do negative staining and positive staining have in common? |
They increase the contrast between the specimen and the background. |
|
|
During staining, the slide & organism is heat fixed in order to… |
Kill the organism and attach the organism firmly to the slide. |
|
|
What cellular morphology features are observed after a simple stain? |
Cell shape and cell arrangement. |
|
|
True Or false: The purpose of simple staining is to elucidate the morphology and arrangement of bacterial cells. |
True. |
|
|
Grams bacterial stains can be characterized by the amount of _________ in the cell wall. |
Peptidoglycan. |
|
|
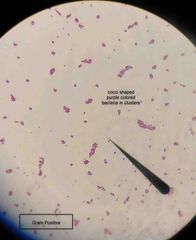
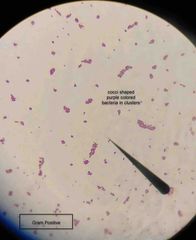
Gram-positive bacteria have cell walls that contain thick layers of peptidoglycan (90%). These stain _____. |
Purple. |
|
|
Gram negative bacteria have walls with thin layers of peptidoglycan, and high lipid content. These stain _______. |
Pink. |
|
|
The performance of the Gram stain on any sample requires four basic steps that include… List the steps. |
(1) apply a primary stain (crystal violet) to a heat fixed smear. (2) add a mordant. (Grams iodine.) (3) rapid decolorization with alcohol, acetone, or a mixture of alcohol and acetone. (4) counterstain with safranin. |
|
|
What are the three basic morphological shapes of bacteria? |
Round shaped cells are cocci, rod shaped cells are bacilli, and spiral shaped cells are spirilla. |
|
|
Why is Gram’s iodine called a mordant? |
The iodine acts as a mordant and binds to the crystal violet. |
|
|
By omitting the iodine step in the Gram-staining procedure, what color would you expect Gram+ bacteria to stain and what color would you expect Gram- bacteria to stain? |
Gram+ : Red. Gram- : Red. |
|
|
True or false: The Gram stain technique is based on the different structure of the cell walls of the two groups. |
True. |
|
|
Gram+ organisms contain a highly cross-linked layer of PTG that retains the primary dye, _______. |
Crystal violet. |
|
|
State 2 mistakes that you could make that would make a gram stain less reliable. |
Over-lengthy decolorization. Putting too much dye & leaving it on too long. |
|
|
True or false: Both gram+ & gram- will be the same color purple if you forgot to use iodine. |
False. |
|
|
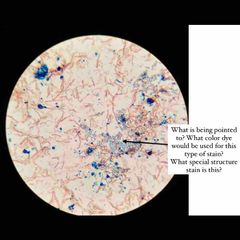
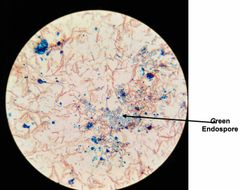
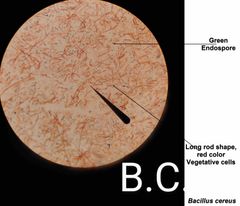
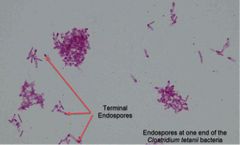
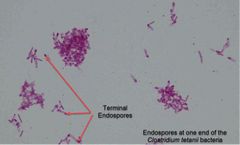
Why do we apply more heat in endospores stain? |
This extended heat fix is used to soften the endospore layer of keratin, to help the malachite green penetrate the endospore coat. |
|
|
What is the counter stain, primary stain, and decolorizer in that order in the endospore stain? |
Safranin, malachite green, & water. |
|
|
The endospore is ___ resistant to environmental stresses ___ the vegetative cell. |
More; than. |
|
|
Capsule stain is similar to what other staining procedure? |
Negative stain. |
|
|
A few genera of bacteria form endospores, ____ & ____. |
Bacillus & Clostridium. |
|
|
_______ are called “resting bodies” because they do not metabolize and are resistant to heat, desiccation, nutrient deprivation, extremes in temp, chemical agents including antibiotics, & ionizing radiation. They are formed when essential nutrients or water are not available. |
Endospores. |
|
|
Endospores are impermeable to most stains, so ____ is used to drive the stain into the endospore. |
Heat. |
|
|
True or false: bacterial stains are non-ionic, so neither acidic nor basic stains will adhere to their surfaces. |
True. |
|
|
True or false: endospores will easily form when the culture is growing in a fresh medium. |
False. |
|
|
Why are flagella so hard to stain? |
Flagella are so think & thread-like. |
|
|
True or false: fewer than 30 colonies on serially diluted and plated culture will give the correct estimate of colony forming units in original sample. |
False. |
|
|
What is the objective of the serial dilution method? |
To estimate the number of viable (living) cell concentration in the original sample. |
|
|
What is the objective of the serial dilution method? |
To estimate the number of viable (living) cell concentration in the original sample. |
|
|
Certain strains of bacterial species produce capsules and slime layers. These structures are composed of layers of polysaccharide or peptide covering the surface of the cell forming a viscous coat. This structure is a ______ when it is round or oval in shape & a ______ when it is irregularly shaped and loosely bound to the bacterium. |
Capsule; slime layer. |
|
|
Capsule staining is a _____ stain. |
Negative. |
|
|
To visualize flagella, we stain them. The stain coats the flagella, thereby increasing their ______. |
Diameter. |
|
|
To visualize flagella, we stain them. The stain coats the flagella, thereby increasing their ______. |
Diameter. |
|
|
2 main types of flagella: ?? |
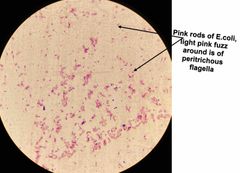
Peritrichous (all around) & polar (at one or both ends). |
|
|
(Special structures lab.) Enterobacter aerogenes or Serratia marcescens are the cultures used for _______ stain. |
Capsule stain. |
|
|
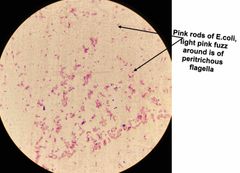
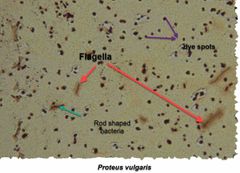
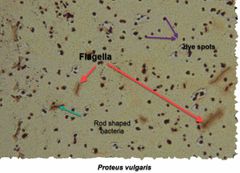
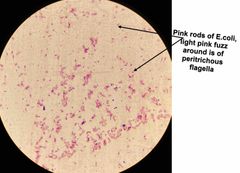
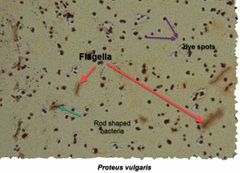
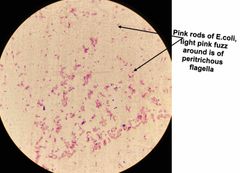
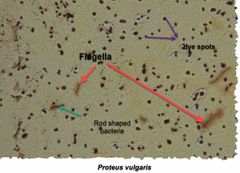
(Special structures lab.) Proteus vulgaris & Escherichia coli are used for _______ stain. |
Flagella stain. |
|
|
What type of stain is used for flagella staining? |
Leifson Flagella Stain. |
|
|
What stains are used in capsule staining? |
Copper sulfate & crystal violet. |
|
|
When endospore staining you counter stain with ____. |
Safranin. |
|
|
True of false: When capsule staining you need to heat fix your smear before you begin staining. |
False!!! Do not heat fix your capsule stain!!! |
|
|
True or false: When you are preparing your flagella stain you must heat fix your smear. |
False!!! Do NOT heat fix your smear, this will destroy the flagella structure. |
|
|
The ________ method involves applying a measured quantity of sample to a petri dish and counting the number of colonies that form. The number of colonies obtained is referred to as a(n) ______________ because only living cells are capable of reproducing and forming a colony. |
Serial dilution; viable cell count. |
|
|
(Serial dilution.) The number given by viable cell count method is called “_________”. |
Colony forming units (CFU) |
|
|
(Serial dilution.) To count individual colonies, it is necessary to have a sample with a low concentration, usually about _____ - _______ CFU/ml. |
100 - 1000. |
|
|
(Serial dilution.) on standard sized petri dishes only, plates with between ____ & _____ colonies can be counted accurately. |
30 and 300 |
|

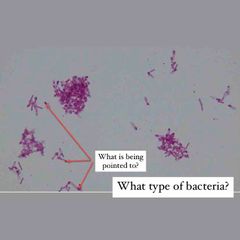
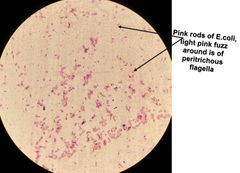
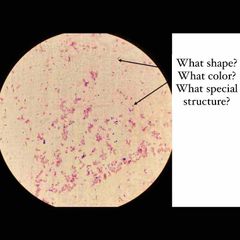
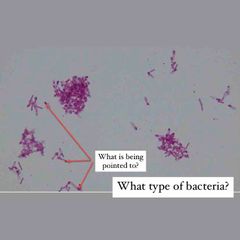
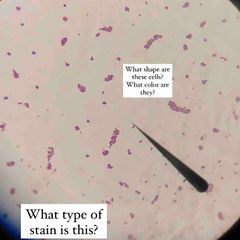
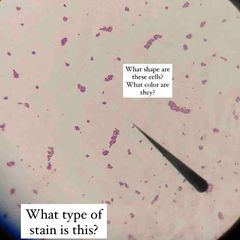
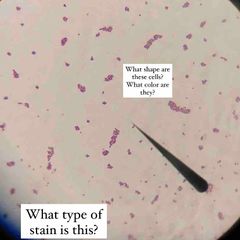
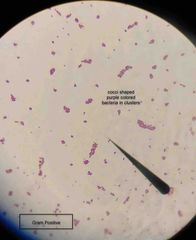
What type of stain is this? What kind of shape are the bacteria? What color dye is used? |

Simple stain. Rod shaped E. coli with Methylene Blue stain. |
|

What color/type dye is this? |
Methylene blue. |
|
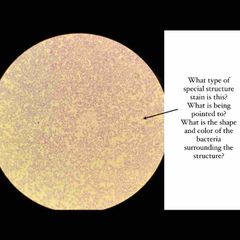
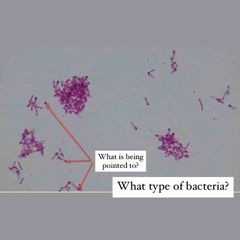
See image for questions! |
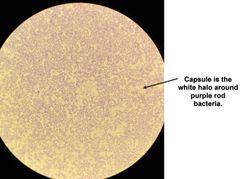
See image for answers! |
|
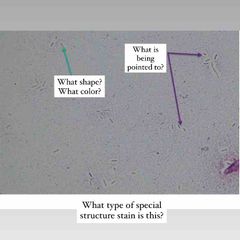
(See image.) |
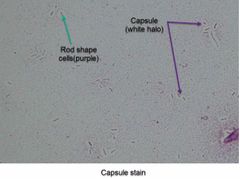
(See image.) |
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|

(See image.) |
(See image.) |
|
(See image.) |
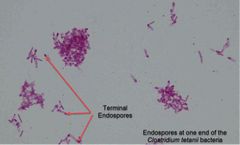
(See image.) |
|
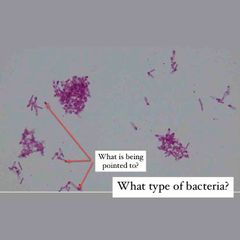
(See image.) |
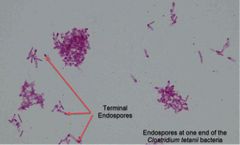
(See image.) |
|
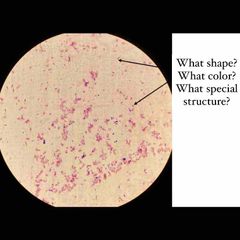
(See image.) |
(See image.) |
|
(See image.) |
(See image.) |
|
(See image.) |
(See image.) |
|

(See image.) |
(See image.) |
|
(See image.) |
(See image.) |
|
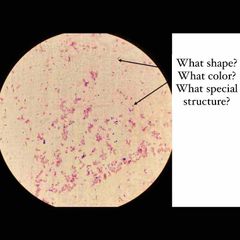
(See image.) |
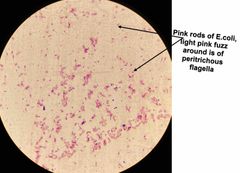
(See image.) |
|

(See image.) |
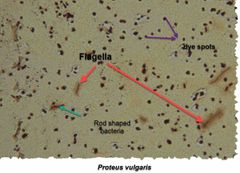
(See image.) |
|
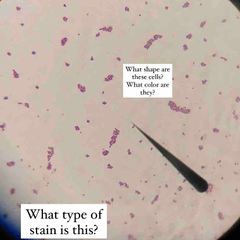
(See image.) |
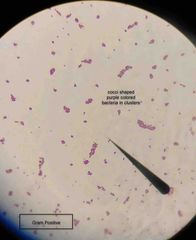
(See image.) |
|
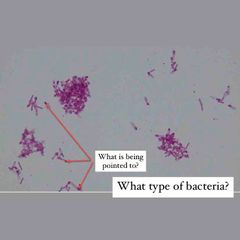
(See image.) |
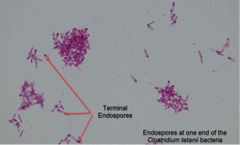
(See image.) |
|
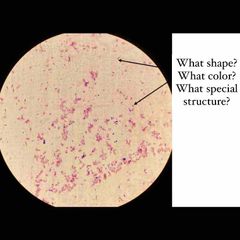
(See image.) |
(See image.) |
|

(See image.) |
(See image.) |
|
(See image.) |
(See image.) |
|
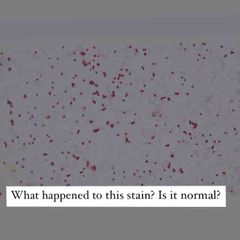
Front (Term) |
Not normal! Decolorizing agent was left on for too long. |
|
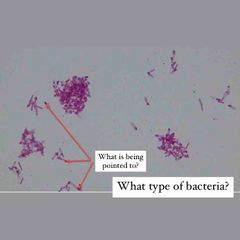
(See image.) |
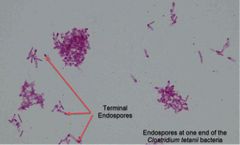
(See image.) |
|
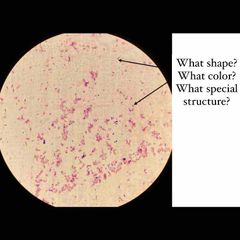
(See image.) |
(See image.) |
|

(See image.) |
(See image.) |
|
(See image.) |
(See image.) |
|
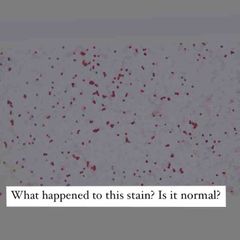
Front (Term) |
Not normal! Decolorizing agent was left on for too long. |
|

(See image.) |

(See image.) |
|
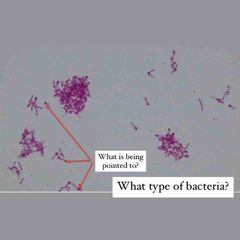
(See image.) |
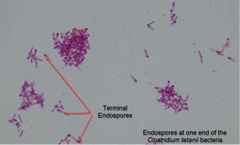
(See image.) |
|
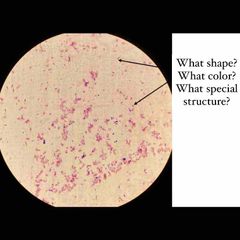
(See image.) |
(See image.) |
|

(See image.) |
(See image.) |
|
(See image.) |
(See image.) |
|
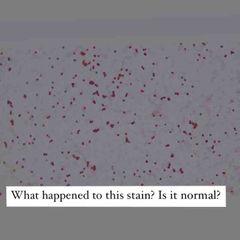
Front (Term) |
Not normal! Decolorizing agent was left on for too long. |
|

(See image.) |

(See image.) |
|
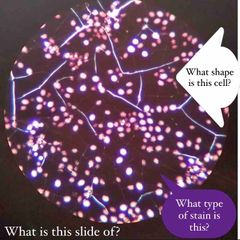
(See image.) |
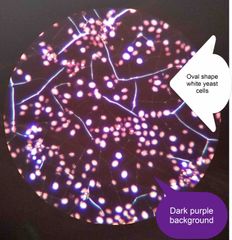
(See image.) |
|
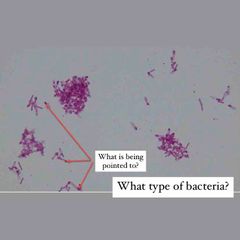
(See image.) |
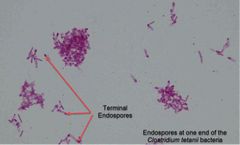
(See image.) |
|
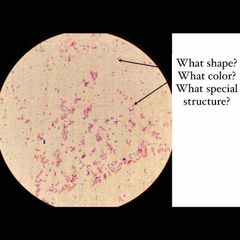
(See image.) |
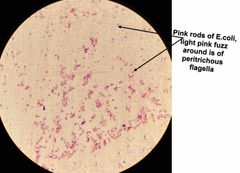
(See image.) |
|

(See image.) |
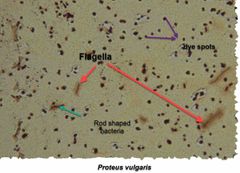
(See image.) |
|
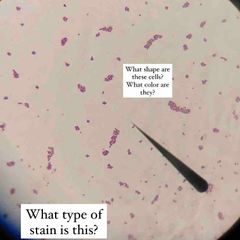
(See image.) |
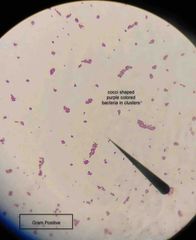
(See image.) |
|
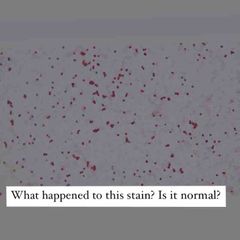
Front (Term) |
Not normal! Decolorizing agent was left on for too long. |
|

(See image.) |

(See image.) |
|
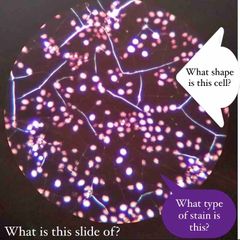
(See image.) |
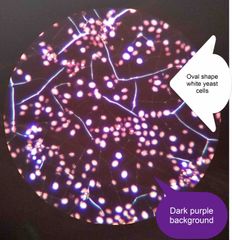
(See image.) |

