![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A ------------- is a fungus that breaks down organic matter. |
decomposer |
|
|
Plant diseases are caused by ------------ fungi. |
pathogenic |
|
|
Certain fungi form ------------- with plant roots in a beneficial association. |
mycorrhizae |
|
|
Fungi called ------------- live compatibly within the leaves of plants. |
Fungi called endophytes live compatibly within the leaves of plants. |
|
|
A ------------ is a cooperative association between fungi and certain types of algae. |
lichen |
|
|
basidiomycetes reproductive cycle |
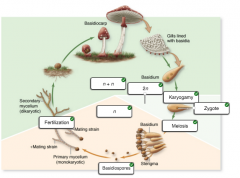
|
|
|
Application of neocallimastigomycetes (3) |
paper manufacturing cattle feed supplement biofuel production |
|
|
Not an application of neocallimastigomycetes (3) |
ice cream production plant cell model paint pigments |
|
|
Unlike other fungi, the Glomeromycota are all noted for their relationship with ------- --------. |
plant roots |
|
|
The term ---------- ------------- fungi is used to describe the Glomeromycota. |
arbuscular mycorrhizae |
|
|
The Glomeromycota live in a -------------- relationship with other organisms. |
mutualistic |
|
|
The Glomeromycota lack ---------- just like the zygomycetes. |
septae |
|
|
Characteristic of Fungi (3) |
mycelium chitin cell walls dikaryotic cells |
|
|
Typical of Other Eukaryotes (3) |
chloroplasts autotrophs cellulose cell walls |
|
|
Which trait contributes most to the value of fungus in symbiotic relationships? a. Fungi rely on both asexual and sexual reproduction. b. Fungi can live in a wide variety of environmental conditions. c. Fungi can break down and release nutrients from living and dead organisms. d. Fungi have spores that can resist severe conditions. |
c |
|
|
Select the true statements concerning reproduction of basidiomycetes. (Check all that apply.) a. The adult forms of a typical basidiomycete consists of a mass of dikaryotic primary mycelia. b. The secondary mycelia fuse to form primary mycelia. The primary mycelia form the fruiting body. c. The gills of an Amanita mushroom contains basidiospores. d. Karyogamy produces a diploid zygote that undergoes meiosis. |
c, d |
|
|
For many years, yeast have been a eukaryotic model for ---------- research. |
genetic |
|
|
Ascomycetes are used for -------------- to give sour taste to certain breads. |
fermentation |
|
|
Certain soil ascomycetes can cause a disease called ------------------. |
coccidioidomycosis |
|
|
Yeast are used for a characteristic research technique called the ---- ------- ------------ to study genomics. |
two-hybrid system |
|
|
What is the advantage of a zygospore? a. It allows for asexual reproduction. b. It allows for the formation of septa between nuclei. c. It initiates karyogamy. d. It can resist harsh conditions. |
d |
|
|
Which property of fungi best explains the reason why fungi are used in bioremediation applications? a. Fungi are NOT typically used for bioremediation because bacteria work well. b. Fungi can modify their DNA to produce chemicals that bind pollutants. c. Fungi grow rapidly and the mycelium can spread out to cover large areas. d. Fungi are very difficult to poison so they can tolerate any type of pollutant. e. Fungi produce enzymes that break down a variety of organic compounds. |
e |
|
|
Among the bryophytes, which of the following contain distinct stemlike axis, small leaves, and rootlike rhizoids? a. cycads b. hornworts c. algae d. liverworts e. mosses |
e |
|
|
Chlorophytes are considered close relatives of land plants because (check all that apply) a. they both contain chlorophyll a. b. they are unicellular. c. they have relatively few proteins in common with plants. d. they both contain chlorophyll b. e. they both contain carotenoids. f. some chlorophytes have a haplodiplontic life cycle like plants. |
a, d, e, f |
|
|
Place the listed structures or processes on the fern life cycle. |
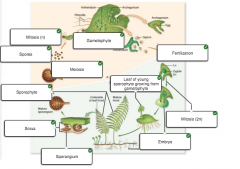
|
|
|
The aquatic ancestry of bryophytes is most clearly demonstrated by what character? a. the use of flagellated motile sperm b. the production of a sporangium c. a nutritionally dependent sporophyte d. mycorrhizal associations with fungi |
a |
|
|
Indicate if the following statements are True or False regarding features of Pterophytes. 1. Ferns, horsetails, and whisk ferns produce archegonia and antheridia. 2. The sperm of whisk ferns and horsetails have flagella but fern sperm lack flagella. 3. The non-photosynthetic leaves of horsetails are called fronds. 4. Ferns produce sporangia in structures called sori. 5. Ferns and horsetails have roots, but whisk ferns have lost this trait since diverging from other Pterophyte lineages. |
1. True-All Pterophytes produce archegonia and antheridia. 2. False-Sperm cells of all Pterophytes have flagella and require water to swim to eggs. 3. False-The leaves of ferns are called fronds. 4. True-Sori are typically found on the undersurface of fronds and contain sporangia where spores are produced. 5. True-Pterophytes have roots but whisk ferns have lost them over the course of evolution. |
|
|
Place the different characteristics on the phylogeny indicating where the traits evolved. |
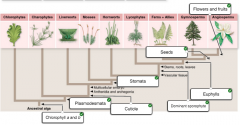
|
|
|
One of the main distinctions between charophytes and land plants is the possession of a cuticle. Why do modern charophytes lack a cuticle? a. Modern Charophytes make up for the absence of a cuticle by having large numbers of stomata. b. Cuticles aren't necessary when living in water. c. Their tough seed coats negate the need for a cuticle. d. Charophytes have a haplodiplontic life cycle. |
b |
|
|
Place the names of these different taxa on the phylogeny. |
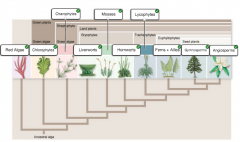
|
|
|
Select the true statements relating to the colonization of land by plants. a. Desiccation is a much more common problem in terrestrial environments. b. Cuticle layers reduce gas exchange. c. Xylem tissue, seeds and stomata are found on both plants and charophytes. d. Without trachids land plant would not have been to able to grow more than just a meter or so tall. |
a, b, d |
|
|
What would be the simplest way for a non-botanist to confirm that the fern is not a small palm tree? a. Leaf shape, only ferns have dissected leaves b. Lack of roots, palms have roots but ferns do not c. Dots on the underside of the leaf, only ferns have sporangia under their fronds d. Height, all ferns are very small |
c |
|
|
Double fertilization produces a ___________ embryo and a _________ endosperm. (ploidy) |
diploid, triploid |
|
|
A feature that is shared by pines, cycads, and gingkos but is not found in flowering plants is a. pollen tube formation. b. non-flagellated sperm. c. partially exposed megaspore. d. wind dispersal of pollen. e. development of a seed. |
c |
|
|
Pollen comes from the a. style. b. carpel. c. anther. d. petal. e. stigma. |
c |
|
|
From what are fruits derived? a. anthers b. ovaries c. stigmas d. styles e. filaments |
b |
|
|
What does it mean if a plant is dioecious? |
There are separate male and female sporophytes. |
|
|
Select all the advantages that seeds have over spores. a. Seeds have increased drought resistance. b. Long term dormancy is possible. c. Sexual reproduction is only possible with seeds. d. Nutrition is packaged with the embryo. e. Widespread dispersal is possible with a seed coat. |
a, b, d |
|
|
Select the true statements concerning sperm and pollen. a. In seed plants the entire male gametophyte is dispersed. b. The pollen fertilizes the egg. c. The pollen tube facilitates the pollination of the ovule. d. Pollen transports the cells that form the sperm but only the sperm fertilizes the egg. e. Unlike mosses and ferns water is not needed for fertilization in seed plants. |
a, d, e |
|
|
Select each type of tissue that may be found in a mature fruit or seed. a. Diploid sporophyte tissue from the previous generation b. Triploid endosperm c. Diploid embryonic tissue d. Haploid sperm cells e. Tissue from the female gametophyte |
a, b, c, e |
|

|
Coniferophyta |
|
|
|
Cycadophyta |
|

|
Gnetophyta |
|

|
Ginkgophyta |
|
|
Angiosperm reproduction often involves ----------- which transport ------------- from one -------------- to another. |
animals, pollen, flower |
|
|
Animal ------------ are often attracted to flowers by visual cues such as colorful -------------. |
pollinators, petals |
|
|
Animals also visit flowers to access food rewards such as ---------- produced by glands called ------------ at the base of the -----------. |
nectar, nectaries, ovary |
|
|
Sponge cells are unique because throughout their development they can -------------- from one type of cell to another. |
differentiate |
|
|
Sponges are truly ---------------- organisms. |
multicellular |
|
|
---------------- are flagellated cells that line internal cavities and are responsible for pumping water and small particles into the sponge. |
Choanocytes |
|
|
The exterior of a sponge is comprised of flattened cells that form an outer ----------------. |
epithelium |
|
|
The inner layer of a sponge, the mesohyl, contains several types of ----------- cells, which secrete materials to form a skeleton-like structure for support. |
amoeboid |
|
|
Which one of the following applies to the phylum Ctenophora? a. often bioluminescent marine animals b. Parazoa c. coelomate d. deuterostome e. protostome |
a |
|
|
All species of animal have general features in common. Check all of the features that would apply to animals. a. Animal cells possess a cell wall and are quite rigid. b. Most animals have the capacity for active movement. c. Animal zygotes undergo mitotic divisions called cleavage. d. Not all animals are multicellular. e. All animals produce diploid spores. f. All animals are heterotrophs. |
b, c, f Explanation: Animals lack cell walls; their cells are usually very flexible. Also, all animals are multicellular; unicellular heterotrophs are members of the kingdom Protista. Finally, animal lifecycles do not follow an alternation of haploid (gametophyte) and diploid (sporophyte) generations as do plants. |
|
|
Systematists use several fundamental criteria to assign animals to phyla. Check all of the criteria that systematists would use to classify animals under specific phyla. a. Feeding behavior b. Adult body symmetry c. Ultimate adult body size d. The embryological formation of body cavities e. Biogeographic distribution f. Gene sequences g. The number of tissue layers |
b, d, f, g Explanation: Feeding behavior is often highly variable among species within the phylum and would not be aligned with a homologous trait. Also, final adult body size would not be a good classification criterion, because size often varies greatly among individuals within a species and among species within a phylum. Finally, animal distribution is shaped by many external factors that are not always related to phylogeny.Feeding behavior is often highly variable among species within the phylum and would not be aligned with a homologous trait. Also, final adult body size would not be a good classification criterion, because size often varies greatly among individuals within a species and among species within a phylum. Finally, animal distribution is shaped by many external factors that are not always related to phylogeny.Feeding behavior is often highly variable among species within the phylum and would not be aligned with a homologous trait. Also, final adult body size would not be a good classification criterion, because size often varies greatly among individuals within a species and among species within a phylum. Finally, animal distribution is shaped by many external factors that are not always related to phylogeny.Feeding behavior is often highly variable among species within the phylum and would not be aligned with a homologous trait. Also, final adult body size would not be a good classification criterion, because size often varies greatly among individuals within a species and among species within a phylum. Finally, animal distribution is shaped by many external factors that are not always related to phylogeny.Feeding behavior is often highly variable among species within the phylum and would not be aligned with a homologous trait. Also, final adult body size would not be a good classification criterion, because size often varies greatly among individuals within a species and among species within a phylum. Finally, animal distribution is shaped by many external factors that are not always related to phylogeny.Feeding behavior is often highly variable among species within the phylum and would not be aligned with a homologous trait. Also, final adult body size would not be a good classification criterion, because size often varies greatly among individuals within a species and among species within a phylum. Finally, animal distribution is shaped by many external factors that are not always related to phylogeny.Feeding behavior is often highly variable among species within the phylum and would not be aligned with a homologous trait. Also, final adult body size would not be a good classification criterion, because size often varies greatly among individuals within a species and among species within a phylum. Finally, animal distribution is shaped by many external factors that are not always related to phylogeny. |
|
|
Parazoa a. have no true tissues. b. exhibit primitive segmentation. c. are pseudocoelomates. d. exhibit bilateral symmetry. e. include Cnidaria and Ctenophora. |
a |
|
|
Select the true statements concerning ctenophores. a. They are diploblastic. b. They have some tissue derived from mesoderm. c. They have a modified radial symmetry. d. They are a type of jellyfish |
b, c |
|
|
The segmentation of animals has allowed for several advantages. Indicate if the following statements concerning segmentation are true or false. A. Locomotion is more efficient in segmented animals because independent segments can move semi-independently. B. Partitions isolate each segment, so each must contract or expand in unison. C. In segmented animals like earthworms (phylum Annelida), each segment may develop a nearly complete set of adult organ systems. D. Redundancy in segmented animals is not an advantage. |
A. True-The capacity for semi-independent movement by each segment allows for more complex locomotive behavior. B. False-Partitions between segments allows them to contract or expand autonomously. C. True-By having a nearly complete set of adult organ systems in each segment, damage to one segment is not necessarily fatal because other segments can duplicate the damaged segment’s functions. D. False-Redundancy among segments allows for functional “back-ups” for the animal, which can be advantageous. |
|
|
Which one of the following terms applies to the phylum Cnidaria? a. pseudocoelomate b. triploblastic c. Parazoa d. radial symmetry e. protostome |
d |
|
|
Which feature would only be found in the Bilateria? a. Nerves and sensory systems b. Anterior cephalization c. Extracellular digestion d. Sexual reproduction |
b |
|
|
Choanocytes a. produce the spicules. b. secrete the mesohyl. c. filter particles out of the water. d. make the spongin protein. |
c |
|
|
Place the labels in the correct locations to show the muscular actions required for an earthworm to move forward through the soil. |
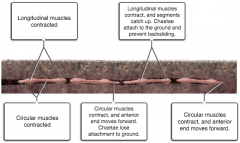
Explanation: When circular muscles contract, the pressure of the fluid in the hydrostatic skeleton increases and the body becomes longer and thinner. When longitudinal muscles contract, the body shortens. |
|
|
Elephantiasis is a human disease that is caused by a parasitic nematode that lives in the circulatory system. What causes the massive swelling of tissue that has given the disease its name? a. Internal bleeding from damage to blood vessels causes the swelling. b. The volume of eggs produced by the worms accounts for the swelling. c. The worm infection damages the kidneys which causes the swelling. d. The worms block the lymph vessels which causes the swelling. |
d |
|
|
Parasitic leeches possess a number of adaptations associated with blood-feeding. Evaluate the following statements about blood-feeding in leeches and determine if they are true or false. 1. All leeches are ectoparasites that suck blood from their hosts. 2. The muscular pharynx acts directly to pump the blood from the host into the leech. 3. Leeches secrete anticoagulant to keep the blood of their host flowing. 4. Leeches avoid being detected when biting their host by injecting an anesthetic into the host’s wound. 5. Blood-feeding leeches often detect hosts by sensing gradients of nitrogen gas (N2) in the environment. |
1. False-Only about half of leech species suck blood from their hosts. 2. True- 3. True 4. True 5. False-Leeches detect prey by sensing gradients of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the environment. |
|

Annelids have a basic body plan that is a tube within a tube. There are, however, major differences between the two principal classes within this phylum. Associate the following characteristics with the appropriate annelid class. |
Polychaeta |
|

Annelids have a basic body plan that is a tube within a tube. There are, however, major differences between the two principal classes within this phylum. Associate the following characteristics with the appropriate annelid class. |
Clitellata |
|
|
Members of the phyla Annelida and Mollusca belong to the spiralian group Lophotrochozoa because they both possess a ______________ and a have marine representatives that undergo a ciliated larvae stage called a _______________. |
coelom; trochophore Explanation: Many members of both groups undergo a larval trochophore stage and all possess a coelom. |
|
|
The high internal pressure and lack of circular muscles means nematodes cannot a. move by changing their diameter. b. flex their bodies dorsoventrally. c. turn around easily. d. move very rapidly. |
a |
|
|
True or False: The scolex of a tapeworm contains the mouth and the anterior neural ganglia. |
False |
|
|
In a tidepool, you discover a worm with a flattened body. What one feature would suggest that it is a nemertean rather than a platyhelminth? a. An exoskeleton that is molted periodically b. A complete gut with mouth and anus c. Two lateral nerve cords d. Eyespots on a cephalized anterior e. Muscles |
b |
|
|
Many parasitic flatworms have complex lifecycles involving several host organisms. For Asian liver flukes, humans are the final host. What would result if humans were not available for a population of Asian liver flukes? a. They could not form metacercarial cysts. b. They would live forever in a quiescent state. c. The eggs would never be able to hatch. d. They could not reproduce. |
d |
|
|
Annelids and arthropods were once considered closely related. Some juvenile forms of arthropods resemble annelids (maggots and caterpillars). However, modern classification schemes separate them into distant groups. What feature suggests a fundamental difference between the two groups? a. The presence or absence of a coelom b. Whether the circulatory system is open or closed c. Whether growth is continuous or step-wise d. The presence or absence of segments |
c |

