![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

1. Rat liver metabolizes glucose by glycolytic and pentose phosphate pathways respectively.Indicate in the blanks whether the following statements are true for glycolysis (G), pentosephosphate pathway (P), both (2), or neither of them (0): |

|
|
|
2. Which molecule does SREBP (= Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Protein) bind after entering the nucleus of the cell? What molecular event is initiated by this binding? |
Binds to sterol regulatory element DNA sequence. Its a transcription factor. Binding causes initiation of transcription of genes involved in cholesterol, triglyceride, and fatty acid synthesis. |
|
|
3. What is the similarity between glucose-alanine cycle and Cori cycle regarding function? |
- Transfer of glucose from liver to muscle via the blood. - Glycolysis occur in the muscle - Gluconeogenesis occur in the liver |
|
|
4. What is the biochemical role of MutH, MutL MutS proteins? |
They are the main components of methyl directed mismatch repair. They all winds up the DNA molecule. MutH also cleaves the unmethylated strand at methylated site |
|
|
5. Name six short RNA types outside of microRNA. |
1. siRNA (small interfering) 2. saRNA (small activating) 3. snRNA (small nuclear) 4- snoRNA (small nucleolar) 5. piRNA (piwi-interacting) 6. tmRNA (transfer mRNA) |
|
|
6. Name the four mechanisms or molecular events that ensure the high fidelity of translation. |
1. Wobble formation, first two bases in codon has strong base pairing with anticodon 2. Proofreading of activity of AA-tRNA synthetases 3. Specific interactions between tRNAs and AA-tRNA synthetases 4. Codon-anticodon pairing check on ribosome |
|
|
7. What is the consequence of the hydroxylation of HIF-1 transcription factor? |
Ubiquitinylation and degredation by proteasomes |
|
|
8. List three hormone families that have nuclear receptors. |
Retinoic acid Thyroid hormones Steriod hormones Vitamin D |
|
|
9. Which molecules can activate PKA, PKC, AMPK, respectively? |
- PKA: cAMP (through glucagon/epinephrine) - PKC: DAG and IP3 --> increased cytosolic Ca2+ - AMPK: increased concentrations. of AMP (compared to ATP) through stress, exercise and leptin (fasting) |
|
|
10. Which subunits of MHC I participate in antigen presentation? |
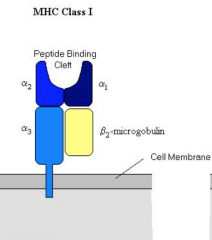
The peptide binding cleft is between the alpha1 and alpha2 domains of the MHC I molecule. |
|
|
11. What is the role of Wee1 kinase in the regulation of the cell cycle? |
Wee1 inhibits Cdk1 by phosphorylation. The timing/regulation of the cell cycle is controlled by Cdks. |
|
|
12. Why does the point mutation of Ras protein (possibly) lead to tumor formation? |
If theres a point mutation that affects the intrinsic GTPase activity of RAS, it will remain active and continously activate Downstream Ser/Thr kinase. --> Increased transcription of genes for growth and cell division. |
|
|
13. Name three diseases associated with collagen synthesis or the mutation of its gene. |
1. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (type 3 collagen) 2. Chondrodysplasias (type 2 collagen) 3. Osteogenesis imperfecta (type 1 collagen) |
|
|
14. Name the enzyme responsible for initiation of zymogen activation. |
Enteropeptidase |
|
|
15. How is iron taken up, transported and stored in human, respectively? |
- Uptake: Heme iron by heme transporter and Fe2+ by DMT1. - Transport: Export out of epithelial cells as Fe2+ by Ferroportin 1. Transported in blood as transferrin. - Storage: Ferritin |
|
|
16. Describe briefly, with reaction equations, the catalytic role of the metal ion (Cu or Mn) in superoxide dismutases. |
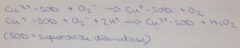
|
|
|
17. Name a mixed function oxidase enzyme requiring vitamin C as cofactor, and one that doesnot. What is the cofactor requirement of the latter enzyme? |
-Required: for proline hydroxylase. -Not req: squalene monoxygenase. -Cofactor req. for squalene monoxygenase: NADPH+H+ and O2 |
|
|
18. Name the three most important functions of albumin. |
- Regulation of oncotic pressure - Buffering - Transport |
|
|
19. What enzyme activity is associated to atrial natriuretic factor and endotoxin receptors? |
Intracellular guanylyl cyclase activity (converts GTP --> cGMP) |
|
|
20. Which hormone, in what direction, and in which tissue regulates the activity of GLUT4? |
- Hormone: Insulin - Tissue: Adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle - Direction: enhances uptake of glucose |
|
|
21. Name three lysosomal lipid storage diseases. |
- Tay-sachs disease - Gaucher disease - Pompe disease |
|
|
22. When a mitochondrion is "uncoupled", what is uncoupled from what? Name a protein that is capable to carry out uncoupling. |
- Respiratory chain is uncoupled from ATP synthase. - Protein: thermogenin |
|
|
23. Why does glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency cause serious problem for the red blood cell? |
-Regenration of GSH from GSSG requires NADPH - The pentose phosphate pathway (G6PD is the rate limiting step) is the only source of reduced glutathione (GSH) in red blood cells. The lack of GSH puts RBCs at a substantial risk of damage from ROS, due to RBCs being oxygen carriers and lacking the ROS-protective functions reduced glutathione (antioxidant) --> hemolytic anemia. |
|
|
24. What are the substrates and cofactors of the human prolyl hydroxylase? |
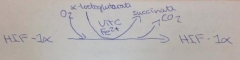
|

