![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. List all enzymatic reactions that produce ATP in an erythrocyte. |
Phosphoglycerate kinase Pyruvate kinase |
|
|
2. Name all human organs where the transformation of glucose into fatty acids is significant.Please underline the organ where the rate of this process is the highest. |
Liver Adipose tissue |
|
|
3. Name all human organs where the gluconeogenesis is significant. Please underline the organwhere the rate of this process is the highest. |
Liver Kidney |
|
|
4. Name three human organs where the β-oxidation of fatty acids is significant. |
Liver Heart Skeletal muscle |
|
|
5. Under conditions of hypoglycemia, the liver is not utilizing glucose as an energy source. Why? |
To prevent the blood sugar to become even lower. So it uses fat or other energy sources instead. |
|
|
6. After eating a meal containing carbohydrates, the monosaccharides must be absorbed from the intestinal lumen. This transport is driven by which enzyme? |
Brush border hydrolases |
|
|
7. An individual contains an inactivating mutation in a particular muscle protein, which leads to weight loss due to unregulated muscle fatty acid oxidation. Such an inactivated protein could be which protein indispensable in fatty acid synthesis? |
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2 |
|
|
8. A 7-year-old boy is brought to the pediatrician due to severe exercise intolerance. In gymclass, the boy has trouble with anaerobic activities. Laboratory tests showed a lack of lactate production under such conditions. The boy was eventually found to have a mutation in which enzyme of which organ? |
Muscle PFK-1 |
|
|
9. Which human organ produces the enzyme that triggers the activation of pancreatic zymogens? |
Pancreatic zymogens are normally only activated after they reach the small intestine. A brush border enzyme, enterokinase, cleaves a peptide from trypsinogen, forming the active enzyme trypsin. Trypsin then activates the other enzymes. |
|
|
10. In which human organs can insulin increase the glucose permeability of the cell membrane? |
Adipose tissue Skeletal muscle Liver (indirect) |
|
|
11. Which enzyme of which cell compartment catalyses the first step of the oxygen dependentdegradation of ethanol in the liver? |
Cytochrome P450 (CYP2E1) - located in microsomes (Ethanol + NADPH + H+ + O2--> NADP + acetaldehyde + 2H2O) |
|
|
12. Which enzyme of which cell compartment catalyses the first step of the oxygen independent degradation of ethanol in the liver? |
Alcohol dehydrogenase - located in cytosol (Ethanol + NAD + --> acetaldehyde + NADH + H+) |
|
|
13. Write with names or abbreviations the reactions catalyzed by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase(PARP). |
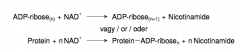
|
|
|
14. Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by phosphatidyl ethanolamine serinetransferase. |
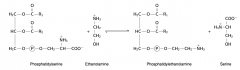
|
|
|
15. Write the carbonic anhydrase reaction. |
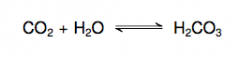
|
|
|
16. Write the CO2 binding reaction of hemoglobin. Give the structure of the involved functionalgroup of hemoglobin. |
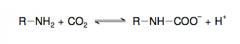
|
|
|
17. Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I. |
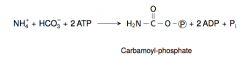
|
|
|
18. Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by ornithine transcarbamoylase. |
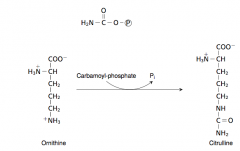
|
|
|
19. Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by argininosuccinate synthetase. |
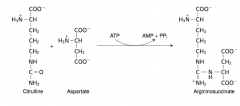
|
|
|
20. Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by argininosuccinase (a.k.a. argininosuccinatelyase). |
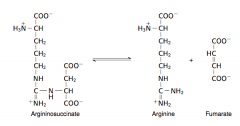
|
|
|
21. Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by arginase. |
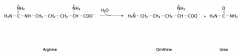
|
|
|
22. Write with structures the overall equation of urea cycle involving the appropriate amino acid. |
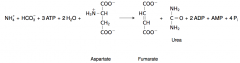
|
|
|
23. Write with structures the overall equation of urea cycle without any amino acid. |
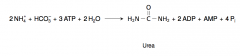
|
|
|
24. Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by NO synthase. |
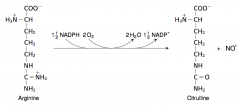
|

