![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
80 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
membrane excitability
|
depolarization leads to higher Na+ permeability, Na+ influx self reinforcing bring to a peak (depolarization and overshoot), K+ permeability increase, repolarization, Na-K pump restore the normal ion concentration gradient. `
|
|
|
cardiac muscle excitability
|
L-type Ca channel
|
|
|
smooth muscle excitability
|
slow Ca channel; lack Na channel
|
|
|
nerve conduction
|
from dendrites to axon
|
|
|
special feature at each part of nerve cell
|
dendrites: graded potential, soma: integrated (temporal summation and spatial summation), axon hillock or trigger zone (dense low threshold of Na channel), Action potential throughout to the axonal end, trigger neurotransmitter release.
|
|
|
how action potential spread in axon?
|
myelinated axon: high Rm, high length constant. potential only spread along the myelin sheath until reach the node of Ranvier (dense low threshold Na channel and non-myelinated) ... saltatory propagation
|
|
|
why myelinated?
|
low Ra, faster spread; low Cm, low time constant; high Rm length constant. shorter charging/depolarization time and less likely to spread outside (low permeability)
|
|
|
graded potential : EPSP, IPSP
|
excitatory postsynaptic potential, inhibitory postsynaptic potential
|
|
|
synaptic transmission chemical
|
presynaptic: opening of voltage dependent Ca channels, influx of Ca, fusion of vesicles carrying neurotransmitter by exocytosis; postsynaptic: ligand-gated ion channels binding of neurotransmiqtter to protein receptor, change polarity of some ions, trigger potential spread
|
|
|
electrical synaptic transmission
|
gap junction called connexons
|
|
|
latent period
|
excitation-contraction coupling
|
|
|
tetanus
|
rapidly delivered stimuli, increase contractile force
|
|
|
5 factors leading to muscle fatigue
|
decrease in glycogen, hypoglycemia, inability to supply ATP, high H+ concentration, metabolic acidosis, electrolyte imbalance, dehydration, damage to skeletal muscle,
|
|
|
Fibrous astrocyte
|
Fibrous astrocyte: found mainly in white matter; has long, usually unbranched processes.
|
|
|
Protoplasmic astrocyte
|
Protoplasmic astrocyte: found mainly in gray matter; has shorter, thicker, highly branched processes.
|
|
|
3 Functions of astrocytes:
|
keep extracellular K+ low; phagocytize neuronal debris and fill in space to form glial scar after injury; Processes of astrocytes also cover surface of capillaries within the CNS and form the structural basis of blood-brain-barrier
|
|
|
formation of Myelin Sheath
|
oligodendrocyte in CNS or Schwann cell in PNS
|
|
|
3 cut of brain
|
Sagittal, Horizontal, Coronal
|
|
|
4 lobes in brain
|
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital lobe
|
|
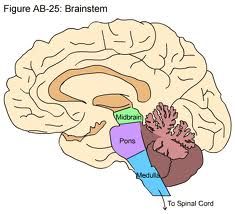
brain stem
|
pon, medulla oblongata, midbrain: ascending and descending pathways pass through; life centers, nuclei of cranial nerve
|
|
|
spinal cord
|
8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal
segments |
|
|
Cerebral cortex
|
Cognition, perception and Voluntary movement
|
|
|
Limbic system
|
memory and Emotion, Sleep and wakefulness
|
|
|
Parkinson's disease cause
|
substantia nigra, basal ganglia
|
|
|
Frontal Lobotomy effects x4
|
lower moral standard, ill-tempered, cannot concentrate, personality change, loss of emotional thought, difficulty in planning
|
|
|
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
|
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
|
|
|
limbic system components 2
|
Amygdala, Hippocampus
|
|
|
where do cell bodies locate?
|
somatic motor system in CNS, somatic sensory in dorsal root ganglion
|
|
:S
|
:S
|
|
|
spinal nerves : 4 plexuses you need to know
|
cervical, brachial, lumbar, sacral
|
|
|
cervical plexus
|
C1-4, Innervates superficial neck, skin of neck and posterior of head
|
|
|
Phrenic nerve
|
C3-5, innervate diaphragm
|
|
|
Brachial Plexus
|
C5-T1, 5 rami, 3 trunks, 6 divisions (anterior,posterior divisions), cords. e.g. Axillary, radial, ulnar, median, Musculocutaneous.
|
|
|
Lumbar plexus
|
L1-4
|
|
|
Sacral plexus
|
L4-S4
|
|
|
4 major nerve from Lumbosacral Plexus
|
Obturator, Femoral, tibial, Common fibular, (Sciatic nerve)
|
|
|
sensory ganglia in dorsal root ganglia
|
Psedo-unipolar neurons surrounded by satellite cells,
|
|
|
Autonomic Ganglia in ______ surrounded by _________.
|
sympathetic trunk, within innovated organs; satellite cells
|
|
|
Seddon’s classification
|
Neuropraxia, Axonotmesis, Neurotmesis
|
|
|
define Neuropraxia
|
injury without any anatomical discontinuity but resulting in functional disruption
|
|
|
define Axonotmesis
|
Axonotmesis: microscopic division of nerve fibers (axon); no obvious discontinuity of the nerve sheath.
|
|
|
in ANS, cell bodies/Center of sympathetic system are from?
|
intermediolateral cell column (lateral horn) of the T1-L3 spinal cord.
|
|
|
in ANS, cell bodies/Center of parasympathetic system is from ?
|
the brain stem and S2-4 spinal cord
|
|
|
Higher center of autonomic system ?
|
hypothalamus
|
|
|
how long is sympathetic trunk?
|
The trunk extends from the base of the skull to the coccyx on the ventrolateral side of the vertebral column
|
|
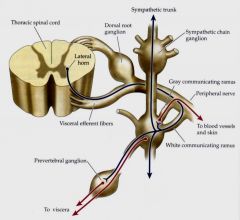
name what the 3 pathways of the preganglionic fibre can do?
|
1. synaptic contacts with postganglionic neurons in the paravertebral ganglion; 2. pass up and down in the sympathetic trunk; 3. communicate with prevertebral ganglia (celiac ganglion, superior mesenteric ganglion, or inferior mesenteric ganglion)
|
|
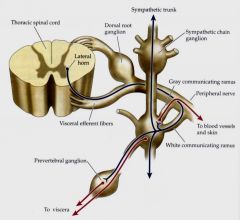
white communicating ramus (T1-L3)
|
preganglionic fibers and visceral afferent fibers
|
|
|
telencephalon function and components
|
cerebral hemispheres - motor, thinking, emotion, sensory, behavior; basal ganglia - motor
|
|
|
not enough vitamin A (retinol) results:
|
1. night blindness, 2. xerophthalmia, 3 .keratinization of the mucus secreting cells, 4. malnutrition and infection
|
|
|
non polar amino acid, hydrophobic, inner core of protein
|
Gly, Ala, Pro, Val, Ile, Leu, Met (Val, Ile, Leu, Met) essential
|
|
|
aa with aromatic group
|
Trp, Phe, Tyr, (essential Trp, Phe) Tyr is essential newborn
|
|
|
aa with polar
|
Ser, thr, cys, asn (asparagine) Gln, (thr essential; cys for newborn)
|
|
|
aa with acidic
|
Glu, Asp
|
|
|
aa with basic
|
Lys, His, Arg, (essential Lys; newborn: His, Arg
|
|
|
with -OH aa
|
threonine, tyrosine, serine
|
|
|
tyrosine make:
|
dopa, dopamine, noradrenaline, adrenaline,
|
|
|
tryptophan make
|
serotonin
|
|
|
Lesch Nyhan syndrome
|
defects in salvaging pathway, depletion of purine and production of uric acid, lead to impaired brain development
|
|
|
salvaging pathway
|
purine --> nucleoside --> hypoxanthine
|
|
|
vitamin E full name
|
alpha tocopherol
|
|
|
vitamins b full name
|
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine), Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin), Vitamin B3 (Niacin); Vitamin B9 (Folic acid); Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine); Vitamin B12 (Cobalamins);
|
|
|
vitamin K
|
Vitamin K1 (Phylloquinone)
|
|
|
Methotrexate. trimethoprim, fluorouracil
|
dihydrofolate --> tetrahydrofolate (blocked)
|
|
|
femoral triangle
|
sartorius, adductor longus, inguinal ligament
|
|
|
dorsalis pedis pulsation
|
lateral to the extensor hallucis longus tendon
|
|
|
passive control of the blood vessel radius
|
transmural pressure and compliance
|
|
|
active control of blood vessel radius
|
metabolic waste autoregulation, myogenic autoregulation, neural, hormonal
|
|
|
factors contribute to compliance 4pt
|
thickness, components, pathology, neurological
|
|
|
three hormones that constrict the blood vessels
|
angiotensin, antidiuretic, adrenaline
|
|
|
fenestrated capillaries sites
|
kidney, endocrine glands, intestine
|
|
|
pericytes
|
pericytes
|
|
|
how lymph drain back into the heart
|
right lymphatic duct, thoracic duct
|
|
|
adenosine receptor can be found in ?
|
cardiomyocytes, neutrophils, endothelial cells, macrophages
|
|
|
haemoglobin breakdown where?
|
extravascular tissue MQ
|
|
|
haemoglobin breakdown into
|
globin, iron and protoporphyrin
|
|
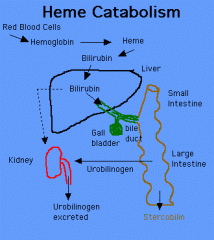
protoporphyrin to urine/stool
|
protoporphyrin, bilirubin, bilirubin glucuronide (liver), urobilinogen and stercobilinogen (intestine)
|
|
|
chronic blood loss 4 pt
|
genital: menorrhagia; gastrointestinal bleeding; pulmonary: haemoptysis; Urinary tract: haematuria
|
|
|
four reasons of anaemia
|
production defect: bone marrow defect (ineffective and inadequate); destruction by haemolysis (RBC enzyme membrane or antibody-mediated, toxin), sequestration (hypersplenism), dilution
|
|
|
anaemia is
|
low haemoglobin / blood volume
|
|
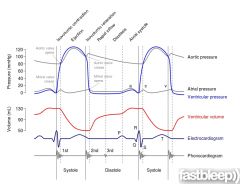
four heart sound heard, ECG diagram
|
P, Q, R, S
|

