![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
softening of the bones (due to impaired mineralisation, with excess accumulation of osteoid), with pain, tenderness, muscular weakness, anorexia and loss of weight, resulting from deficiency of vitamin D and calcium.
|
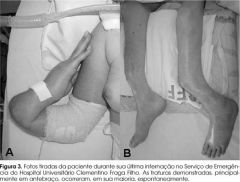
osteomalacia
|
|
|
The progressive erosion of cartilage, common in the knee joint where it is known as chondromalacia patella.
Symptoms of chondromalacia in the knee joint include knee pain with hill climbing or stair climbing. |
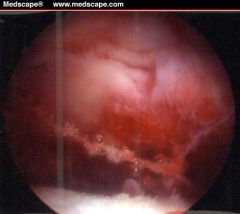
chondromalacia
|
|
|
bending of a bone with incomplete fracture involving the convex side of the curve only.
|
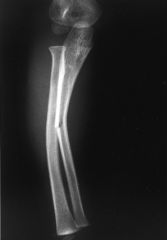
greenstick fracture
|
|
|
A fracture in which the bone is broken into pieces.
|
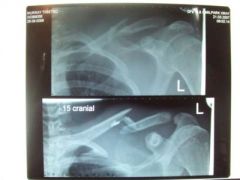
comminuted fracture
|
|
|
Fracture in which the skin is perforated and there is an open wound down to the fracture.
Synonym: compound fracture. |
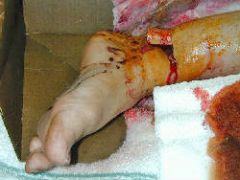
open or compound fracture
|
|
|
closed or simple fracture
|
A fracture in which skin is intact at site of fracture
|
|
|
myeloma
|
<oncology, tumour> A malignant tumour composed of plasma cells of the type normally found in the bone marrow.
|
|
|
pathology> Inflammation of a voluntary muscle.
|
myositis
|
|
|
osteitis
|
<medicine> Inflammation of bone.
|
|
|
pathology> Inflammation of bone caused by a pyogenic organism. It may remain localised or may spread through the bone to involve the marrow, cortex, cancellous tissue and periosteum.
|

osteomyelitis
|
|
|
<oncology, tumour> Malignant tumour of bone (probably neoplasia of osteocytes).
|
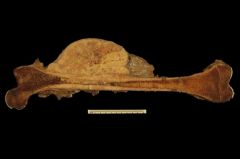
osteosarcoma
|
|
|
<neurology> Paralysis of the legs and lower part of the body.
|

paraplegia
|
|
|
obstetrics, procedure> A procedure where by a needle in introduced into a joint space for the purpose of removing joint fluid for diagnostic purposes. This procedure can also be therapeutic if an anaesthetic or corticosteroid medication is injected into the joint during the procedure.
(27 Sep 1997) |
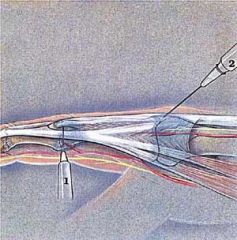
arthrocentesis
|
|
|
orthopaedics> The surgical immobilisation of a joint (joint fusion).
|
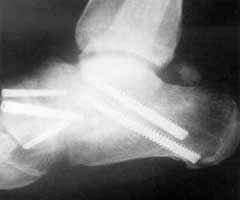
arthrodesis
|
|
|
investigation, radiology> A X-ray procedure involving the injection of radiopaque dye into a joint space to demonstrate the anatomy of the joint by X-ray.
|
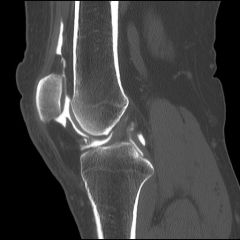
arthrogram
|
|
|
<orthopaedics> The surgical repair of a joint.
|
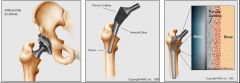
arthroplasty
|
|
|
<procedure> Surgical removal of a bursa.
|
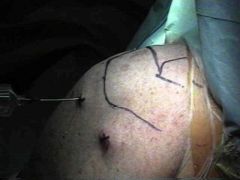
bursectomy
|
|
|
investigation> A test which measures muscle response to nerve stimulation. Used to evaluate muscle weakness and to determine if the weakness is related to the muscles themselves or a problem with the nerves that supply the muscles.
|

electromyography
|
|
|
Plastic surgery of muscular tissue.
|
myoplasty
|
|
|
claudication
|
Origin: L. Claudicatio = limping or lameness.
|
|
|
<oncology, tumour> A benign fibroid tumour of the uterus.
|
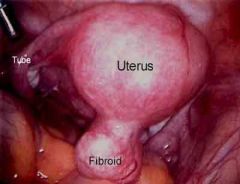
myoma
|
|
|
gynaecology, tumour> Benign uterine tumours also referred to as uterine fibroids. Uterine fibroids can cause pelvic pain and irregular vaginal bleeding in some females.
|
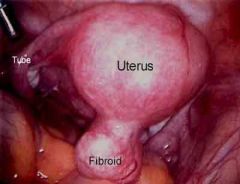
leiomyoma
|
|
|
<orthopaedics, rheumatology> Fusion of bones across a joint. Complication of chronic inflammation.
|
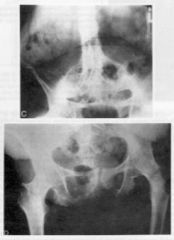
ankylosis
|
|
|
arthralgia
|
<symptom> Pain in a joint.
|
|
|
ataxia
|
<neurology> Failure of muscular coordination, irregularity of muscular action.
|
|
|
dyskinesia
|
<neurology> The impairment of the power of voluntary movement, resulting in fragmentary or incomplete movements.
|
|
|
pathology> Any disorder arising from defective or faulty nutrition, especially the muscular dystrophies.
|
dystrophy
|
|
|
The enlargement or overgrowth of an organ or part due to an increase in size of its constituent cells.
|
hypertrophy
|
|
|
A swelling or deformity at the head of the first metatarsal of the great toe (big toe).
|
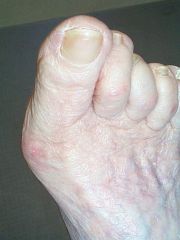
bunion
|
|
|
<paediatrics> A birth deformity characterised by imperfect bone formation. It results in dwarfs with normal-sized heads but short arms and legs.
|

achondroplasia
|
|
|
A posterior curvature of the thoracic spine usually the result of a disease (lung disease, Paget's disease) or a congenital problem.
|
kyphosis
|
|
|
Accentuation of the lumbar curvature of the spine.
|
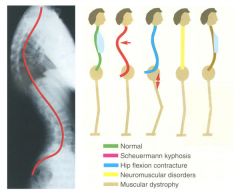
lordosis
|
|
|
periosteum
|
<anatomy> The membrane of fibrous connective tissue which closely invests all bones except at the articular surfaces.
|
|
|
tendon
|
anatomy> A fibrous, strong, connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. The laceration of a tendon can result in the inability to flex or extend at a joint.
|
|
|
ligament
|
> A band of fibrous tissue that connects bones or cartilages, serving to support and strengthen joints.
|
|
|
epiphysis
|
A part of a long bone where growth bone growth occurs from.
|
|
|
diaphysis
|
The shaft of a long bone.
|
|
|
bursa
|
<anatomy> A tissue space (fibrous sac) that is lined with synovial membrane (joint tissue) and contains a small quantity of synovial fluid (joint fluid). Bursas are found in between tendon and bone, skin and bone and muscles. They function to facilitate fluid movement.
|
|
|
fascia
|
natomy> The flat layers of fibrous tissue that separate differnet layers of tissue.
|
|
|
illium
|
anatomy> The upper and largest, part of the bony pelvic girdle (iliac wing). The ilium articulates on its inner aspect with the sacrum (sacroiliac joint).
|

