![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
91 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Class Notes: |
Study Below: |
|
|
What are the 4 P's? |
1. Product. 2. Price. 3. Promotion. 4. Place. |
|
|
What are the 7 External Environments? |
1. Demographic. 2. Economic. 3. Political/Legal. 4. Socio-cultural. 5. Technological. 6. Global. 7. Natural. |
|
|
What are the different types of Survey Research and the Pros/Cons for each? |
- In-home Personal Interview: Pro: Can provide highly detailed information. Con: Very expensive to send interviewer to customer locations. - Mall Intercept Review: Pro: Ability of interviewer to probe when necessary. Con: Hard to get a representative sample of the population. |
|
|
What are the different types of Survey Research and the Pros/Cons for each (continued)? |
- Mail Surveys: Pro: Low cost, centralized control. Con: Produce low response rates. - Executive Interview: Pro: Directly interviewing business people. Con: Very difficult due to many factors (time and place to meet, cancellations, etc.). - Focus Groups: Pro: Allows for consumer response to a product. Con: None. |
|
|
What are the different types of Questionnaire Design Research and what are their benefits? |
- Open-ended question: Encourages an answer phrased in the respondent's words. - Closed-Ended Question: Asks the respondent to make a selection from a limited list of responses. - Scaled-response question: Measures the intensity of a respondent's answer. |
|
|
What are the different types of Observational Research and the Pros/Cons for each (continued)? |
- Mystery Shoppers: Pro: Directly observing and collecting data from real-time shopping. Con: Does not do direct interaction with customers, but instead observes their behavior. - Behavioral Targeting: Pro: Tracks consumers browser history to discover their likes and interests. Con: Does not directly influence their buying decisions. |
|
|
What is Ethnographic Research? |
Directly studies the population of people and records their behavior, culture, etc. |
|
|
What is Virtual Shopping? |
The act in virtually placing goods on a website and records each customer's interests based on what they look at, for how long, and the order the goods were placed in. |
|
|
How can Surveys be biased? |
By stating the survey's purpose at the beginning of the interview, it improves clarity but allows for more biased answers. Respondents post answers that the interviewer wants to hear instead of what the respondents wants the interviewer to hear. |
|
|
What is another common error in survey questions? |
Asking 2 questions in 1. Most questions should be short and detailed, but not too long and not too detailed. |
|
|
What is Primary Data? |
Information collected for the first time. |
|
|
What is Secondary Data? |
Data that is previously collected for any purpose other than the one at hand. |
|
|
What is Big Data? |
The exponential growth of information and the development of complex new tools to analyze such data.
|
|
|
What is Social Media Data? |
Typically data recorded on the internet (Likes, Google searches, etc.) that tells the company your likes and interests in order to better serve you. |
|
|
What is experimental research? |
Gathers primary data by altering one or more variable while also observing the effects of those alterations on another variable. |
|
|
What is the BCG Model? |
A model that is used to classify each Strategic Business Unit by its present or forecast growth and market share. |
|
|
What are the 4 factors in the BCG Model? |
1. Star: Fast growing market leader. 2. Cash Cow: Dominant market share in a low-growth market. 3. Problem Child (Question Mark): Low-Market Share in a High-growth industry. 4. Dogs: Small market-share with low growth potential. |
|
|
BCG Model: |

|
|
|
Is it good to market in bad times? |
- Companies should focus more on consumers instead of their image to continue profit and sales in tougher times. - If a company markets, focus on consumer's needs rather than wants. |
|
|
How does a company market in tough times? |
1. Learn more about customer needs. 2. Call in favors from your vendors. 3. Focus on frequent customers. 4. Focus on more direct revenue. 5. Reach out to family values. |
|
|
What is the New Product Development Process? |

|
|
|
What is E-Curve Analysis? |
Analyzing a firm's experience a firm has and their efficiency over time. - Cost to produce will go down. - Entrant in a new market will never catch up to the leader. |
|
|
E-Curve: |
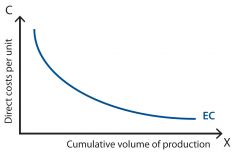
|
|
|
What are Market Development Strategies? |
- Attracting new customers to existing products. 1. Product: Starbucks develops powdered instant coffee called Via. 2. Diversification: Starbucks launches Hear Music and buys Ethos Water. |
|
|
What are Market Penetration Strategies? |
- Increasing market share among existing customers. 1. Penetration: Selling more coffee to customers with re-loadable Starbucks Cards. 2. Development: Starbucks opens a store in Chile. |
|
|
What is a Product Line, Mix, and Depth? |
- Line: A group of closely related products (I.E. A wide variety of different soup flavors). - Depth: The number of product items in a product line. - Mix: All the products a company sells (I.E. Campbell's soup, drinks, biscuits are its mix). |
|
|
What are the types of goods consumers purchase? |
- Convenience Products: Products that don't take much effort to find (Candy). - Shopping Products: Usually more expensive and is found in lesser stores. - Homogeneous (fruits). - Heterogeneous (digital watch vs regular). - Specialty Products: Products that require extensive searching. (Omega Watches). - Unsought Products: Products unknown to the buyer. |
|
|
Chapter 2 Definitions: |
Study Below: |
|
|
Strategic Planning: |
The managerial process of creating and maintaining a fit between the organization’s objectives and resources and the evolving market opportunities. |
|
|
Strategic business unit (SBU) |
A subgroup of a single business or collection of related businesses within the larger organization. |
|
|
Market Penetration: |
A marketing strategy that tries to increase market share among existing customers. |
|
|
Market Development: |
A marketing strategy that entails attracting new customers to existing products. |
|
|
Product Development: |
A marketing strategy that entails the creation of new products for present markets. |
|
|
Diversification: |
A strategy to increase sales by introducing new products into new markets. |
|
|
Portfolio Matrix: |
Distributes resources among products or strategic business units using market share and market growth rate. |
|
|
Planning: |
Anticipating future events and determining strategies to achieve organizational objectives in the future. |
|
|
Marketing Planning: |
Designing activities relating to marketing objectives and the changing marketing environment. |
|
|
Marketing Plan: |
A written document that acts as a guidebook of marketing activities for the marketing manager. |
|
|
Mission Statement: |
A statement that explains the company's purpose for existing. |
|
|
Marketing Myopia: |
Defining a business in terms of goods and services rather than in terms of the benefits customers seek. |
|
|
SWOT Analysis: |
Identifying internal strengths (S) and weaknesses (W) and also examining external opportunities (O) and threats (T). |
|
|
Environmental Scanning: |
Information in the external environment that may affect the future of the organizations or market plan. |
|
|
Competitive Advantage: |
A company's products that are considered to be superior to the competitor's products. |
|
|
Cost Competitive Advantage: |
Being the low-cost competitor in an industry while maintaining satisfactory profit margins. |
|
|
Sustainable Comparative Advantage: |
An advantage that cannot be copied by the competition. |
|
|
Marketing Objective: |
A statement of what is to be accomplished through marketing activities. |
|
|
Marketing Strategy: |
Describing one or more target markets, and developing/maintaining a marketing mix that will produce mutually satisfying exchanges. |
|
|
Implementation: |
The process that turns a marketing plan into action assignments. |
|
|
Evaluation: |
Determining the extent to which the marketing objectives have been achieved during the specified time period. |
|
|
Control: |
Correcting the actions in a Marketing Plan that do not help the organization reach its objectives. |
|
|
Chapter 4: |
Study Below: |
|
|
Target Market: |
An organization's marketing mix that is intended to meet the need of a particular group. |
|
|
Environmental Management: |
Strategies that attempt to shape the external environment it operates in. |
|
|
Component Lifestyles: |
Choosing goods and services that meet one’s diverse needs. |
|
|
Demography: |
The study of people's age, race, ethnicity, and location. |
|
|
Millennials: |
People born between 1979 and 1994. |
|
|
Generation X: |
People born between 1965 and 1978. |
|
|
Baby Boomers: |
People born between 1946 and 1964. |
|
|
Purchasing Power: |
Income versus the relative cost of a standard set of goods and services in different geographic areas. |
|
|
Inflation: |
A measure of the decrease in the value of money. |
|
|
Recession: |
A period of economic activity characterized by negative growth, lowers demand. |
|
|
Basic and Applied Research: |
Basic: Aims to confirm an existing theory or to learn more about a concept or phenomenon. Applied: Attempts to develop new or improved products. |
|
|
Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC): |
Federal Agency that protects the health and safety of consumers in and around their homes. |
|
|
Food and Drug Administration (FDA): |
Federal Agency that enforces regulations against selling and distributing adulterated, mis-branded, or hazardous food and drug products. |
|
|
Federal Trade Commission (FTC): |
Federal Agency that prevents persons or corporations from using unfair methods of competition in commerce. |
|
|
Chapter 9 Vocab: |
Study Below: |
|
|
Marketing Research: |
Planning, collecting, and analyzing data relevant to a marketing decision. |
|
|
Marketing Research Problem: |
Determining what information is needed and how it can be used effectively. |
|
|
Marketing Research Objective: |
Specific information needed to solve a marketing research problem. |
|
|
Management decision problem: |
Problem that utilizes market research so that managers can take the right actions. |
|
|
4 Types of Experiment Errors: |
1. Measurement: Difference between information desired and information provided. 2. Sampling: Sample doesn't represent target population. 3. Frame: Sample drawn from a population is different from the target population. 4. Random: Selected sample is a bad representation of the overall population. |
|
|
Competitive Intelligence: |
Aids managers in assessing their competition in order to become more efficient. |
|
|
Chapter 10 Definitions: |
Study Below: |
|
|
Product: |
Everything, both favorable and unfavorable, that a person receives in an exchange. |
|
|
Product Item: |
Specific version of a product that can be designated as a distinct offering among an organization's products. |
|
|
Product Modification: |
Changing one or more of a product's characteristics. |
|
|
Planned Obsolescence: |
Modifying products so those that have already been sold become obsolete before replacement. |
|
|
Product Line Extension: |
Adding additional products to an existing product line in order to complete more broadly in the industry. |
|
|
All the different type of brands: |
Brand: Identity of the product. Brand Name: Part that can be spoken. Brand Mark: Elements of brand that cannot be spoken. Brand Equity: Value of a company. Global Brand: Obtains 1/3 of earnings outside of its home country. |
|
|
All the different type of brands (cont.): |
Brand Loyalty: Preference for one brand over the others. Manufacturer's Brand: Name of manufacture. Private Brand: Owned by a wholesaler/retailer. Captive Brand: Manufactured by 3rd party for an exclusive retailer. |
|
|
All the different type of brands (cont.): |
Individual Branding: Different names for different products. Family Branding: Several products with different names in the same brand. Co-Branding: Placing two or more brand names on a product or its package. Trademark: Exclusive right to use a brand. |
|
|
Persuasive and informational labeling: |
Persuasive: Focuses on promoting a theme or logo. Informational: Helps consumers make proper product selections. |
|
|
Warranties: |
Warranty: Confirmation of the quality or performance of a good or service. Express Warranty: Written guarantee. Implied Warranty: Unwritten guarantee that the good or service is fit for its purpose. |
|
|
Chapter 11 Definitions: |
Study Below: |
|
|
New Product: |
A product new to the world, market, producer, seller, or any combination of these. |
|
|
New Product Strategy: |
A plan to link new product development with the objectives of the marketing department. |
|
|
Product Development: |
Creating marketable products. |
|
|
Brainstorming: |
Getting a group to think of unlimited ways to vary a product or solve a problem. |
|
|
Screening: |
First filter that eliminates ideas that are inconsistent with the organization's strategy. |
|
|
What was Howard Moskowitz's breakthrough? |
People won't tell you what they want, you have to pleasantly surprise them with what they've always wanted, but never knew they wanted it (Extra Chunky Spaghetti Sauce for example). |

