![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
244 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Antipsychotic Medications are used for what? (4) |
Schizophrenia Mania Autism Symptoms of psychosis |
|
|
|
Atypical means what ? |
New medication with less side effects |
|
|
|
Typical medication means what? |
Older medication |
|
|
|
Typical drugs end in what ? |
-ZINE |
|
|
|
Atypical drugs end in what |
-ZOLE -INE -DONE |
Z... I’m done with you |
|
|
Pharmacokinetics for atypical and typical antipsychotics |
Food, smoking, antacids, and co-administration of anticholinergics can interfere with absorption |
|
|
|
Long acting antipsychotic medications. When are they administered? |
2 weeks- 3 months via Z track |
|
|
|
The oil based injection ___, ___ are viscous liquids. They need to be administered with ____ gauge needle. |
Fluphenazine and haloperidol 21 |
|
|
|
Cardiovascular side effects with antipsychotics |
Orthostatic hypotension Prolongation of the QTc interval |
|
|
|
Anticholinergic side effects |
Results from blockade of ACH Patient may complain of dry mouth, urinary retention, constipation, dry eyes, vaginal dryness, blurred vision, nasal congestion. Think of the patient being DRY |
|
|
|
Weight gain is a common side effect of the _____ antipsychotics. Particularly ____, ______ which can cause a weight gain of up to 20 Ib within 1 year. ____, _____, and _____ are associates with little to no weight gain. |
Common side effects of atypical antipsychotics. Particularly clozapine, olanzapine. Ziprasidone, aripiprazole, lurasidone cause little to no weight gain |
|
|
|
What is one of the more serious side effects of antipsychotics? (Atypical) |
Type 2 diabetes |
|
|
|
Sexual side effects of antipsychotics result primarily from the blockade of dopamine. As a result blood levels of ____ increase? |
Prolactin particularly with risperidone and the typical antipsychotics |
|
|
|
Increased prolactin causes what with antipsychotics? |
Breast enlargement Galactorrhea Decreased sexual drive Amenorrhea Menstrual irregularities Increased risk for breast cancer Retrograde ejaculation Erectile dysfunction Anorgasmia |
|
|
|
Blood disorders with antipsychotics (agranulocytosis, neutropenia) |
Rare but can occur with clozapine!! The most notable symptoms are high fever, sore throat, and mouth sores Requires weekly blood samples for the first 6 months of treatment and then every 2 weeks after that for as long as the drug is taken. Blood draws must continue 4 weeks after the medication is discontinued |
|
|
|
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome |
Happens with the use of antipsychotics Characterized by high fever and rigidity |
|
|
|
Medication related movement disorders |
Happens more with typical antipsychotics EPS is acute and happens because of an imbalance of ACH, dopamine, & GABA Chronic syndromes ( tardive dyskinesia ) |
|
|
|
Dystonia |
Is an acute movement disorder that consist of impaired muscle tone Characterized by involuntary muscle spasms that leads to abnormal posture, especially of the head and neck muscles |
|
|
|
What is the treatment of dystonia ? |
Anticholinergic agents that inhibit ACH and thereby restore the balance of neurotransmitters |
|
|
|
Pseudoparkinsonism |
Drug induced Parkinsonism. Older patients are at a greater risk The treatment is the reduction in dosage or a change of antipsychotic Anticholinergic medication is sometimes given |
|
|
|
Akathisia |
Is the inability to sit still or restlessness and is more common in middle- aged patients Anticholinergics don’t really help with this condition |
|
|
|
Drug therapies for acute medication related movement disorders |
Anticholinergics ( benztropine, trihexyohebidyl, biperiden ) Antihistamines ( diphenhydramine ) Dopamine agonists ( amantadine ) Beta blockers ( propranolol ) Benzodiazepines ( Lorazepam, Diazepam, Clonazepam ) |
|
|
|
Chronic syndromes |
Tardive dyskinesia Develops from long term use of antipsychotics The most well known, involves irregular, repetitive involuntary movements of the mouth, face, and tongue. Including chewing, tongue protrusion, lip smacking, Pickering of the lips, and rapid eye blinking |
|
|
|
Treatment for TD ( medication ) |
Valbenzine |
|
|
|
Risk factors for tardive dyskinesia |
Woman Older age Long time use High doses of medication |
|
|
|
Mood stabilizers/ antimanic medications |
Stabilize mood swings ( bipolar ) Lithium is the oldest and gold standard |
|
|
|
Lithium indications |
Symptoms of mania, rapid speech, flight of ideas, grandiose thinking, impulsiveness, agitation |
|
|
|
Pharmacokinetics of lithium |
Peak blood lvls: 1-4 hours Completely absorbed in 8 hours Onset: 5-7 days but can take a week Hospital: morning lithium should not be given until blood is drawn to assess blood levels |
|
|
|
Therapeutic range of lithium and maintenance levels? |
Blood levels: 0.8-1.4 mEq/L Maintenance: 0.4-1mEq/L |
|
|
|
Side effects of mood stabilizers |
Excessive thirst Metallic taste USE SUGARLESS LOZENGES Diarrhea Frequent urination Fine hand tremor Drowsiness Mild diarrhea Weight gain |
|
|
|
Severe diarrhea, vomiting, drowsiness, muscular weakness, lack of coordination are signs of what ???? |
Lithium toxicity |
|
|
|
Severe diarrhea, vomiting, drowsiness, muscular weakness, lack of coordination are signs of what ???? |
Lithium toxicity |
|
|
|
What do you need to monitor q 6 months when taking lithium ? |
CBC Kidney function Thyroid hormones ( MAY BE ALTERTED BETWEEN 6-18 MONTHS OF TAKING THE MEDICATION ) |
|
|
|
Anticonvulsants |
Commonly treat bipolar disorder; considered mood stabilizer & mixed episodes |
|
|
|
Anticonvulsant drugs |
Valproic acid Carbamazepine Lamotrigine |
|
|
|
Drugs that inhibit the breakdown of anticonvulsants? (3) |
Erythromycin Verapamil Cimetidine |
|
|
|
Drugs that inhibit the breakdown of anticonvulsants? (3) |
Erythromycin Verapamil Cimetidine |
|
|
|
Teaching points for patients taking anticonvulsants? |
Patients need to let their HCP know if they are taking carbamazepine. Oral contraceptive use is decreased if taking these medications |
|
|
|
Side effects of taking carbamazepine? |
Tremor Drowsiness Vomiting Dizziness Visual disturbance Nausea |
|
|
|
ADVERSE reactions when taking carbamazepine |
Aplastic anemia Agranulocytosis Severe rash Rare cardiac problems SIADH |
|
|
|
Adverse reactions to valproic acid |
Weight gain Hair loss |
|
|
|
What supplements can be helpful when taking valproic acid for hair loss ? (2) |
Zinc and selenium |
|
|
|
Adverse reactions to lamtrigine ??? |
Benign skin rash !!! In rare cases, it can produce severe life threatening rashes that usually occur 2-8 weeks of treatment ( more common in children ) |
|
|
|
Benzodiazepines are used for |
Anti anxiety/ sedative hypnotic medications |
|
|
|
Alprazolam Lorazepam Diazepam Chlordiazepoxide Flurazepam Triazolam |
Benzodiazepines |
|
|
|
Oxazepam and lorazepam are preferred for who ??? |
Liver disease and older patients |
|
|
|
Side effects of benzodiazepines |
Drowsiness Intellectual impairment Memory Impairment Ataxia If prescribed for sleep, may wake up with a hangover feeling |
|
|
|
Phlebitis and thrombosis @ the site |
Is common with IV benzodiazepines |
|
|
|
What can increase the side effects of benzodiazepines? |
Alcohol !! |
|
|
|
Rebound insomnia or anxiety can occur when with benzodiazepines? |
Abrupt discontinuation |
|
|
|
Non benzodiazepines |
Buspirone |
|
|
|
Are effective for treating anxiety disorders without the CNS depressant effects or the potential for abuse and withdrawal syndromes |
Buspirone |
|
|
|
MAOIs can cause ____ if ____ foods are taken in |
Hypertensive crisis Tyramine- rich foods |
|
|
|
Foods with tyramine |
Spoiled foods Aged and mature cheeses ( American processed, cheddar, Colby, blue, brie, mozzarella, Parmesan, yogurt, sour cream ) Meats Sausages Beef or chicken liver Dried and pickled herring Pepperoni Tenderized meats Fava beans Alcohol ( except white wines ) |
|
|
|
The largest region of the human brain, fills the entire upper portion of the cranium |
Cerebrum |
|
|
|
Outermost surface of the cerebrum, makes up about 80% of the human brain |
Cortex |
|
|
|
The grooves on the cortex are called ____ if they extend deep into the brain and ____ if they are shallower. The bumps or convolutions are called ____. |
Fissures Sulci Gyri |
|
|
|
The ____ hemisphere is dominant in ____% of people but about ____% of individuals have mixed dominance |
Left 95% 5% |
|
|
|
What are the left and right hemispheres connected by ? |
Corpus callosum; it allows information to be exchanged quickly between the right and left hemispheres |
|
|
|
Frontal lobe contains ____ area which controls the ____ function of speech |
Broca Motor |
|
|
|
Damage to ____ area produces ______ aphasia |
Broca Expressive |
|
|
|
____ memory is an important aspect of frontal lobe functioning. |
Working memory: important aspect of frontal lobe function including the ability to plan and initiate activity with future goals in mind |
|
|
|
When normal frontal lobe functioning is altered changes in ___ and ____ can occur |
Mood and personality |
|
|
|
Parietal lobe Damage to this area produces ____ |
Complex sensory deficits |
|
|
|
Temporal lobes |
Contains the primary auditory and olfactory Wernickes; is responsible for receptive speech |
|
|
|
Occipital lobes |
Visual area Damage results to cortical blindness Object and facial recognition |
|
|
|
Association cortex |
Allows the lobes of the cortex to often share functions with an area of the adjacent lobe |
|
|
|
Subcritical gray matter areas in both the right and left hemispheres that contain many cell bodies or nuclei Repetitive activities, become automatic |
Basal ganglia |
|
|
|
Basic emotions, needs, drives, instinct begin and modulated by the |
Limbic system |
|
|
|
Structures in the limbic system |
Hippocampus, Amyglada, hypothalamus, thalamus, limbic midbteain nuclei |
|
|
|
The limbic system is involved in aspects of ____. |
Memory |
|
|
|
The ____ is involves in storing information, especially the emotions attached to a memory. I remember those days I looked like a hippo, it brought my confidence down I cried everyday |
Hippocampus |
|
|
|
Sometimes called the relay switching center, this structure functions as a regulatory structure to relay all sensory information except smell |
Thalamus |
|
|
|
Sleep rest patterns Body temperature Hunger Sex |
Hypothalamus |
|
|
|
Sense of smell |
Amygdala |
|
|
|
Impulsive acts of aggression and violence have been linked to dysregulatuon of the |
Amygdala |
|
|
|
Appear to play a role in the biological basis of addiction Feel good Drug abuse happens |
Limbic midbrain nuclei |
|
|
|
Contributes to understanding how function or how an individual may react over time to continuous pharmacotherapy regimens |
Neuroplascity |
|
|
|
Excitatory neurons |
ALL EXCEPT GABA |
|
|
|
Higher levels of ACH is associated with AYE COME HELP WITH MY HOMEWORK! |
Higher intellectual functioning and memory |
|
|
|
Feel good neurotransmitter Levels are decreased in Parkinson’s High levels associated with schizophrenia |
Dopamine |
|
|
|
“NO ! I’m not in a good mood!!!” |
Norepinephrine Decreased levels are associated with depression Increased levels are associated with maniac symptoms |
|
|
|
Serotonin |
Page 94 |
|
|
|
Histamine |
95 |
|
|
|
GABA |
Primary INHIBITORY neurotransmitter |
|
|
|
GABA |
Primary INHIBITORY neurotransmitter |
|
|
|
Dysregulation of GABA and GABA receptors has been associated with anxiety disorders (2) |
Anxiety Development of seizure disorders |
|
|
|
Involved in pain disorders/ play roles in pain transmission |
Neuropeptides |
|
|
|
Phases of drug treatment and the nurses role Initiation phase |
Before the initiation of medications, patients must undergo several assessments - a psychiatric evaluation - assessment that includes cultural beliefs - physical exam ( CBC , liver, kidney function, electrolyte, urinalysis, ECG - “Test dose” -patient should be monitored and this is where most of the teaching occurs |
|
|
|
The prescriber adjusts or titrates the medication dosage to achieve the maximum amount of improvement with a minimum of side effects Therapeutic drug monitoring is most important in this phase of treatment (lithium) |
Stabilization phase |
|
|
|
At times, an individual may show only partial improvement from a medication and the prescriber may try an _____ strategy by adding another medication. |
Augmentation |
|
|
|
After the individuals target symptoms have improved medications are usually continued to prevent ____ or return of symptoms. What phase is this ? |
Relapse Maintenance |
|
|
|
After the individuals target symptoms have improved medications are usually continued to prevent ____ or return of symptoms. What phase is this ? |
Relapse Maintenance |
|
|
|
The last phase which may require tapering of a medication |
Discontinuation |
|
|
|
A persons physical condition can affect mental health Many physical disorders may present first What assessment do you do ? |
Biological ( physical ) domain assessment |
|
|
|
What do you assess in a biological domain |
Current and past health history Physical exam ( body systems review ) Neurological status Lab results ( hepatic, renal, CBC ) Elimination ( some drugs cause urinary hesitancy such as anticholinergics and lithium causes urinary frequency ) Activity & exercise ( some medications cause weight gain, you want to know if the patient is active and you want to find out what they like to do ) Sleep pattern Appetite and nutrition ( obesity is one problem for psychiatric patients ) a BMI and eating pattern should be obtained Hydration Sexuality Self care ( altered in depressed patients ) Pharmacological assessment ( what drugs are you taking, assess for interactions, herbal like St. John’s wort ) |
|
|
|
What do you assess in a biological domain |
Current and past health history Physical exam ( body systems review ) Neurological status Lab results ( hepatic, renal, CBC ) Elimination ( some drugs cause urinary hesitancy such as anticholinergics and lithium causes urinary frequency ) Activity & exercise ( some medications cause weight gain, you want to know if the patient is active and you want to find out what they like to do ) Sleep pattern Appetite and nutrition ( obesity is one problem for psychiatric patients ) a BMI and eating pattern should be obtained Hydration Sexuality Self care ( altered in depressed patients ) Pharmacological assessment ( what drugs are you taking, assess for interactions, herbal like St. John’s wort ) |
|
|
|
Is an organized systemic approach to assessment of an individuals current psychiatric condition |
MSE |
|
|
|
Prominent sustained overall emotions that the person expresses and exhibits |
Mood |
|
|
|
Euthymic |
Normal mood |
|
|
|
Euphoric |
Elated mood |
|
|
|
Changeable mood is called |
Labile |
|
|
|
Depressed and restless mood is called |
Dysphoric |
|
|
|
Testing attention and concentration |
Start with 100 and subtract 7 until they get to 65 or start with 20 and subtract 3 |
|
|
|
Abstract reasoning and comprehension |
The nurse gives the patient a proverb to interpret When life gives you lemons make lemonade |
|
|
|
Checking immediate/ short term memory |
Give 3 words Have them repeat it right after and at 5 and 15 minute intervals |
|
|
|
Recent memory |
A recent holiday or event that happened in the world |
|
|
|
Long term/ remote memory |
Event that happened a long time ago (9/11) |
|
|
|
A persons awareness of his or her own thoughts and feelings and ability to compare them with the thoughts and feelings of others; outlook |
Insight |
|
|
|
A persons awareness of his or her own thoughts and feelings and ability to compare them with the thoughts and feelings of others; outlook |
Insight |
|
|
|
Judgement question |
What would you do if you saw a person drop some money ? Would you give it back or would you keep it ? |
|
|
|
Recovery oriented nursing interventions |
Page 142 |
|
|
|
____ and ____ are fundamental ethical concepts |
Autonomy Beneficence |
|
|
|
____ and ____ are fundamental ethical concepts |
Autonomy Beneficence |
|
|
|
A patient wants to stop taking medication |
Autonomy |
|
|
|
The nurse urges the patient to continue The HCP used knowledge of science and incorporates the art of caring to develop an environment in which individuals achieve their maximal health care potential |
Beneficence |
|
|
|
Is the duty to treat all fairly |
Justice |
|
|
|
Is the duty to treat all fairly |
Justice |
|
|
|
Nonmaleficence |
Is the duty to cause no harm, both individual and for all |
|
|
|
Is the duty to treat all fairly |
Justice |
|
|
|
Nonmaleficence |
Is the duty to cause no harm, both individual and for all |
|
|
|
Is the belief that knowledge and education authorize professionals to make decisions for the good of the patient |
Paternalism |
|
|
|
Is the duty to treat all fairly |
Justice |
|
|
|
Nonmaleficence |
Is the duty to cause no harm, both individual and for all |
|
|
|
Is the belief that knowledge and education authorize professionals to make decisions for the good of the patient |
Paternalism |
|
|
|
Veracity |
Duty to tell the truth |
|
|
|
Keeping promises |
Fidelity |
|
|
|
Standards of practice (6) |
Assessment Diagnosis Outcome identification Implementation Evaluation |
|
|
|
Health promotion and health maintenance Intake screening, evaluation, and triage Case management Provision of therapeutic and safe environments Milieu therapy Promotion of self care activities Administration of psychobiologic treatment and monitoring responses Complementary interventions Crisis intervention and stabilization Psychiatric rehab |
PMH- RN |
|
|
|
What can an advanced practice registered nurse do ? (7) PPPCCCC mnemonic |
Psychopharmalogic interventions Psychotherapy Program development and management Community interventions Case management Clinical supervision Consultation and liaison |
|
|
|
Is a well recognized, holistic model for organizing patient health care issues |
The biopsychosocial framework |
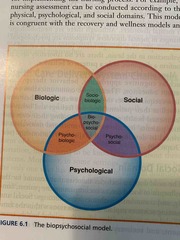
|
|
|
____ domain consists of the biologic theories related to mental disorders and problems and problems as well as all of the biologic activity related to other health problems |
Biologic |
|
|
|
Which domain is this ? Thoughts, feelings, and behavior that influence ones emotion, cognition, and behavior. |
Psychological |
|
|
|
____ domain includes theories that account for the influence of social forces encompassing the patient, family, and community within cultural settings. |
Social |
|
|
|
Collaborate in defining the boundaries of psychiatric- mental health nursing and informing society about the parameters of practice |
The ANA and psychiatric nursing organizations |
|
|
|
The ____ PMH RN organization with the primary mission of advancing PMH nursing practice improving MH care for culturally diverse individuals, families, groups, and community’s, & shaping health policy for the delivery of MH services |
APNA |
|
|
|
ISPN consists of 4 specialists divisions The association of ____ and ____ psychiatric nurses International society of psychiatric consultation ____ nurses Society for ____ and ____ in psychiatric mental health nursing ____ and geropsychiatric- mental health nurses |
Adult |
|
|
|
ID , ego, and superego |
Freuds personality structure |
|
|
|
Is formed by unconscious desires , primitive instincts, and instructed drives including sexual aggressiveness and tendencies that arise from the body |
ID |
|
|
|
Consists of the sum of certain MENTAL MECHANISMS such as perception, memory, and motor control, as well as specific defense mechanisms. The ____ controls movement, perception, and contact with reality. The capacity to form mutually satisfying relationships is a fundamental function of the ___ which is not present at birth but is formed throughout the child development |
Ego |
|
|
|
Consists of the sum of certain MENTAL MECHANISMS such as perception, memory, and motor control, as well as specific defense mechanisms. The ____ controls movement, perception, and contact with reality. The capacity to form mutually satisfying relationships is a fundamental function of the ___ which is not present at birth but is formed throughout the child development |
Ego |
|
|
|
Superego |
Is that part of the personality structure associated with ethics, standards, and self- criticism |
|
|
|
___ developed _____, a therapeutic process of accessing the unconscious conflicts that originate in childhood and then resolving the issue with a mature mind |
Freud Psychoanalysis |
|
|
|
Transference |
The displacement of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors originally associated with significant others from childhood onto a person in a current therapeutic relationship |
|
|
|
Countertransference |
Direction of all the therapist feelings toward the patient |
|
|
|
Student of freuds who believed that the motivating force on human life is an intolerable sense of inferiority |
Alfred Adler |
|
|
|
Created a model called analytical psychology; believed in the existence of two basically different types of personalities extroverted and introverted |
Carl Jung |
|
|
|
Karen horney |
Challenged many of freuds basic concepts and introduced principles of feminine psychology; recognizing a male bias in psychoanalysis She was the first to challenge the belief that women felt disadvantaged because of their genitalia organs Penis envy |
|
|
|
Otto rank |
Was also freuds student All neurotic disturbances to the primary trauma of birth Birth trauma |
|
|
|
You need interaction from society |
Focused on the relationship of society and the individual Believed the needs and desires of individuals are largely formed by their society |
|
|
|
Klein needs outside play time, she is only 4. |
Devised play therapy-techniques to demonstrate how a child’s interaction with toys reveals earlier infantile-fantasies and anxieties |
Why you tell kids to draw hoe they feel |
|
|
Carl Rodgers |
Client centered therapy Empathy |
|
|
|
Gestalt therapy |
Inability to express natural biologic and psychological desires causes anxiety |
|
|
|
Maslows hierarchy |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Noticed that stomach secretions of dogs were stimulated by triggers other than food reaching the stomach Found that sight and smell of food triggered stomach secretions |

Ivan Pavlov |
|
|
|
Behaviorism, a learning theory that only focuses on objectively observable behaviors Frequency recency , what are they ? |

John b Watson Frequency : the more often a response is made to a stimulus, the more likely the response to that stimulus will be repeated Recency : the closer in time a response is to a particular stimulus, the more likely the response will be repeated |
|
|
|
Do animals solve problems by reasoning or instinct? First reinforcement theorist |
Thorndike |
|
|
|
Do animals solve problems by reasoning or instinct? First reinforcement theorist |
Thorndike |
|
|
|
Studies operant behavior The focus is on the consequence If a behavior is reinforced or rewarded with success, the more likely it will be repeated |
B F Skinner |
A child climbing on a chair to get cookies out of the jar. The child successfully gets the cookies, the child does the same thing after dinner. |
|
|
Learning by watching others Modeling |
Albert bandura |
|
|
|
Psychosocial development |
Erik Erickson Trust vs. mistrust (infant) birth-1 year Autonomy vs. shame and doubt (toddler) 1-3 Initiative vs guilt (preschooler) 3-5 Industry vs. inferiority (school aged) 5-12 Identity vs role confusion (adolescent) 12-20 Intimacy vs isolation (young adult) Generativity vs stagnation (adult hood) Ego integrity vs despair (maturity) |
|
|
|
Cognitive growth is like embryonic growth: an organized structure becomes more and more differentiated over time |
Jean Piaget |
|
|
|
Piaget’s periods of intellectual development |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Carol Gillian |
Most developmental models are male centered and therefore inappropriate for girls and women Preconventional (what is best for me ) Conventional ( responsibility to other , self sacrifice is goodness ) Post conventional ( do not hurt others or self she is a person too ) |
|
|
|
Formal social support |
Large organizations such as hospitals and nursing homes that provide care to individuals |
Formal social support |
|
|
Family friends and neighbors are |

Informal social support |
|
|
|
The power of empathy Focused on the nurse patient relationship in her book interpersonal relations in nursing in 1952 Empathetic linkage , what is it ? Anxiety |
Peplau Ability to feel in oneself the feelings experienced by another person Needs not met |
|
|
|
Levels of anxiety |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Ida Jean Orlando |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Dorothea Orem |
Self care is the focus |
|
|
|
Is the process of understanding ones own beliefs, thoughts, motivations, biases, limitations, & recognizing how they affect others |
Self awareness |
|
|

Know thyself page 106 |

Apart of self awareness |
|
|
|
Telling the patient personal information generally is not a good idea “ let’s talk about you “ |
Avoid self disclosure unless it’s used for a therapeutic purpose |
|
|
|
Passive listening |
Sitting quietly and letting the patient talk |
|
|
|
Active listening |
The nurse focuses on what the patient is saying to interpret and respond to the message objectively |
|
|
|
Verbal communication techniques |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Considerations for effective communication and relationships (5) |
Rapport Empathetic linkages Boundaries and body space Recognition of defense mechanisms Empathy |
|
|
|
Personal boundaries |
Intimate zone Personal zone Social zone Public zone |
|
|
|
Intimate zone |
Whispering and embracing 6-18 inches 15-46 cm |
|
|
|
Personal zone |
Is for close friends 18-47 cm 46 cm- 1.2 m |
|
|
|
Personal zone |
Is for close friends 18-47 cm 46 cm- 1.2 m |
|
|
|
Social zone |
For acquaintances 47 in - 3 yd 1.2- 3.6 m |
|
|
|
Public zone |
For strangers Over 3 yd Over 3.6 m |
|
|
|
Defense mechanisms |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
the nurse patient relationship phases (3) explain them |
Orientation phase Working phase Termination phase |
|
|
|
Phases of the nurse patient relationship |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Body’s tendency to resist physiologic change and hold bodily functions relatively consistent, well- coordinated, and usually stable Equilibrium ( blood glucose, PH, and oxygen ) |
Homeostasis |
|
|
|
Maintains homeostasis through a process of adaptation |
Allostasis |
|
|
|
Flight and fight physiologic changes Sympathetic Parasympathetic |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
_____ an intense biopsychosocial reaction to a threatening event, is time limited ( less than a month ) but can occur repeatedly. Can have a negative impact on a persons health. |
Acute stress |
|
|
|
Flight and fight physiologic changes Sympathetic Parasympathetic |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
_____ an intense biopsychosocial reaction to a threatening event, is time limited ( less than a month ) but can occur repeatedly. Can have a negative impact on a persons health. |
Acute stress |
|
|
|
What hormones are secreted when the hippocampus and amyglada sense danger ? |
Epinephrine, cortisol , adrenaline |
|
|
|
____ is an ongoing physiologic reaction to events resulting in wear and tear on the body and negatively impacts health and well being |
Chronic stress |
|
|
|
The GAS was created by who ? |
Hans seyle |
|
|
|
Three stages of general adaptation syndrome |
Alarm Resistance Exhaustion |
|
|
|
Coping mechanisms are used to try to reestablish homeostasis |
Resistance |
|
|
|
Occurs if homeostasis is not achieved |
Exhaustion |
|
|
|
Alarm |
A threat is perceived and the body responds physiologically |
|
|
|
Is the consequence of wear and tear on the body and brains and leads to ill health |
Allostatic load |
|
|
|
Chronic stress can make you more susceptible to ____ |
Illness |
|
|
|
Genetic predisposition increases susceptibility of developing a disorder |
Diathesis |
|
|
|
What personality is being described ? Competitive aggressive ambitious impatient alert tense and restless |
Type A |
|
|
|
Increased negative emotion Pessimism Unlikely to show emotions toward others Research support that this personality type is associated with mental health disorders and poor physical health |
Type D |
|
|
|
This personality is more relaxed , easygoing , and easily satisfied |
Type B |
|
|
|
This personality is more relaxed , easygoing , and easily satisfied |
Type B |
|
|
|
Type C personality |
Introverted , difficulty expressing emotion , respectful , conforming , compliant , they respond to stress with depression and hopelessness Associated with cancer |
|
|
|
How many levels of social networks are there ? |
3 |
|
|
|
How many levels of social networks are there ? |
3 |
|
|
|
Explain level 1 |
Consists of 6-12 people |
|
|
|
Level 2 |
30-40 people who that person sees regularly |
|
|
|
Level 3 |
Whom a person has direct contact such as the grocer and mail carrier, and can represent several hundred people |
|
|
|
Examples of social support |
Emotional Tangible Informational |
|
|
|
Who created the recent life changed questionnaire to evaluate the frequency and significance of life changing events? |
Rahe |
|
|
|
The different emotional response (4) |
Negative emotions Positive emotions Borderline emotions Nonemotions ( awe, confidence, confusion, excitement ) |
|
|
|
Two types of coping |
Problem focused : attacks the situation & changes it Emotion focused: reinterprets the situation to change its meaning |
|
|
|
Reappraisal |
Is the same as appraisal , but happens after coping provides feedback about the outcomes and allows for continual adjustment to new information |
|
|
|
She had an holistic view of a patient who lives within a family and community . She was especially sensitive to human emotions and recommended interactions that today would be classified as therapeutic communication |
Florence nightingale |
|
|
|
The first trained nurse in the United States opened the Boston city hospital training |
Linda Richards |
|
|
|
The first trained nurse in the United States opened the Boston city hospital training |
Linda Richards |
|
|
|
Effie Taylor |
Integrated psychiatric nursing at the john Hopkins phipps clinic |
|
|
|
The first trained nurse in the United States opened the Boston city hospital training |
Linda Richards |
|
|
|
Effie Taylor |
Integrated psychiatric nursing at the john Hopkins phipps clinic |
|
|
|
The first psychiatric nursing textbook , nursing mental disease was written by ____ |
Harriet Bailey In 1920 |
|
|
|
Defines mental health as a state of well being in which the individual realizes his or her own abilities, can cope with life’s normal stresses, can work productively and fruitfully, and can make a contribution to society |
WHO |
|
|
|
Eight dimensions of wellness |
Emotional Financial Social Spiritual Occupational Physical Intellectual Environmental |
|
|
|
A set of symptoms that cluster together that may have multiple causes and may represent several different disease states that have not yet been identified |
Syndromes |
|
|
|
DSM- 5 |
Diagnosis of mental health conditions |
|
|
|
DSM- 5 |
Diagnosis of mental health conditions |
|
|
|
The study of patterns of disease distribution and determinants of health within populations |
Epidemiology |
|
|
|
DSM- 5 |
Diagnosis of mental health conditions |
|
|
|
The study of patterns of disease distribution and determinants of health within populations |
Epidemiology |
|
|
|
Cases in population/ total population ( cases and non cases ) |
Rate |
|
|
|
The total number of people who have the disorder within a given population at a specified time |
Prevalence |
|
|
|
Cases at specific time/ population at specific time |
Point prevalence |
|
|
|
Only new cases that have occurred within a clearly defined time period |
Incidence |
|
|
|
Ordered the removal of chains stopped the abuses of drugging and bloodletting and placed the patients under care of the physicians |
Phillip pinel |
|
|
|
Member of the society of friends raised funds for member who had mental disorders. Opened the youth retreat in 1796 |
William tuke |
|
|
|
The Quaker’s |
Stopped blood letting and kept a human and supportive attitude and influenced changing techniques of caring for those with mental disorders |
|
|
|
Believed in humane treatment of patients with mental illness and was responsible for much of the reform of the mental health care system Influenced 20 states by enlarging state hospitals |
Dorothea Dix |
|
|
|
Recovered from a mental disorder and became an advocate of humane treatment Published an autobiography a mind that found itself, he was beaten chocked imprisoned Formed a national committee for mental hygiene |
Clifford beers |
|
|
|
Main goal for a patient with mental illness |
Recovery |
|
|
|
Atypical antipsychotic medications differ from the typical antipsychotics in that they block ___ receptors more potently than the ____ receptors |
Serotonin Dopamine |
|
|
|
Atypical antipsychotics associated with little to no weight gain (ZAL) |
Ziprasidone Aripiprazole Lurasidone |
|

