![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the ssx of vitiligo? |
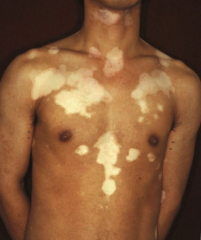
1. Asymptomatic, flat, well-demarcated
|
|
|
What are the MCC of vitiligo? |
1. Pernicious anemia 2. Addison's 3. Hashimoto |
|
|
What are ephelides? |
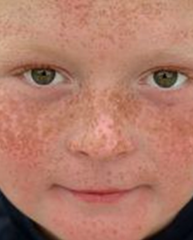
1. Freckles |
|
|
What are the ssx of lentigo? |
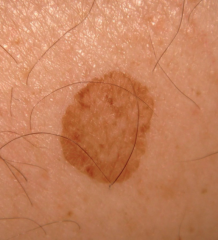
1. Benign localized hyperplasia of melanocytes 2. DO NOT darken when exposed to sunlight |
|
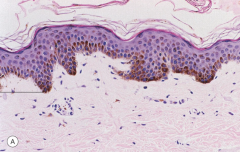
|
1. Lentigo simplex histology 2. Hyperpigmented rete ridges |
|
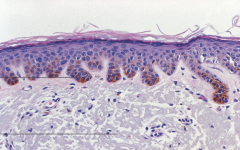
|
1. Solar lentigo histology 2. Hyperpigmented rete ridges 3. Solar elastosis |
|
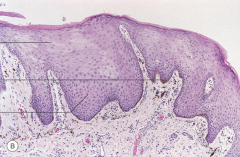
|
1. Labial lentigo 2. Basal layer hyperpigmentation 3. Broad rete ridges |
|
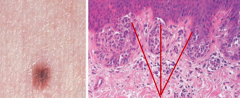
|
1. Junctional nevus |
|
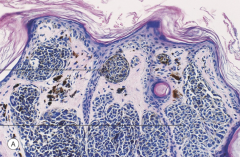
|
Compound nevus |
|
|
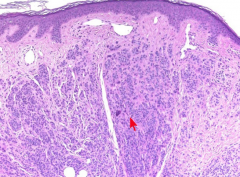
Intradermal nevus |
|
|
Dysplastic nevus |
|
|
What are the risk factors for melanoma? |
1. Fair skin 2. FHx 3. Exposure to carcinogens 4. Presence of multiple birthmarks |
|
|
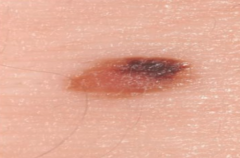
What are the signs of a malignant melanoma? |
1. Asymmetric 2. Borders uneven 3. Two or more colors 4. Larger than 1/4 inch 5. Changes in size, color, or other trait |
|
|
What occurs in the radial growth phase of melanoma? |
1. Horizontal spread within epidermis to superficial dermis 2. Lack capacity to metastasize |
|
|
What is lentigo maligna? |
1. Indolent lesion on face 2. May remain in radial growth phase for several decades |
|
|
What is the superficial spreading class of melanoma? |
1. Most common type 2. Involves sun-exposed skin |
|
|
What is the acral/lentiginous melanoma class of melanoma? |
1. Unrelated to sun exposure |
|
|
What is the vertical growth phase of melanoma? |
1. Tumor cells invade downward into deeper dermal layers 2. Appearance of nodule 3. Maturation is absent from deep invasive portion of melanoma |
|
|
What are the prognostic factors for melanoma? |
1. Depth (Breslow thickness) 2. number of mitoses 3. Tumor regression 4. Number of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes 5. Gender (female is better) 6. Location |

