![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Marketing |
activity ofcreating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that benefits itscustomers, the organization, its stakeholders and society at large |
|
|
§ Factors that influence marketing actions: |
· To asses and satisfy consumer needs· **key to achieving these objectives is the idea of EXCHANGE trade of things ofvalue between a buyer and a seller so that each is better off after thetrade |
|
|
FACTORS THAT ALLOW MARKETING TO OCCUR |
· 1. 2 plus parities with unsatisfied needs · 2. Desire and ability to satisfy those needs · 3. Ways for parities to communicate (coupon in mail,drive by store) · 4. Something to exchange (money for pizza) |
|
|
What does marketing try and do? |
Marketing tries to satisfy both costumers wantsand needs |
|
|
need |
o occurs when a person feels deprived of basicnecessities such as food, clothing, and shelter |
|
|
want |
o want is a need that is shaped by a per-son’s knowledge, culture, and personality o effective marketing can shape a personswants |
|
|
Market |
· people with both the desire and the ability tobuy a specific offering. (made up ofpotential costumers) |
|
|
MARKETING ORGANIZATION |
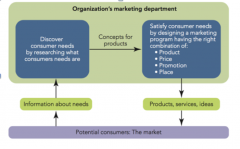
|
|
|
target market |
· one or more specific groups of potentialconsumers toward which an organization directs its marketing program. |
|
|
CONTROLLABLE MARKETING MIX |
1. Product. A good, service, oridea to satisfy the consumer’s needs. 2. Price. What is exchanged for theproduct. 3. Promotion. A means ofcommunication between the seller and buyer. 4. Place. A means of gettingthe product to the consumer. **** MarketingMix these four elements are the controllable factors—product, price,promotion, and place—that can be used by the marketing manager to solve amarketing problem. · controllable factors bc under control of the marketingdep in an organization |
|
|
Product. |
1. . A good, service, or idea tosatisfy the consumer’s needs. |
|
|
Price. |
1. Whatis exchanged for the product. |
|
|
Promotion |
A means of communication between theseller and buyer. |
|
|
Place. |
1. Ameans of getting the product to the consumer. |
|
|
Marketing Mix |
Mix thesefour elements are the controllablefactors—product, price, promotion, and place—that can be used by themarketing manager to solve a marketing problem. |
|
|
what does designing an effective marketing mix display? |
a clear customer value proposition |
|
|
customer value proposition |
cluster of benefits that an organizationpromises customers to satisfy their needs. ex: walmarts--> everyday low prices from a broad range of products at convenient locations |
|
|
forces that are beyond marketers control 5 Environmental forces |
consist of social, economic, technological and competitive and regulatory issues (govt restrictions) |
|
|
costumer value |
uniquecombination of benefits received by targeted buyers that includes quality, convenience, on-time delivery, and both before-sale and after-sale service at a spe-cific price |
|
|
1-4 Explainhow organizations build strong customer relationships and customer valuethrough marketing. |
firms seek to build long-term relationships with customers by providingunique value to them. Many successful firms deliver outstanding customer valuewith one of three value strategies: best price, best product, or best service. firm ieves meaningful customer relationships by creating connections with itscustomers through careful coordination of the product, its price, the way it’s promoted, and how it’s placed. |
|
|
what are the 3 main costumer value strategys? |
firms do outstanding value with either one of the 3: 1. best value 2. best product 3. best service |
|
|
how does a firm achieve meaningful costumer relationships? |
firm ieves meaningful customer relationships by creating connections with its customers through careful coordination of the product, its price, the way it’s promoted, and how it’s placed. (called relationship marketing) |
|
|
relationship marketing |
personal, ongoing relationship betweenthe organization and its individual customers that begins before and continues afterthe sale. |
|
|
marketingprogram |
pdf a plan that integrates the marketing mix to provide a good, service, oridea to prospective buyers. |
|
|
market segments |
relatively homogeneous groups of prospective buyers that (1) have com-mon needs and (2) will respond similarly to a marketing action. This action mightbe a product feature, a promotion, or a price. |
|
|
1-4. An organization can’t satisfy the needs of all consumers, so it mustfocus on one or more subgroups, which are its __________. |
target market |
|
|
1-5. What are the four marketing mix elements that make up theorganization’s marketing program? |
1. product 2. price 3. place 4. promotion |
|
|
f 1-6. What are environmental forces? |
forces that are beyond marketers control 5 Environmental forces consist of social, economic, technological and competitive and regulatory issues (govt restrictions) |
|
|
marketing mix example |
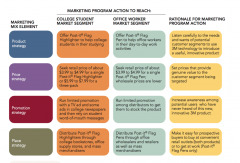
|
|
|
success of product lines will lead to... |
extending the product line |
|
|
marketing concept |
theidea that an organization should (1) strive to satisfy the needs of consumers while also(2) trying to achieve the organization’s goals. |
|
|
an organization that has a market orientationfocuses its efforts on... |
(1) continuously collecting information about customers’ needs,(2) sharing this information across departments, and (3) using it to create customer value.31 |
|
|
LO 1-5 Describe howtoday’s customerrelationship eradiffers from prioreras. |
production era, covers the early years of the United Statesup until the 1920s. Goods were scarce and buyers were willing to accept virtually anygoods that were available and make do with them.29 In the sales era from the 1920s tothe 1960s, manufacturers found they could produce more goods than buyers couldconsume. then the marketing concept era came about. today we have the customer relationship era, began in the 1980s andoccurs as firms continuously seek to satisfy the high expectations of customers. |
|
|
costumer relationship era |
-occurs as firms continuously seek to satisfy the high expectations of customers, due to the adze of social media -organizations and their customers develop relationships throughsocial media websites such as Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube, among others. Thisfocus has allowed organizations to understand and market to current and prospectivecustomers in ways that are still evolving, such as in using social media. ** due to this, COSTUMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT HAS EVOLVED |
|
|
what are the 4 eras? |
1. production era 2. sales era 3. marketing concept era 4. coustmer realtionship era (current) organizations and their customers develop relationships through social media |
|
|
COSTUMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM) |
process of identifying pro-spective buyers, understanding them intimately, and developing favorable long-termperceptions of the organization and its offerings so that buyers will choose them in themarketplace |
|
|
what is the foundation of CRM? |
costumer experience |
|
|
costumer experience |
is the internal response that customers have to all aspects of an organization andits offering (both direct and indirect contact with the company) |
|
|
direct contact |
d irect contacts include the customer’s contacts with theseller through buying, using, and obtaining service. |
|
|
indirect contact |
most ofteninvolve unplanned “touches” with the company through word-of-mouth commentsfrom other customers, reviewers, and news reports. |
|
|
social responsibility |
the idea that organizations are accountable to a larger society. |
|
|
societal marketingconcept |
the view that organizations should satisfy the needs of consumers in a waythat provides for society’s well-being.36 For example, Scotch-Brite® Never RustTMsoap pads from 3M—which are made from recycled plastic bottles—are more expen-sive than those offered by competitors (SOS and Brillo) but are superior because theydon’t rust or scratch |
|
|
What is marketed? |
1. goods - tangable objects 2. services- intangible objects (trips,, mesums) 3. ideas ** goods, services and ideas are all considered PRODUCTS |
|
|
product |
is a good, service, or idea consisting of a bundle of tangible and intangible attributes that satisfies consumers’ needs and is received in exchange for money or something else of value |
|
|
who buys and uses what is marketed? |
individuals and orgainzations |
|
|
ultimate consumers v. organizational buyers |
people who use the products and services purchased for a household those manfacters, wholesalers, retailers, and govt agencies that buy products and service for their own use or for resale |
|
|
utility (4 types) |
The benefits or cus-tomer value received by users of the product. This utility is the result of the marketingexchange process and the way society benefits from marketing. 1. form utility 2. place utility 3. time utility 4. posession utility |
|
|
form utility |
The production of the product or ser-vice constitutes |
|
|
place utility |
having the offering available whereconsumers need it |
|
|
time utility |
means having it available when needed |
|
|
posession utility |
is the value of making an item easy to purchase through the provisionof credit cards or financial arrangements. |
|
|
how does marketing create utilities |
arketing creates its utilities by bridgingspace (place utility) and hours (time utility) to provide pro ducts (form utility) forconsumers to own and use (possession utility). |
|
|
1-7. What are the two key characteristics of the marketing concept? |
idea that an organization should (1) strive to satisfy the needs of consumers while also(2) trying to achieve the organization’s goals. |
|
|
f 1-8. What is the difference between ultimate consumers and organizational buyers? |
ultimate consumers- people who use the products and services purchased for a household organizational buyers- those manfacters, wholesalers, retailers, and govt agencies that buy products and service for their own use or for resale |
|
|
LO 1-1 Define marketing and identify the diverse factors thatinfluence marketing actions. |
Marketing is an organizational function and a set of processesfor creating, communicating, and delivering value to customersand for managing customer relationships in ways that benefitthe organization and its stakeholders. This definition relates totwo primary goals of marketing: (a) discovering the needs ofprospective customers and (b) satisfying them. Achieving thesetwo goals also involves the four marketing mix factors largelycontrolled by the organization and the five environmental forcesthat are generally outside its control. |
|
|
LO2 Explain how marketing discovers and satisfiesconsumer needs. |
The first objective in marketing is discovering the needs and wantsof consumers who are prospective buyers and customers. This is noteasy because consumers may not always know or be able to de-scribe what they need and want. A need occurs when a person feelsdeprived of basic necessities such as food, clothing, and shelter. Awant is a need that is shaped by a person’s knowledge, culture, andpersonality. Effective marketing can clearly shape a person’s wantsand tries to influence what he or she buys. The second objective inmarketing is satisfying the needs of targeted consumers. Because anorganization obviously can’t satisfy all consumer needs, it mustconcentrate its efforts on certain needs of a specific group of poten-tial consumers or target market—one or more specific groups ofpotential consumers toward which an organization directs its mar-keting program. It then selects its target market segment(s), whichare relatively homogeneous groups of prospective buyers that(1) have common needs and (2) will respond similarly to a market. Finally, the organization develops a set of marketingactions in the form of a unique marketing program to reach them. |
|
|
LO3 distinguish between marketing mix factors andenvironmental forces. |
Four elements in a marketing program designed to satisfy cus-tomer needs are product, price, promotion, and place. Theseelements are called the marketing mix, the four Ps, or the mar-keter’s controllable variables. The marketing mix also providesa clear customer value proposition—a cluster of benefits that anoffering satisfies. Environmental forces, also called uncontrol-lable variables, are largely beyond the organization’s control.These include social, economic, technological, competitive,and regulatory forces. |
|
|
Explain how organizations build strong customerrelationships and customer value through marketing. |
The essence of successful marketing is to provide sufficient valueto gain loyal, long-term customers. Customer value is the uniquecombination of benefits received by targeted buyers that usuallyincludes quality, price, convenience, on-time delivery, and bothbefore-sale and after-sale service. Marketers do this by using oneof three value strategies: best price, best product, or best service. |
|
|
Describe how today’s customer relationship eradiffers from prior eras. |
business history is divided into four overlapping periods: theproduction era, the sales era, the marketing concept era, and thecurrent customer relationship era. The production era coversthe period up until the 1920s, when buyers were willing to acceptvirtually any goods that were available. The central notion wasthat products would sell themselves. The sales era lasted from the CHAPTER 1 Creating Customer Relationships and Value through Marketing 1920s to the 1960s. Manufacturers found they could producemore goods than buyers could consume, and competition grew,so the solution was to hire more salespeople to find new buyers.In the late 1950s, the marketing concept era dawned when orga-nizations adopted a strong market orientation and integrated FOCUSING ON KEY TERMS marketing into each phase of their business. In today’s customerrelationship era, organizations continuously seek to satisfy thehigh expectations of customers—an aggressive extension ofthe marketing concept era. This is increasingly done throughsocial media. |
|
|
exchange |
which is the trade of things of value between a buyer and a seller so that each is betteroff after the trade |
|
|
environmental forces |
affect a marketing de-cision, which consist of social, economic, technological, competitive, and regula-tory force |

