![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. Name the lipoproteins that serve as vehicles for transport of cholesterol in blood. What is the difference between them by the direction of transport? |
1. Chylomicrons: From intestines to liver, skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. 2. VLDL: From liver to other tissues 2. LDL: carry to extra-hepatic tissue with specific plasma membrane receptors. 3. HDL: Removes cholesterol from the blood,carrying it to the liver |
|
|
2. Name the reactions the total cholesterol determination is based on. |
We measure the total cholesterol by measuring the absorbance of the 3rd reaction (horseraddish peroxidase). But this absorption is dependent and proportional to the concentration of total cholesterol which is found in reaction 2 (cholesterol oxidase). |
|
|
3. Why is the reaction catalysed by peroxidase necessary for cholesterol determination? |
Peroxidase reaction is necessary as the change that happens in cholesterol oxidase cant be measured as it doesn't lead to an absorbance change at an accessible wavelength The cholesterol oxidase reaction does generate an amount of hydrogen peroxide which reacts with phenol and reduced dye in the 3rd reaction. The product of the peroxidase reaction gives us a maximum absorbance at 492 |
|
|
4. What compound can be determined using an enzyme mixture that contains cholesterol oxidase and peroxidase but not cholesterol esterase? |
Represents free cholesterol in serum |
|
|
5. Cholesterol has no absorbance at 492 nm. How is it still possible to determine its concentration using a photometric method? |
Because we use a coupled reaction with peroxidase, which produces a product that has maximum absorbance at 492 nm.
The absorbance change due to production of the oxidized dye is directly proportional to the concentration of total cholesterol in the sample |
|
|
6. List 2 biological/physiological processes where cholesterol plays an important role. |
Component of cellular membranes Precursor of steroid hormones and bile acids |
|
|
7. Give the names and the formulas of activated isoprenoids formed during the cholesterol synthesis. |
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate - C5H12O7P2 Isopentenyl pyrophosphate - C5H12O7P2 |
|
|
8. Name the 10, 15 and 30 carbon atom containing precursors of cholesterol |
C10: Geranyl-pp C15: Farnesyl-pp C30: Squalene |
|
|
9. Why are statins applicable in the therapy of diseases with high blood cholesterol? Give the molecular basis of their mode of action. |
Statins resemble mevalonate and are competitive inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase |
|
|
10. Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by HMG-CoA synthase. |
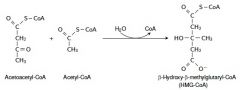
|
|
|
11. Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by HMG-CoA reductase. |

|
|
|
12. Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by HMG-CoA lyase. |

|
|
|
13. Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. |

|
|
|
14. Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by β-ketoacyl-CoA transferase. |

|
|
|
15. Write with structures the first reaction catalyzed by prenyl transferase. |

|
|
|
16. Write with names or abbreviations the second reaction catalyzed by prenyl transferase. |

|
|
|
17. Write with names or abbreviations a reaction catalyzed by squalene synthase. |

|
|
|
18. Write with names or abbreviations the reaction catalyzed by acetyl-CoA:cholesterol acetyltransferase (ACAT). |

|
|
|
19. Write with names or abbreviations the reaction catalyzed by lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT). |

|
|
|
20. What components build up a lipoprotein? |
Triglyceride Cholesterol Phospholipid Protein |
|
|
21. List the lipoproteins. Indicate the one containing the most cholesterol and the one containing the most triglyceride. |
Chylomicrons - Most triglycerides VLDL IDL LDL - most cholesterol HDL |
|
|
22. Which enzyme in which cellular compartment is necessary for the transformation of HMG-CoA into ketone bodies or into cholesterol, respectively? |
Ketone bodies: HMG-CoA lyase, mitochondria Cholesterol: HMG-CoA reductase, cytosol |
|
|
23. Name the NADPH-requiring reactions of the cholesterol synthesis. |
HMG-CoA reductase Squalene synthase |
|
|
24. Write with names the enzyme reaction using cholesterol as a substrate and as an activator as well. |
Acyl-CoA: Cholesterol acyltransferase - ACAT Cholesterol functions as an activator on ACAT |

