![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Acinus |
Milk producing element of the breast located within the alveolar glands |
|
|
|
Chemotherapy |
An adjunctive therapy involving use of drugs to treat cancer |
|
|
|
Coopers ligament |
Also called suspensory ligaments Strands of connective tissue that run between skin and deep fascia to support the lobes of the breast |
|
|
|
Fibrocystic Breast |
Common in females When breast thicken of the alveoli in addition to one of more cysts Often lumpy, swollen or tender |
|
|
|
Gynecomastia |
Enlargement of male breast due to growth of ducts and supporting tissue |
|
|
|
Involution |
Describes a process that begins at menopause as the breast loses supportive tissue to fat |
|
|
|
Klinefelters syndrome |
First identified in 1942 by Dr Harry Klinefelter Patients with this often referred as XXY males: instead of 46 chromosomes they have 47 chromosomes with two Xs and one Y |
|
|
|
Klinefelters syndrome |
First identified in 1942 by Dr Harry Klinefelter Patients with this often referred as XXY males: instead of 46 chromosomes they have 47 chromosomes with two Xs and one Y |
|
|
|
Lactiferous |
Are ducts within the breast conveying milk to the nipple |
|
|
|
Lactiferous Sinus |
Widening of the connecting duct immediately behind the nipple Ampulla= pouch like structure that holds milk |
|
|
|
Montgomery Glands |
Also called glands of Montgomery or areolar glands Large modified sebaceous glands on the areola of the breast They secret a fatty fluid that protects the nipple during nursing |
|
|
|
Morgagni's Tubercles
|
Refers to protrusions on the nipple |
|
|
|
Palliative treatments |
refers to treatment used to relieve or alleviate the pain/symptoms of a disease without actually curing the disease.
|
|
|
|
Retromammary space |
is an area of fatty tissue separating the breast from pectoral muscle |
|
|
|
Sebaceous Glands |
Are oil-secreting glands in the skin |
|
|
|
Tail of spence |
- Upper outer quadrant of breast -extends towards the axilla -thickest portion of breast |
|
|
|
Breast extends Blank from the clavicle Breast extends Blank from the mid sternum |
-vertical -horizontally |
|
|
|
Breast are what kind of glands of the reproductive system? |
Accessory |
|
|
|
What lies at the center point of the breast |
The nipple |
|
|
|
what is the smooth circular darken area surrounding the nipple? what does it contain? |
Areola, contains small protrusions on its surface called margognis tubercles |
|
|
|
How many lobes does the breast approximately have? |
15 to 20 lobes |
|
|
|
The lobule hold the milk producing glands called what? |
alveolar glands |
|
|
|
The lobule is sometimes called a what or the what? |
Ductule or Terminal Ductal lobular unit |
|
|
|
The ETD is surrounded by what kind of tissue and lined by what kind of cells? |
-Elastic Tissue -Columnar cells |
|
|
|
ITD has no surrounding elastic tissue and contains what kind of cells |
Cuboidal cells |
|
|
|
In the immature breast, the ducts and alveoli are lined by how many layers epithelium cells? |
Two layers |
|
|
|
after puberty, the epithelium of the lobes proliferates, becoming multilayered forming how many cell types? |
3 alveolar cell types |
|
|
|
What are the cell types for the three alveolar cells? |
-superficial (lumina) a cells -basal B cells (chief cells) -myoepithelial cells |
|
|
|
What is a thin Sheet of fiber that provides support and acts as a semi-permeable filter under the epithelium? |
basement membrane |
|
|
|
Lymphatic Drainage - Lateral breast drain to this first then to axillary nodes. - Medial breast drain to this. - medial breast drain to this, this or the other breast. |
- Pectoral group - internal mammary lymph nodes -mediastinal nodes, parasternal nodes or the other breast tissue |
|
|
|
What are the 5 groups of axillary lymph nodes? where are each axillary lymph node? |
Anterior group : deep below the pectoralis major muscle, along lower boarder of pectoralis minor and also referred to as pectoral node. Posterior group: along subscapular vessels and also referred as subscapular nodes Lateral group: along axillary vein Central Group: in axillary tissues, this is the most palpable group Apical group: above pectoralis minor at the apex of the axilla and behind the clavicle |
|
|
|
What kind of Breast tissue is more radiolucent and therefore shows up as a higher optical density? (Black) |
Adipose tissue |
|
|
|
What kind of breast tissue are less Radiolucent and show lower optical density areas on mammogram? (white)
|
Fibrous and glandular tissue |
|
|
|
What factors affect breast tissue composition?
|
-Hormones -menarche -hormonal fluctuation -pregnancy and lactation -involution -perimenopause and menopause -weight gain/loss |
|
|
|
What hormones effect the breast and what effect do they have on them? |
*Estrogen- growth of ducts *Progesterone- lobular development *Prolactin- lobular development during pregnancy *Adrenal steroids- responsible for cell metabolism *Insulin- necessary for glucose absorption *Growth hormone- controls overall growth of all cell and tissue *Thyroid hormone- cellular activity and metabolism |
|
|
|
WHAT AGE IS THE BREAST FULLY DEVELOPED? |
2O YEARS OLD |
|
|
|
What age does the maturation of the breast completely occur?
|
AGE 30 |
|
|
|
What are the two most prominent hormones active in the breast? |
Estrogen- responsible for ductal proliferation (growth of ducts) Progesterone- responsible for lobular proliferation and growth |
|
|
|
GREATER # OF MENSTRUAL CYCLES= |
INCREASE RISK OF BREAST CANCER |
|
|
|
IF A WOMEN IS HAVING IRREGULAR OR HEAVY MESTRUAL CYCLES THEN THEY ARE.... |
PERIMENOPAUSE |
|
|
|
When is it official start of menopause? What age does menopause occur? |
-NO PERIOD FOR A WHOLE YEAR -Occurs between ages 45- 54 |
|
|
|
When is a women in post menopause? |
Involution and atrophy |
|
|
|
What are positive effects of hormone therapy? |
relieves symptoms of menopause -hot flashes -sleep disturbance -fatigue -osteoporosis -insomnia |
|
|
|
What are negative effects of Hormone Therapy? |
-Breast or Uterine cancer -asthma -dementia -heart attracts -strokes -blood clots |
|
|
|
Can you image a breast that is lactating? |
yes the must patient fully expressed her breast before imaging |
|
|
|
When should a patient that is lactating be scheduled for a mammogram? |
Mammograms should not be scheduled during lactation unless they are DIAGNOSTIC. |
|
|
|
Term: carried pregnancy to point of viability 20 weeks of gestation (regardless of the outcome) |
Parity |
|
|
|
Term: Borne more than one child |
Multiparity |
|
|
|
Term: Delivered a child of a least 500g (or 29 weeks gestation) |
Primiparity |
|
|
|
Term: Never given birth to a viable offspring |
Nulliparous |
|
|
|
Male breast cancer is what percent |
1% |
|
|
|
What condition can increase the risk for a man to develop breast cancer? |
Klinefelters Syndrome |
|
|
|
What other condition can increase the risk for male breast cancer? |
Gynecomastia |
|
|
|
What are breast cancer risks for men? |
-Age -heredity -breast cancer gene -radiation exposure -use of hormone -Klinefleters syndrome |
|
|

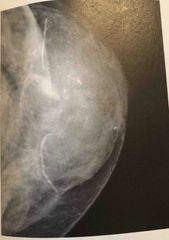
What tumor is seen in this image is a characteristic of? |
A malignant tumor |
|
|
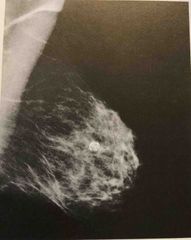
The calcifications seen in this image have the typical appearance of? |
Malignant type calcifications |
|
|
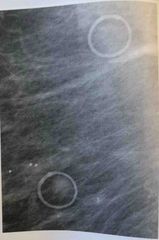
The calcifications seen in this image have the typical appearance of? |
Oil cyst Eggshell-like calcifications |
|
|
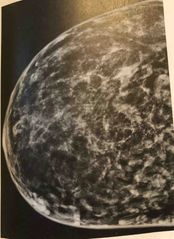
The low optical density radio plaque lesions seen here are characteristic of a? |
Skin mole |
|
|
The calcifications seen here are characteristic of |
Benign calcifications but further test are needed |
|
|
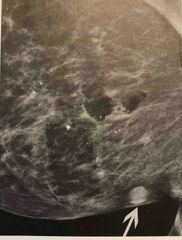
The circular mixed radio plaque/radiolucent lesions seen here are characteristics of |
Epidermoid cysts |
|
|
|
Sclerosis Adenosis or Ductal Hyperplasia |
A result of increased cellular activity in ducts and surrounding tissue. This condition can produce calcifications that tend to be linear and segmental but are sometimes malignant appearing |
|
|
|
Oil cysts |
Show up as high optical density’s tumors with lucent centers and EGGSHELL-LIKE calcifications Usually form as a result of fat necrosis or are calcifying hematoma |
|
|
|
Ductal Ectasia or PLASMA CELL MASTITIS |
Produces large calcifications Periductal calcifications will have radiolucent centers representing the non calcified centers of the duct due to calcifications are within the ducts They are linear and fragmental forming along the long axis and toward the nipple Often bilateral and symmetrical in distribution |
|
|
|
What is Ductal Carcinoma in Situ |
Cancer is confined to the duct and does not invade the duct walls |
|
|
|
The calcifications seen in this image have the typical appearance of? |
Malignant type calcifications |
|
|
|
The calcifications seen in this image have the typical appearance of? |
Oil cyst Eggshell-like calcifications |
|
|
|
The low optical density radio plaque lesions seen here are characteristic of a? |
Skin mole |
|
|
|
The calcifications seen here are characteristic of |
Benign calcifications but further test are needed |
|
|
|
The circular mixed radio plaque/radiolucent lesions seen here are characteristics of |
Epidermoid cysts |
|
|
|
Immediately behind the nipple is the pouch like office called what? |
Lactiferous sinus OR ampulla Know Both terms! |
|
|
|
What are some positive effects of Hormone Therapy? |
Prevents osteoporosis and symptoms of menopause |
|
|
|
Negative effects of Hormone Therapy |
Increased risk for breast cancer Increase risk for uterine cancer Asthma Dementia Heart attacks Stroke |
|
|
|
The process of increasing the size of the breast is termed |
Augmentation |
|
|

What tumor is seen in this image is a characteristic of? |
A malignant tumor |
|
|
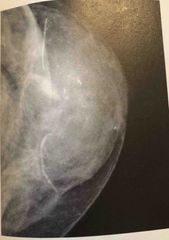
The calcifications seen in this image have the typical appearance of? |
Malignant type calcifications |
|
|
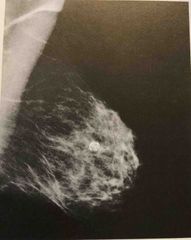
The calcifications seen in this image have the typical appearance of? |
Oil cyst Eggshell-like calcifications |
|
|
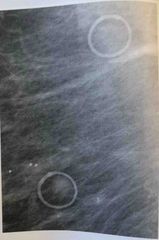
The low optical density radio plaque lesions seen here are characteristic of a? |
Skin mole |
|
|
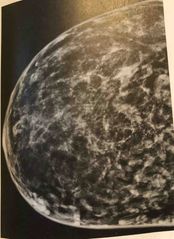
The calcifications seen here are characteristic of |
Benign calcifications but further test are needed |
|
|
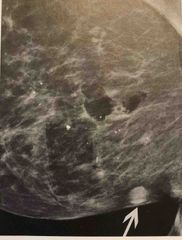
The circular mixed radio plaque/radiolucent lesions seen here are characteristics of |
Epidermoid cysts |
|
|
|
Sclerosis Adenosis or Ductal Hyperplasia |
A result of increased cellular activity in ducts and surrounding tissue. This condition can produce calcifications that tend to be linear and segmental but are sometimes malignant appearing |
|
|
|
Oil cysts |
Show up as high optical density’s tumors with lucent centers and EGGSHELL-LIKE calcifications Usually form as a result of fat necrosis or are calcifying hematoma |
|
|
|
Ductal Ectasia or PLASMA CELL MASTITIS |
Produces large calcifications Periductal calcifications will have radiolucent centers representing the non calcified centers of the duct due to calcifications are within the ducts They are linear and fragmental forming along the long axis and toward the nipple Often bilateral and symmetrical in distribution |
|
|
|
What is Ductal Carcinoma in Situ |
Cancer is confined to the duct and does not invade the duct walls |
|
|
|
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma |
Cancer spread from the ducts into the surrounding stromal tissue and may or may not extend into the pectoral fascia and muscle |
|
|
|
The calcifications seen in this image have the typical appearance of? |
Malignant type calcifications |
|
|
|
The calcifications seen in this image have the typical appearance of? |
Oil cyst Eggshell-like calcifications |
|
|
|
The low optical density radio plaque lesions seen here are characteristic of a? |
Skin mole |
|
|
|
The calcifications seen here are characteristic of |
Benign calcifications but further test are needed |
|
|
|
The circular mixed radio plaque/radiolucent lesions seen here are characteristics of |
Epidermoid cysts |
|
|
|
Immediately behind the nipple is the pouch like office called what? |
Lactiferous sinus OR ampulla Know Both terms! |
|
|
|
What are some positive effects of Hormone Therapy? |
Prevents osteoporosis and symptoms of menopause |
|
|
|
Negative effects of Hormone Therapy |
Increased risk for breast cancer Increase risk for uterine cancer Asthma Dementia Heart attacks Stroke |
|
|
|
The process of increasing the size of the breast is termed |
Augmentation |
|
|
|
Lobular Carcinoma in situ |
Often not seen mammographically Abnormal cells grow within the lobules but do not penetrate through the lobule walls |
Sometimes referred as lobular neoplasia |
|
|
Invasive Lobular carcinoma |
Hard to perceive on radiographs May have a sider web appearance or cause skin reaction |
|

