![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
• Transition to services economy (concepts not #s)
|
o Services compose a much greater portion of US economic output (over 75%)
o Development of other countries’ economies lead to a greater portion of US GDP made up of services o Most new jobs are generated by services o Services are essential inputs into the production of virtually all products. The price and quality of services influence costs and productivity in all other sectors in an economy, including manufacturing and agriculture. o There are potential risks and rewards to becoming a economy based 100% on services |
|
|
• What is transforming our service markets
|
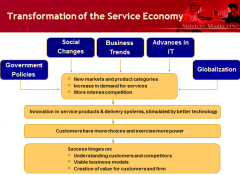
this is reshaping demand, supply, the competitive landscape, and customers’ styles of decision making
|
|
|
• Definition of services
|
Are economic activities offered by one party to another
In exchange for their money, time, effort-service customers expect to obtain value from (but don’t take ownership of any physical elements involved): Rented goods/services, space and time rental, labor and expertise, access to systems and networks Most commonly employ time-based performances to bring about desired results in: recipients themselves objects or other assets for which purchasers have responsibility Can be a product, customer service, add value to a good, embedded in a tangible product |
|
|
• 4 characteristics of services
|
(SHIP)
o Simultaneity- Production and consumption are simultaneous and inseparable o Heterogeneity- Product varies across customer, provider and for the same provider and customer from one consumption occasion to the next o Intangibility- Product is a process, deed or a performance o Perishability- Product cannot be stored and can only be produced after customer initiates |
|
|
• Lovelock grid – categories of services
|
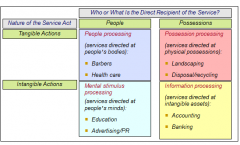
|
|
|
7 P's of Marketing services
|
Product
Price Place Promotion People Physical Environment Process |
|
|
• Standard consumer decision making model applied to services vs products
|
o Consumer Choice/ Prepurchase Stage
Need recognition, Information Search, Evaluation of alternatives, purchase o Consumer Experience/ Service Encounter Stage Request service from chosen suplplier or initiate self-service o Postexperience evaluation/ Post Encounter Stage Evaluation of service performance and future intentions -Awareness, Info search, alternatives, action/decision |
|
|
Risks in a services context and service company's risk reduction strategies
|
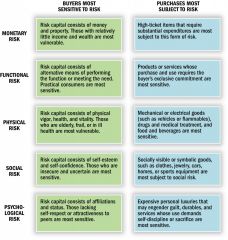
-Many services are hard to evaluate so they are perceived as riskier
-Firm must provide more of a reward to get people to buy/use -Offer free trials, guarantees, previews, etc. to reduce risk |
|
|
• High contact vs. low contact
|
o High Contact: Interaction throughout the service delivery between the customer and the organization- many points of contact and moments of truth- ie: nursing home, haircut, hotel, airlines
o Low contact- Little, if any, contact between customer and service provider- ie: cable, insurance, internet based services- Mostly delivered via websites, equipment, or call centers |
|
|
Back Stage vs. Front Stage
|
o Front stage= visible, tangible- common in high contact services= service delivery system- creates the service experience
o Back stage= invisible components- common in low contact services= technical core to a service |
|
|
Search Attributes
|
Easy to evaluate,mostly goods like clothes, cars, food
|
|
|
Experience Attributes
|
Restaurant meals, haircut, entertainment
|
|
|
Credence Attributes
|
Difficult to evaluate- education, legal services, health services
|
|
|
• Customer delight issues
|
Unexpectedly high levels of performance
Arousal (e.g., surprise, excitement) Positive affect (e.g., pleasure, joy, or happiness) Issues: Should delight always be the goal, is it better than profitability, does it set unrealistic expectations You should not try to exceed customer expectation all of the time because eventually customer satisfaction will become unattainable-“the point of diminishing returns” |
|
|
Positioning (for a svcs business)
|
o Strategy is concerned with creating, communicating, and maintaining distinctive differences that will be noticed and valued by those customers with whom the firm would most like to develop a long term relationship
o Company must understand their target customers’ preferences, their conception of value and the characteristics of their competitors offerings o Distinguishes a brand from its competitors o Avoid trap of investing too heavily in points that are easily copied |
|
|
Positioning is often associated with
|
-Price and product attributes
-Customer service processes- convenience and ease of use -Service distribution and delivery systems -service environment- luxury and functionality -Service personnel |
|
|
• Determinant attributes
|
o Those which actually determine buyer’s choice between competing alternatives
o May be way down on the list of features important to purchasers but are attributes in which the customers see significant differences between competing alternatives |
|
|
• “focused” strategies for creating competitive advantage
|
-Providing relatively small product mix to particular market segment
-Market segmentation forms the basis for focused strategies o 4 Basic strategies: Fully Focused-service and market Market Focused-Firm serves few or many markets Service Focused-Extent to which a firm provides few or many services Unfocused- serve too broad of a market and too many services-not advisable for firms to do |
|
|
• Flower of service
|
o Includes core product and two types of supplementary services that surround it: facilitating and enhancing
o All parts of the flower are important to delivering a well-designed and well-managed service product o Flower petals are arranged in clockwise order based on order they would likely occur in the process |
|
|
o Core Service
|
-the center of the flower of service
-Provides the principal, problem-solving benefits customers seek |
|
|
Supplementary services
|
Augment the core product- facilitaing its use and enhancing its value and appeal to the customers overall experience
-Where companies can gain a competitive advantage, increase the services value, and charge a higher price |
|
|
Facilitating services
|
Aid in the use of the core product and sometimes required for service delivery
-ie: information, order taking, billing, payment |
|
|
Enhancing services
|
Add extra value for customers
-ie: consultation, hospitality, safekeeping, exceptions |
|
|
• Positioning in competitive markets
|
o Want to try and be a specific thing to a specific person
o Understand your customers, who you want for customers, and how you stand in their minds; understand value proposition; know your competitors; know if your services meet target consumer needs |
|
|
• Distribution options
|
o Customers visit service site
o Service providers go to customers- more expensive/time consuming for service provider o Service transaction conducted remotely |
|
|
Foundation of any service distribution strategy
|
What? How? Where? When? Responses to those questions
|
|
|
3 Flows of a service distribution strategy
|
1. Information and promotion flows- information and consultation
2. Negotiation Flow- order-taking, billing, payment 3. Product Flow- core service and other petals of flower |
|
|
Channel Preferences
|
-Driven by customer preferences
-CONVENIENCE is key driver -Prefer remote (impersonal/Self-serve) channels when they have high confidence and knowledge about the product and are technology savvy -Prefer personal channels for complex and high perceived risk services and there are social motives behind the transaction |
|
|
Role of intermediaries
|
Used by service firms to distribute some of the supplementary services of the core product
-May be more cost effective to outsource certain tasks |
|
|
Franchises +/-
|
o Advantages
Allows company to expand delivery of effective service concept A fast growth strategy when resources are limited and long term commitment of store managers is crucial and local knowledge is important o Cost effective way to expand operations o Disadvantages Loss of control over delivery system and ultimately over how customers experience the actual service Effective quality control is difficult (but very important) Conflict between franchisees may arise especially as they gain experience High attrition (failure) rate |
|
|
Opportunities/Challenges for emerging technologies in services
|
Opportunities
-Convenience and customer satisfaction through self service -Self-service technology -can create new business opportunities and intermediary roles Challenges -Legal Issues involved -Is it considered unfair competition if the smartphone apps are not adhering to the same regualtions and standards for the NIST and Handbook 44; operating in gray area of services between taxis and for hire services -liability issues within the industry the are operating in (taxi and transportation) |

