![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
all of the chemical reactions that occur in the body?
A. catabolism B. metabolism C. anabolism D. glycolysis |
metabolism
|
|
|
chemical reactions that breakdown complex organic molecules into simple ones; these process are exergonic, meaning they produce more energy then they consume?
A. catabolism B. anabolism C. metabolism D. oxidative phosphorylation |
catabolism
|
|
|
chemical reactions that combine simple molecules and monomers to form the body's complex structural and functional components; these processes are endergonic meaning they consume more energy then they produce?
A. catabolism B. anabolism C. metabolism D. glycolysis |
anabolism
|
|
|
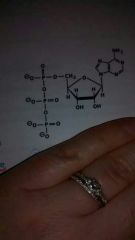
ATP consists of three distinct components which are?
A. adenine molecule, glycolysis, electron transport chain. B. formation of acetyl coenzyme A, pyruvate, mitochondrial membrane. C. mitochondrial membrane, glycolysis, ribose molecule. D. adenine molecule, A ribose molecule, three phosphate groups bonded to each other. |
adenine molecule , A ribose molecule, 3 phosphate group bonded to each other
|
|
|
The terminal phosphate group is broken off and ATP and high-energy reactions required in living cells producing a blank?
A. nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide B flavin adenine C adenosine triphosphate D. adenosine diphosphate |
adenosine diphosphate
|
|
|
what two coenzymes are commonly used by animals to transfer hydrogen atoms?
A. adenosine triphosphate, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. B. flavin adenine dinucleotide, A ribose molecule. C. nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, flavin adenine dinucleotide. D. adenosine diphosphate, glycolysis molecule. |
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, flavin adenine dinucleotide
|
|
|
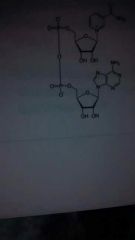
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) - a derivative of B vitamin niacin
flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)- hey drivative of the B vitamin riboflavin |
oxidative NAD+ / reduced NADH
oxidative FAD+/ reduced FADH2 |
|
|
NAD
|
|
|
ATP
|
|
|
The addition of phosphate group to molecule is called?
A. substrate-level phosphorylation B. oxidative phosphorylation C. phosphorylation D. photophosporylation |
phosphorylation
|
|
|
Organisms use three mechanisms of phosphorylation to generate ATP what are they?
A substrate level phosphorylation, oxidative phosphorylation, photophosporylation. B. oxidative phosphorylation, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, glycolysis C. photophosphorylation, Krebs cycle reactions, electron transport chain reactions D. Substrate level phosphorylation, photophosphorylation, glycolysis |
substrate-level phosphorylation, oxidative phosphorylation,photophosphorylation
|
|
|
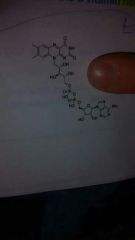
FAD
|
|
|
The oxidation of glucose to produce ATP is known as what and involves four set of individual reactions?
A. pyruvate; glycolysis, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, oxidative phosphorylation, chylomicrons B. homeostasis; Low-density lipoproteins, amino acids, triglycerides , C. Cellular respiration; glycolysis, formation of acetyl coenzyme, Krebs cycle reactions, electron transport chain reactions D. anabolism; catabolism metabolism vitamins chromium |
cellular respiration glycolysis formation of acetyl coenzymes Krebs cycle reaction electron transport chain reactions
|
|
|
Series of reactions that occur in the cytosol yielding to net ATP molecules when oxygen is involved glycolysis also aerobically produces pyruvic acid without oxygen involved glycolysis anaerobically produces lactic acid?
A. Electron transport chain reaction B. Formation of acetyl coenzyme C. glycolysis D. Krebs cycle reaction |
Glycolysis
|
|
|
Performed in the matrix of the mitochondria a transition step in aerobic respiration that prepares pyruvate to enter the Krebs cycle by producing acetyl CoA?
A.Formation of acetyl coenzyme-A B Krebs cycle reaction C electron transport chain reactions D glycolysis |
Formation of the acetyl coenzyme A
|
|
|
acetyl CoA produces co2 ATP NADH and fadh2 in the mitochondrial matrix?
A formation of the acetyl coenzyme A B glycolysis C Krebs cycle reactions D electron transport chain reaction |
Krebs cycle reactions
|
|
|
Ned h and fadh2 become oxidized in transfer electrons through a series of electron carrie in the inner mitochondrial membrane to reduce large quantities of ATP?
A. Formation of acetyl coenzyme A B. glycolysis C. Krebs cycle reaction D. electron transport chain reactions |
Electron transport chain
|
|
|
ten steps constitute glycolysis, specifically aerobic glycolysis in the presence of what? A. water B. oxygen C. pyruvate D. metabolism |
oxygen |
|
|
2 ATP are necessary at the beginning of glycolysis to begin the process and blank, blank ?are eventually produced from these 10 reactions using a net of blank? A 4 ADP 2ADP B 5ATP 10ATP C 2FAD 4 FAD D 4 ATP 2 ATP |
4ATP, 2ATP |
|
|
blank is modified by several enzymes which form an E1,E2,E3, complex? A. glycolysis B. pyruvate C. ATP D. krebs cycle |
pyruvate |
|
|
The__ __ __, also known as the citric acid cycle is important because it yields a large amount of NADH, and FADH2 that can eventually be used to produce larger quantities of blank?
___ ___ ___ this also takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria?
A. essential amino acid, triglycerides, high-density lipoproteins B. Flow density lipoproteins, ATP, krebs cycle C. Krebs cycle, ATP, Krebs cycle D. pyruvic acid, ADP, essential amino acid,
|
Krebs cycle ATP kreb cycle |
|
|
The products from the Krebs cycle enter the _ _ _ in the inner mitochondrial membrane? A. Electron transport chain B. Mitochondria C. Chylomicrons D. Lipolysis |
Electron transport chain |
|
|
Glucose not immediately needed for ATP production is attached to many other glucose molecules to produce glycogen in approximately 75% of glycogen is in muscle fibers and 25% of glycogen is stored in the liver? A. Glycolysis B. Glyogenesis C. gluconeogenesis D. Glycogenolysis |
Glycogenesis |
|
|
The breakdown of glycogen to glucose? A. Glycolysis B. Glyogenesis C. Gluconeogenesis D.glycogenolysis |
Glycogenolysis |
|
|
Small substrates such as triglycerides lactic acid or certain amino acids can be used to drive the production of new glucose molecules when glucose is not readily available? A. Glycolysis B. Gluconeogenesis C. Glyogenesis D. Glycogenolysis |
Gluconeogenesis |
|
|
In order to transport lipids in watery blood , they must first be made more water soluble by attaching proteins from the blank and blank? A. Gallbladder and stomach B. liver and pancreas C. Intestine and pancreas D. Liver and intestines |
Liver and intestines |
|
|
Blank and blank, together to form lipoproteins, spherical particles that are surrounded on the outside by specialized protons termed blank? A. Adipose and lipolysis , glycolysis B. fatty acid |
Lipid and protein, apoprotein |

