![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
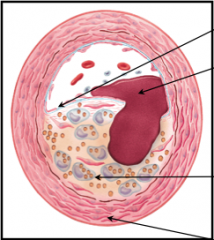
Match the following:
- Thin Fibrosis Cap - Media - Lipid core and Macrophages - Thrombus |
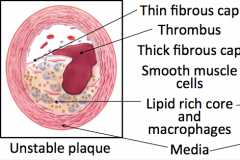
|
|
|
Approximately how much of a blood vessel needs to be occluded before angina is experienced?
|
70% - Via Giacomontonio lecture
80% - Pelzer lecture so between 70-80% then |
|
|
What are 3 symptoms of angina?
|
1. Discomfort in chest (pressure, burning, tighness) can be either side
2. Pain radiation (arms, neck, back, jaw) 3. Nausea, fatigue, short of breath, sweating, light headedness , palpitations or weakness |
|
|
Describe the difference between stable angina and unstable angina
|
Stable Angina:
- occurs in physical exertion -pain is predictable each time - last 5-15 minutes - pain spreads to arms and back - relieved with rest and medications (nitro) Unstable angina - occurs at rest, nighttime, very little exertion - unpredictable pattern of occurrence - last longer (some over 30 minutes) - pain builds - medications not effective for relief - can lead to MI (heart cell death) |
|
|
Women typically experience angina as a ________ (dull / stabbing chest pain), _________ (appreciate/depreciate) shortness of breath and expeience ________ (more / less) nausea and abdominal pain
|
stabbing, appreciate, more
|
|
|
Variant or "Prinzmetals" angina occurs during the night / early morning hours. What is the main cause of this kind of angina?
|
Caused by Vasospasm of the coronary arteries.
Also: relieved by nitro and calcium channel blockers |
|
|
Describe the ankle-brachial index (ABI) and what its useful for
|
ABI is taking the systolic blood pressure in the brachial artery and dividing it by the ankle pressure.
1.2-1 = normal 0.9-1= acceptable 0.7-0.9 = abnormal, mild Peripheral artery disease 0.5-0.7 = moderate peripheral artery disease |
|
|
"Just for fun:
Moyamoya disease is ……….." |
The blood vessels develop collateral circulation around the blocked vessels to compensate for the blockage, but the collateral vessels are small, weak, and prone to hemorrhage, aneurysm and thrombosis. On X-rays, these collateral vessels have the appearance of a "puff of smoke" ("もやもや (moyamoya)" in Japanese)
|
|
|
What are symptoms that differential GI disturbances from cardiac disturbances:
|
"-Burning is epigastic/ lower sternum (cardiac is usually higher)
- More food association and not physical exertion - bending over makes worse / water brash present ***- responds to Proton pump inhibitor but * will also respond to nitroglycerin so USE PPI first to rule out GI |
|
|
What is the main cause of renal artery disease?
|
Atherosclerosis 60-80%
followed by fibrous dysplasia 20-40% (beads in renal artery) |
|
|
What Glomular filtration rate (GFR) cutoff is usually associated with development of renal symptoms/problems ?
|
"60 ml/min
Just FYI: Stage 1 (asymptomatic) - 90+ ml/min Stage 2 (asymptomatic - mild reduction) 60-89 ml/min Stage 3 (symptoms - Moderate reduction) 30-59 ml/min Stage 4 (symptoms - severe reduction) 15-29 ml/min Stage 5 (kidney failure) - less than 15 ml/min |
|
|
Name 5 of the 12 symptoms (stage 3 and beyond) listed in lecture of chronic kidney disease:
also what drug should patients be started on with poor functioning kidneys? |
1. HTN
2. Edema (peripheral or general) 3. SOB / Congestive heart failure 4. Chest Pain (pericaditis or angina) 5. Arrythemia (Hyperkalemia/metabolic acidosis) 6. Increased Urinary Frequency (esp. nigh-time) 7. Fatigue/ Weakness (from anemia) 8. Loss of appetite 9. Poor platelet function (bruising and bleeds) 10. Bone Pain/Fractures (poor PTH, Ca2+, phosphorus retention) 11.Erectile dysfunction 12. Headache, Peripheral neuropathy, restless leg syndrome (electrolytes) EPO - Erythropoietin (normally made in kidney) to increase RBC production |
|
|
Renal Ischemia is bad bacuse the kidney will do what in response?
|
1. increase renin -> angiotensin II & aldosterone
2. increase TPR 3. increases Na+ absorption (via aldosterone) and therefore cardiac output (increased volume) 4. increase BP via above mechanisms |
|
|
Risk factors for heart and vascular disease
modifiable and non-modifiable |
Non modifiable:
Age (men > 45; women > 55) family Hx (first degree relative [Male < 55, female < 65]) male sex modifiable smoking HTN DLP DM LVD obesity sedentary life style excess alcohol proteinuria |
|
|
CCS functional classification of angina
|

|
|
|
what are the 5 categories of ischemic stroke?
|
- thrombosis (obstruction of a blood vessel by a blood clot forming locally)
- embolism (obstruction due to an embolus from elsewhere in the body) - systemic hypoperfusion ("shock", watershed areas) - venous thrombosis - cryptogenic (of unknown origin) |
|
|
Suspicious symptoms of CVA/stroke
|
weakness : sudden weakness, numbness and/or tingling in the face arm or leg
Trouble speaking: sudden temporary loss of speech or trouble understanding speech Vision problems: Sudden loss of vision, particularly in one eye or double vision headache: sudden severe and unusual headache Dizziness: sudden loss of balance, especially with any of the other symptoms |

