![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
100 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where are kelp forests found? |
Coldwater |
|
|
How many oceans are there? |
4 |
|
|
What are the name of the four oceans? |
Indian, Pacific (biggest) , Atlantic, Arctic (smallest) |
|

Know |
Parts of continental shelf |
|
|
Hard bottoms.... |
Kelp forest, coral reefs |
|
|
Soft bottoms.... |
Unvegetated seagrass beds |
|
|
What drives the currents? |
Winds |
|
|
what drives the winds? |
Heat from the Sun |
|
|
What are the three major categories of winds? |
tradewinds, westerlies, polar easterlies |
|
|
Where do the horse latitudes occur? |
30 degrees north and 30 degrees south |
|
|
Where are the three major categories of winds located on a globe in what directions do they blow? |

Know |
|
|
In the Coriolis effect everything in the northern hemisphere shifts... |
Right |
|
|
In the Coriolis effect everything in the southern hemisphere shifts... |
Left |
|

What is this? |
Ekman transport |
|
|
In Ekman transport the Northern Hemisphere wind direction causes water to shift_______ to the _______ of the wind. |
90 degrees, right |
|
|
In Ekman transport the Southern Hemisphere wind direction causes water to shift_______ to the _______ of the wind. |
90 degrees, left |
|
|
Because of ekman transport, the direction of the winds, and the Coriolis effect, Gyres in the Northern Hemisphere move..... |
Clockwise |
|
|
Because of ekman transport, the direction of the winds, and the Coriolis effect, Gyres in the Southern Hemisphere move..... |
Counter clockwise |
|
|
Where is the California Current? What is its movement Direction? What is the temperature of the water? |

Movement direction: down Temp of water: cold |
|
|
Where is the Gulf Stream? What is its movement Direction? What is the temperature of the water? |
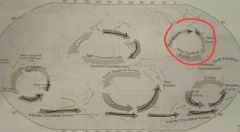
Movement direction: up east coast Temp of water: warm |
|
|
What types of kelps are found in kelp forests? |

(Brown algae looks like forest) |
|
|
What organisms resource partition the holdfast in the kelp forest? |
Polychaetes, crustaceans, brittle stars, |
|
|
What organisms resource partition the blade in the kelp forest? |
Bryozoans, tunicates |
|
|
What organisms resource partition the surroundings in the kelp forest? |
Filter feeders: sponges, hydriods, barnacles Grazers: SEA URCHINS, chitons, limpets Carnivores: sea stars, fishes, lobsters, sea otters |
|
|
What eats California's sea urchins? |
California sheephead |
|
|
Sea otters are........ |
Keystone predators |
|

|
Know what's going on |
|
|
What types of substrates are found in unvegetated soft bottom communities? |
Mud, sand, gravel |
|
|
What determines if a species is found in an area? |

Sediment type, currents, temperature, depth, salinity, other organisms, light |
|
|
In unvegetated soft bottom communities the suspension feeders are... |
Brittle star, sea pen, pollychaetes, amphipods |
|
|
In unvegetated soft bottom communities the deposit feeders are... |
Polychaetes, heart urchins, sand dollars |
|
|
In unvegetated soft bottom communities the predators/scavengers are... |
Crabs/lobster, fish, sea star, whelks, moon snail |
|
|
In unvegetated soft bottom communities the animals and organisms eat.. |
Detritus |
|

Know |
Why certain types of animals are found in certain substrates |
|
|
What two types of organisms are important in unvegetated soft bottom communities? |
Bioturbators and tube builders |
|
|
Bioturbators are..... |
organisms that mix-up and oxygenate the sediment |
|
|
Tube-builders.... |
Stabilize the sediment |
|
|
what plants dominate seagrass beds? |
Seagrass |
|
|
Where do seagrass beds tend to grow? |
Mostly tropical or subtropical areas in shallow waters with sandy/muddy substrates |
|
|
What is limiting in seagrass beds? |
Light penetration (need sunlight) |
|
|
What herbivores are found in seagrass beds? |
Sea urchins, sea turtles, fish, Manatee, dugong |
|
|
What deposit feeders are found in seagrass beds? |
Sea cucumbers, polychaetes |
|
|
What filter feeders are found in seagrass beds? |
Clams |
|
|
What predators are found in seagrass beds? |
Sea stars, fish, sea birds |
|
|
What is Pangaea? |
All the continents together |
|
|
When was Pangea in existence? |
190 million years ago |
|
|
What is the process that broke Pangea up? |
Continental drift and plate tectonics |
|
|
What are two forms of plate tectonics? |
Mid-ocean ridge and seafloor spreading, subduction zones |
|
|
What is mid-ocean ridge and seafloor spreading? Give an example. |
A continuous chain of Submarine volcanic mountains that encircle the globe like seams on a baseball, Mid-Atlantic Ridge |
|
|
What is subduction zones? Give an example. |
Areas where two tectonic plates come together. If one is oceanic (therefore denser) then it will be pulled under the lighter plate, Aleutian Islands |
|
|
Two ways volcanic islands are formed..... |
Through subduction and hot spots |
|
|
What play are we on? |
Pacific Plate |
|
|
How did the Pacific Rim / Ring of Fire get its name? |
Because they are volcanoes and earthquakes surrounding it |
|

What is this? Know. |
Pacific Rim/Ring of fire |
|
|
Describe what a hot spot is and give an example of a hot spot. |

Hotspot stays in the same place there is a plate that moves over it creating volcanic islands. Example Hawaii |
|
|
What are the two types of corals? |
Hermatypic Corals and Ahermatypic Corals |
|
|
What are hermatypic corals? |
Hard corals, Limestone skeleton, build reefs |
|
|
What are Ahermatypic Corals? |
Soft corals, no skeleton, don't help build coral reefs |
|
|
How do corals feed? |
Through Polyp nutrition and Zooxanthellae |
|
|
How do Zooxanthellae help coral? |
Dinoflagellates that live in coral are Symbionts that give coral most of nutrients. Active during day. |
|
|
How does polyp nutrition help coral? |
Filter feed or mucus feed, absorb DOM. Active at night. |
|
|
Two important players in coral reefs... |
Coralline algae and Calcareous green algae |
|
|
Coralline algae... |
Red algae, grows in hard mats, help cement Coral to itself |
|
|
Calcareous Green Algae..... |
CaCO3 in tissues, makes up a lot of the coral rubble sediment. Example: Halimeda |
|
|
What do coral reefs need to grow? |
A lot of light, warm water, salty water, clear water (not a lot of sediments in water). Sometimes use Eutrophication. |
|
|
Where do coral reefs grow? |

|
|
|
What are three types of reefs? |
Fringing reef, barrier reef, atoll |
|
|
What is a fringing reef? |
Reefs very close to shore, grow in narrow bands or fringes along shore. Most common and simplest. |
|
|
What is a barrier reef? |
Similar to fringing but further away. Lagoons may have batch reefs or coral pinnacles. |
|
|
What is it atoll? How are atolls formed? Where is it found? |

Circular rings around sunken volcano Island. Mostly found in Indo West Pacific. |
|
|
What do corals compete for? |
Light and space |
|
|
How do hermatypic corals compete with other hermatypic corals? |
Grow fast up, branch out. Eat away other corals. Sweeper tentacles. |
|
|
How do corals compete with algae? (Algae grow over coral and block light) |
Seaweeds don't grow well where corals are. Algae on coral reefs are nutrient Limited. Herbivores that eat algae helps Coral. |
|
|
How do hermatypic Coral compete with ahermatypic Coral? |
Ahermatypic Corals grow fast and have lots of predator resistance. Hermatypic corals grow slower and are more resistant to wave turbulence. Waves help reduce ahermatypic corals. |
|

What is happening in this diagram? What does this mean about the nutrients in the water? |
Nutrient recycling. Most nutrients in ecosystem remain in Coral. |
|
|
What two zones compromise the epipelagic Zone? |
Oceanic, neritic |
|
|
What are Picoplankton? |
Bacteria and archae |
|
|
What is Femtoplankton? |
Viruses |
|
|
Holoplankton- |
Spend entire life as plankton |
|
|
Meroplankton- |
Spend part of life as plankton |
|
|
What plankton is too small to capture in an net? |
Femtoplankton, Picoplankton, and Hanoplankton |
|
|
Which plankton is too large to capture in a net? |
Megaplankton |
|
|
What plankton is considered net plankton?(can be caught in net) |
Microplankton, mesoplankton, macroplankton |
|

Know |
Sizes of plankton |
|
|
What types of phytoplankton are found in epipelagic Zone? |
Diatoms (coldwater), dinoflagellates (warm water) |
|
|
What types of zooplankton are found in the epipelagic Zone? |
Protozoans (foraminiferans, radiolarians, ciliates). Animals (copepods, jellyfish, krill, salps, siphonophores, Arrow worms) |
|
|
What is ENSO? |
Happens when abnormally low pressure occurs in southeast Pacific and high pressure in Indian Pacific. Weakens Trade Winds and decreases up swelling off Coasts. |
|
|
What are two issues in the epipelagic zone? |
Staying afloat and predation |
|
|
How do organisms cope with staying afloat in the epipelagic Zone? |
-Increased resistance / drag (be flat or have a lot of projections) -Increase buoyancy (swim bladder or store lipids) -Floaters / gas-filled sacks (pleuston vs neuston) |
|
|
How do organisms cope with predation in the epipelagic Zone? |
Sense organs, coloration and camouflage (transparency, countershaded, silversides), swimming, vertical migrations |
|
|
What is the most common vertebrate in the world? |
Bristlemouths |
|
|
How much of the world is deep ocean? |
53 - 54% |
|
|
Know the levels of the pelagic ocean |

Epipealigic (0-200m), Mesopelagic (200-1,000m), Bathypelagic (1,000-4,000m) Abyssalpelagic (4,000-6,000m), Hadalpelagic (6,000m and below) |
|
|
What are the challenges of living in the deep ocean? |
No Light, No food, nowhere to hide, hard to find a mate |
|
|
What is whale fall? Why are they important in the deep ocean? |
When animals die (whales and sharks ect) they sink to the bottom which gives off food and creates habitats for the deep ocean |
|
|
What is deep sea gigantism? |
Organisms have a large body size (the bigger you are the longer you can go in between meals) |
|
|
What food adaptations do organisms have to live in the deep ocean? |
Large teeth, distended Jaws, relatively slower metabolisms, distended stomachs |
|
|
What hiding / light adaptations do organisms have to live in the deep ocean? |
Enlarged and specialized eyes, highly developed lateral line or antenna that detects water movement, find food or mates by smell. Can be transparent, reflective, red in pigment, bioluminescence, photophores. |
|
|
Sex in the deep ocean..... |
Hermaphroditism-both male and female (easier to find mate) or angler fish solution/parasitic males- males bite and permanently fuse to females body |
|
|
How do scientists study the deep ocean? |
Manned submersibles, ROVs autonomous cameras, trawls (net dragged bottom of boat), bottom long lines |

