![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
106 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is anatomical position? |
A standard position anatomists refer to when they are describing location of structures or pathologies. |
|
|
How 6 things must a person do to stand in anatomical position? |
1. Stands erect 2. head and eyes to the front 3. Upper limbs by the sides 4. Palms front 5. lower limbs close together 6. toes directed to the front |
|
|
How does a person in supine position lie? |
flat on the back, face up. |
|
|
How does a person in prone position lie? |
lies face down. |
|
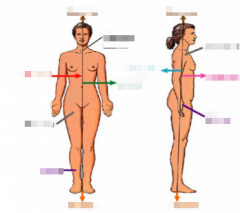
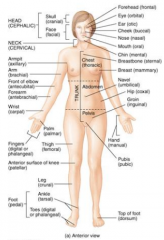
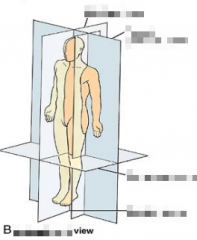
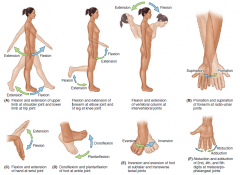
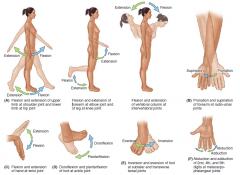
Name the arrows. |
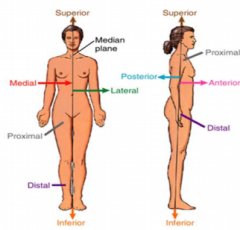
|
|
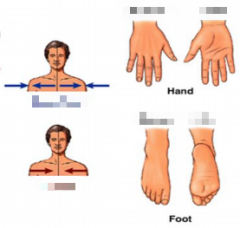
Name the arrows and sides of the hand and foot. |
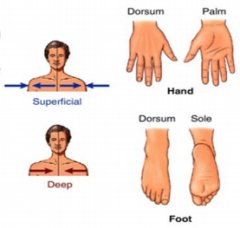
|
|
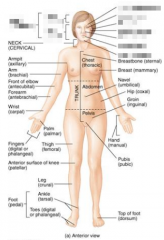
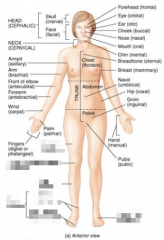
Name the blurred parts of the head. |
|
|
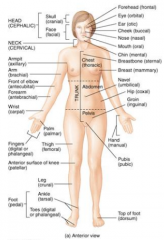
Name the blurred parts of the trunk. |
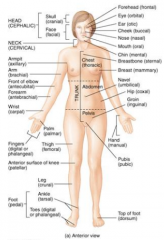
|
|
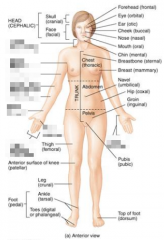
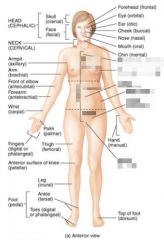
Name the blurred parts of the neck and arm. |
|
|
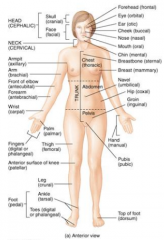
Name the blurred parts of the leg. |
|
|
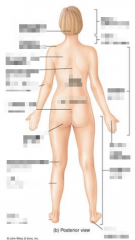
Name the parts of the posterior. |
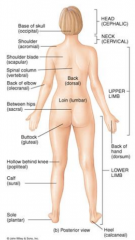
|
|
|
What is a plane? |
An imaginary flat surface that passes through the body. |
|
|
What is a section? |
One of the 2 surfaces (pieces) that results when the body is cut by a plane passing through it. |
|
|
What is the median or midsagittal plane? |
A line that passes vertically through the center of the body and divides the body into equal left and right halves. |
|
|
What are parasagittal planes? |
Planes that run parallel to the median plane. There can be many parasagittal planes. |
|
|
What are coronal planes? |
Planes that are passing vertically at the right angle to the medium plane. There can be more than one coronal plane. |
|
|
What are the names of the 2 portion that a coronal planes divide called? |
1. Anterior 2. Posterior |
|
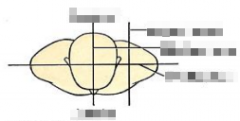
Name the planes of the superior view. |
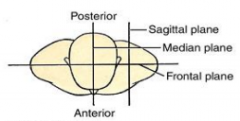
|
|
Name the planes of the anteriolaterial view. |
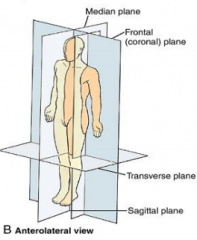
|
|
|
What are transverse planes? |
Planes passing horizontally at the right angle to the median and coronal plane. |
|
|
What 2 sections do transverse planes divide the body into? |
1. Superior 2. Inferior |
|
|
What are Oblique planes? |
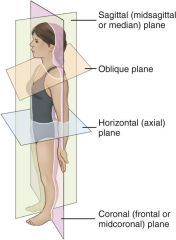
Planes not parallel to the median coronal and transverse planes. |
|
|
Symmetrical and paired structures occurring on both sides of the body or having left and right members. |
Bilaterial |
|
|
Structures which only occur in one side of the body. |
Unilateral |
|
|
What is ipsilateral? |
The structure of event that occurs on the same side of the body. |
|
|
What is contralaterial? |
"on the opposite side of the body" |
|
|
What are cavities inside the body? |
Spaces or potential spaces inside the body. |
|
|
What are 2 major cavities in the body? |
1. Ventral Cavity 2. Dorsal Cavity |
|
|
What is the cavity derived from embryonic gut and divided by the diaphragm into thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities? |
Ventral Cavity |
|
|
What is the cavity that develops from embryonic neural tube and is divided into cranial cavity formed by the skull and holds the brain and spinal canal? |
Cranial cavity |
|
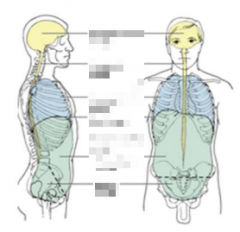
Name the different cavities. |
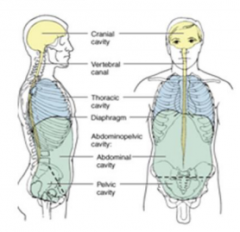
|
|
|
What kind of membranes are body cavities usually lined by? |
Connective tissue membranes. |
|
|
What is the dorsal cavity lined by? |
Meninges |
|
|
What is the meninges? |
The 3 membranes covering the brain and spinal cord: dura mater, archnoid, and pia mater. |
|
|
What membranes is the ventral cavity lined by? |
Fascia and serous membranes. |
|
|
What do serous membrane used for? |
Separating and wrapping organs of the ventral cavity. |
|
|
What is the pleura? |
A serous membrane around lungs. |
|
|
What is the pericardium? |
A serous membrane around the heart. |
|
|
What is peritoneum? |
A serous membrane around the abdominal viscera. |
|
|
What are the 2 layers of serous capsule? |
1. The visceral layer closest to the organ. 2. The parietal layer lining the cavity. |
|
|
What is the thoracic cavity filled with? |
Lungs and mediastinum. |
|
|
What is the mediastinum? |
The space between lungs that contain the heart, esophagus, trachea, important nerves and blood vessels. |
|
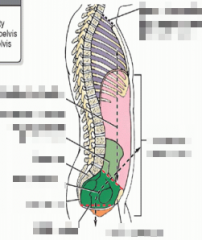
Name where the arrow is pointing. |
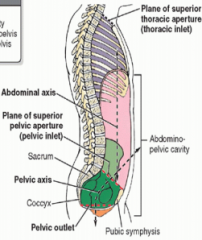
|
|
Name where the arrow is pointing. |
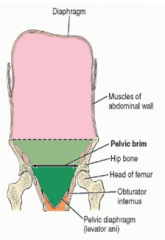
|
|
|
What is the abdominopelvic cavity? |
The largest cavity which is divided into four quadrants or nine regions. |
|
|
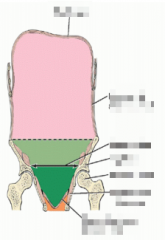
The abdominal quadrants are defined by what 2 planes? |
The median and transumbilical planes. |
|
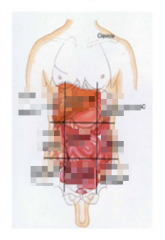
Name the 9 regions |
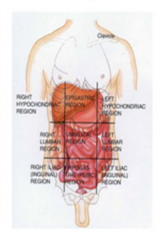
|
|
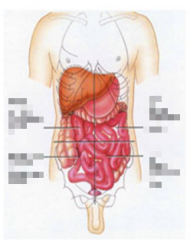
Name the 4 quadrant |
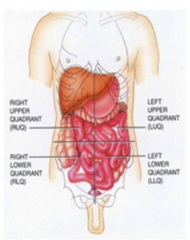
|
|
|
|
|
|
Memorize fibrous joints |
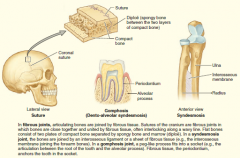
|
|
|
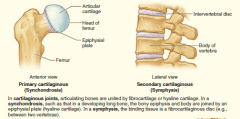
Memorize cartilaginous joints |
|
|
|
Memorize synovial joint |

|
|
|
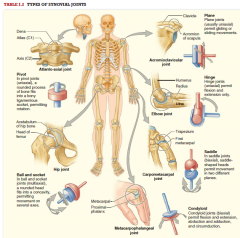
Memorize TYPES OF SYNOVIAL JOINTS |
|
|

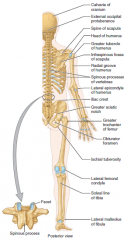
Memorize bone markings |
|
|
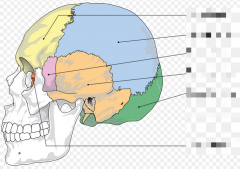
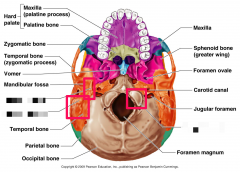
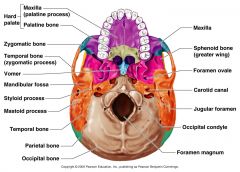
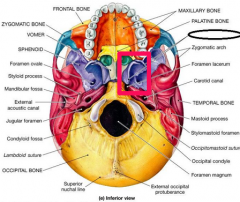
Identify Cranial Bones (neocranium) |
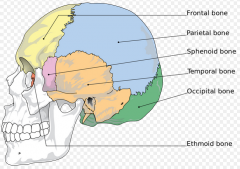
|
|
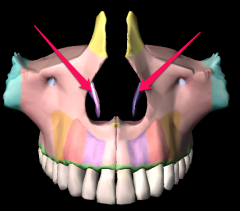
|
Inferior concha |
|
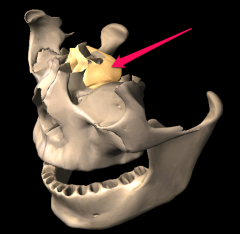
|
Ethmoid |
|
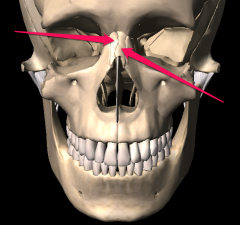
|
Nasal |
|
|
Maxilla |
|
|
Lacrimal |
|
|
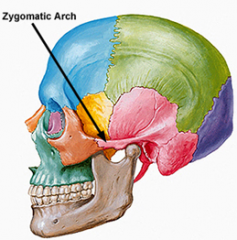
Zygomatic |
|
|
Palatine |
|
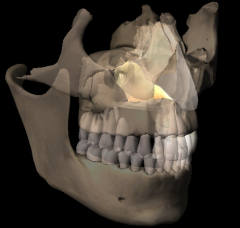
|
Volmer |
|
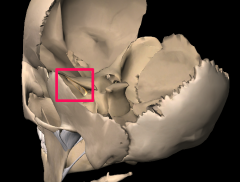
|
Superior Orbital Fissure |
|
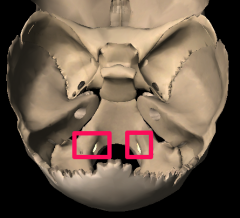
|
Hypoglossal canal |
|
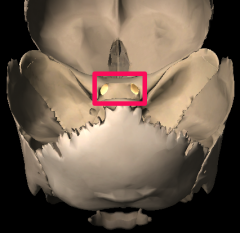
|
Optics foramen |
|
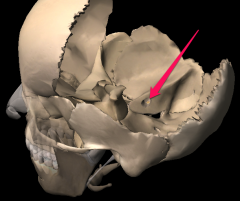
|
Stylomastoid foramen |
|
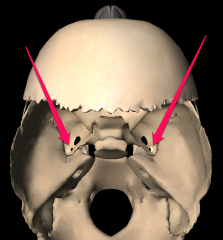
|
Spinosum foramen |
|
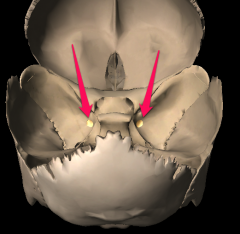
|
Rotundum foramen |
|
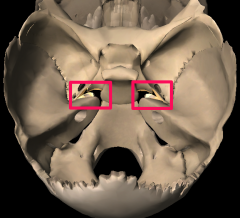
|
Lacerum foramen |
|
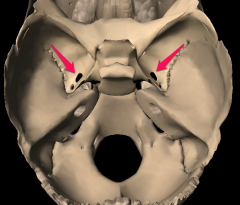
|
Ovale foramen |
|
|
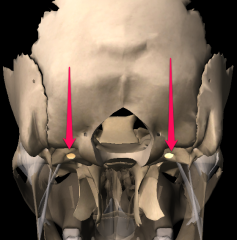
Carotid canal |
|
|
Jugular foremen |
|
|
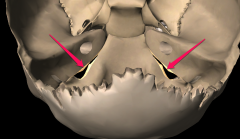
What is a foremen? |
A natural hole in a bone which nerves and blood vessels pass. |
|
|
|
|
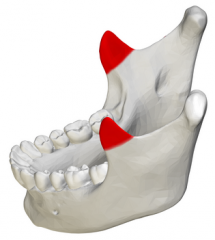
|
coronoid process |
|
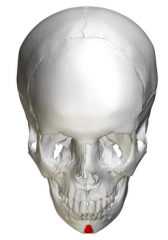
|
Mental protuberance |
|
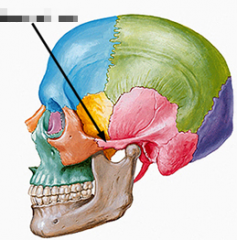
|
|
|
|
pterygoid process |
|
|
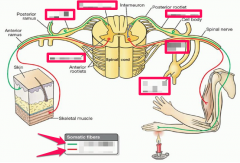
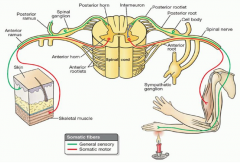
What are the 2 major divisions of the nervous system? |
1. CNS, Central Nervous System 2. PNS, Peripheral Nervous System |
|
|
What is the function of the CNS? |
Integrate and coordinate neural signals and perform higher mental function. |
|
|
What is the CNS made of? |
The brain and spinal cord. |
|
|
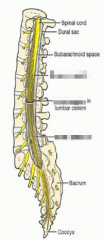
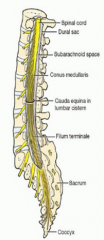
What cavity does the brain occupy? |
The cranial cavity. |
|
|
What cavity does the spinal cord occupy? |
Vertebral canal. |
|
|
What are the 4 parts of the PNS? |
1. Peripheral Nerves 2. Ganglia 3. Receptors 4. Enteric Plexus |
|
|
What is the function of the PNS? |
Carry signals to and from the CNS. |
|
|
What are the roles of sensory fibers? |
Conducting impulses from receptors (sensors) to the CNS. |
|
|
What is the role of motor fibers? |
Conducting impulses from the CNS to the effectors (muscles or glands). |
|
|
The motor division of the nervous system consists of what 2 systems? |
1. SNS, Somatic Nervous System (voluntary), controls skeletal muscles. 2. ANS, Autonomic Nervous System (involuntary), controls cardiac muscle, smooth muscles and glands. |
|
|
What 2 divisions is the Autonomic Nervous System divided into? |
The sympathetic and parasympathic division. |
|
|
What does the neurocranium accommodate? |
The brain. |
|
|
What are the 3 fossae of the floor of the cranium? |
1. Anterior fossa 2. Middle fossa 3. Posterior fossa |
|
|
How many cranial peripheral nerves are there? |
12 pairs |
|
|
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there? |
31 pairs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
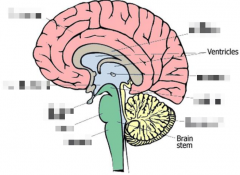
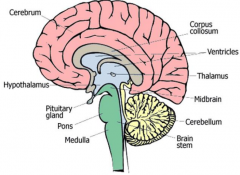
What are the cavities in the hollow human brain called? |
Ventricles |
|
|
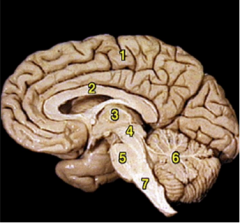
1 |
|
|
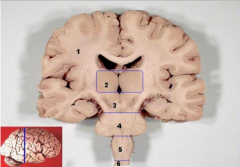
1 |
|
|
What are Ganglia? |
Collections of neural cell bodies located outside the CNS. |
|
|
What are nuclei? |
Collections of neural cell bodies inside the CNS. |
|
|
What is Dura Mater? |
A thick membrane that is the outermost layer of the meninges. |
|
|
What is Arachnoid Mater? |
Spider-web like appearance, forms the arachnoid villi which allow CSF to exit into the blood stream. |
|
|
What is Pia Mater |
The delicate innermost layer of the meninges. |
|
|
What is the meninges? |
The system of membranes that envelops and protects the CNS. |
|
|
|

