![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
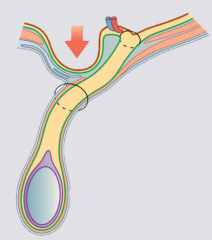
What is the inguinal canal? |
Canal through which the testes descend from the posterior abdomen to the scrotum. From deep inguinal ring to superficial inguinal ring |
|
|
What does the inguinal ring contain? |
Genitofemoral nerve Spermatic cord Round ligament Ilio-inguinal ligament |
|
|
What are the three paired structures in the scrotum? |
Testis Epididymis Spermatic cord |
|
|
Which muscle regulates the temperature of the scrotum? |
Dartos |
|
|
What is the vasculature of the scrotum? |
Anterior and posterior scrotal arteries (Ant. Is from external pudendal. Posterior is from internal pudendal) Scrotal veins |
|
|
What is the innervation of the scrotum? |
Genitofemoral nerve Anterior scrotal nerve Posterior scrotal nerve Perineal branches of posterior femoral cutaneous nerve |
|
|
What are the different layers of the scrotum? |
SOME- skin DAMN - dartos ENGLISHMAN- external spermatic fascia CALLED- cremasteris artery IT- internal spermatic fascia THE- tunica vaginalis TESTIS- tunica albuginea |
|
|
What are the three layers of the testes? |
Tunica vaginalis Tunica albuginea Tunica vasculosa- blood vessels |
|
|
What is the tunica vaginalis? |
External layer of the testis |
|
|
What is the tunica albuginea? |
Middle layer of the testis Encases and creates pouches into the seminiferous tubules |
|
|
What is the tunica vasculosa? |
The innermost layer of the testis Contains vessels and connective tissues |
|
|
From where does the spermatic cord run? |
The beginning of the inguinal canal to the testis |
|
|
What does the spermatic cord contain? |
PILLS- pampiniform plexus DON'T- ductus deferens CONTRIBUTE- cremasteric artery and vein TO- testicular artery A- autonomic nerves GOOD- genitofemoral nerve SEX- sympathetics LIFE- autonomics |
|
|
What is the pampiniform plexus and its function? |
Network of veins which is responsible for the drainage of then testes Wrap around the testicular arteries and act as heat exchanger cooling the blood before it reaches the testes |
|
|
What are the three parts of the penis? |
Root Shaft Glans |
|
|
Anal canal |
|
|
Anus |
|
|
Bulbourethral gland |
|
|
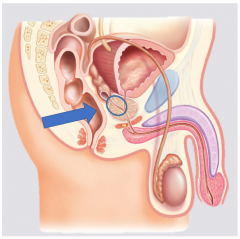
Central zone of the prostate |
|
|
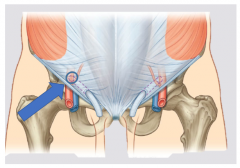
Deep inguinal ring |
|
|
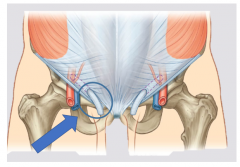
Direct hernia |
|
|
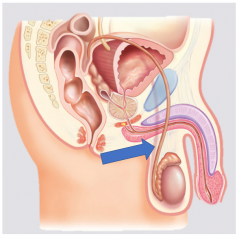
Ductus deferens |
|
|
Ejaculatory duct |
|
|
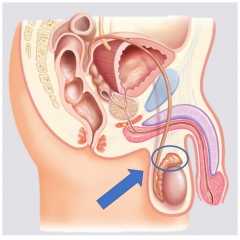
Epididymus |
|
|
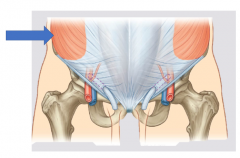
External oblique |
|
|
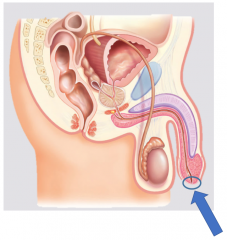
External urethral meatus |
|
|
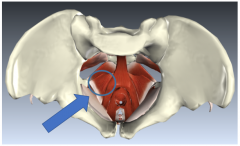
Iliococcygeus |
|
|
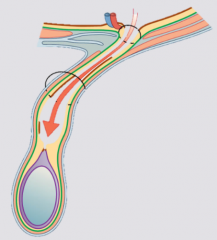
Indirect hernia |
|
|
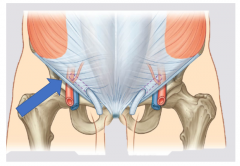
Inguinal canal |
|
|
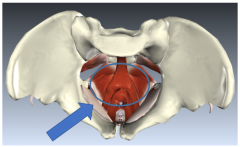
Inguinal ligament |
|
|
Levator ani |
|
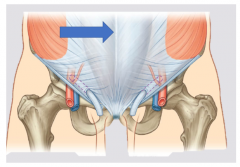
|
Linea alba |
|
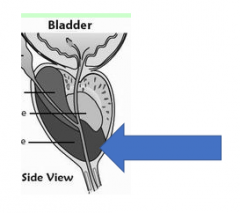
|
Peripheral zone of the prostate |
|
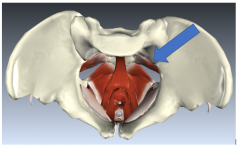
|
Piriformis |
|
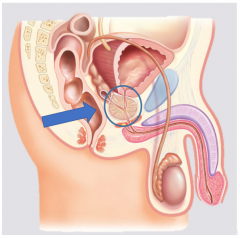
|
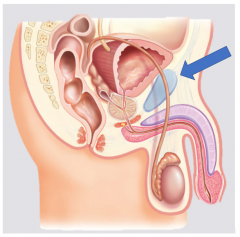
Prostate |
|
|
Pubic symphisis |
|
|
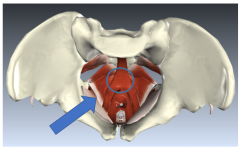
Pubococcygeus |
|
|
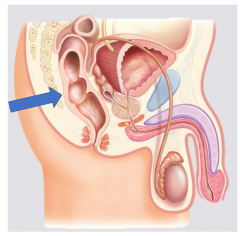
Rectum |
|
|
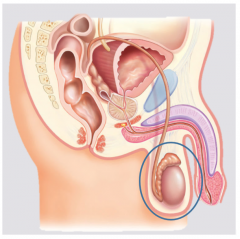
Scrotum |
|
|
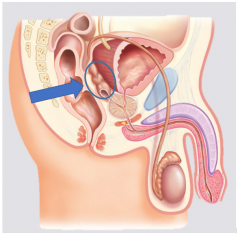
Seminal vesicle |
|
|
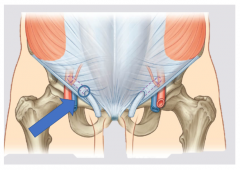
Superficial inguinal ring |
|
|
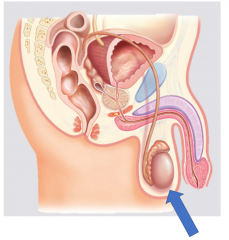
Testes |
|
|
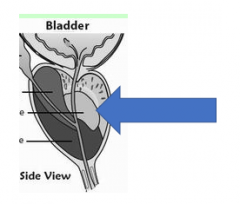
Transitional zone of the prostate |
|
|
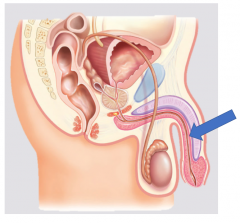
Urethra |
|
|
What are the erectile tissues of the penis? |
Root: left and right cura and the bulb of the penis Body: crura form the corpora cavernosa and bulb forms corpus spongiosum (contains urethra) |
|
|
What is the vasculature of the penis? |
From the internal pudendal artery 1) dorsal arteries 2) deep arteries 3) bulbourethral |
|
|
What is the innervation of the penis? |
S2-S4 Sympathetic- pudendal nerve Parasympathetic- prostatic nerve plexus |
|
|
What are the three zones of the prostate? |
Central zone- surrounds ejaculatory duct Transitional zone- surrounds urethra Peripheral zone- main body of the gland |
|
|
What is the pathway of sperm? |
Testes -> Epididymis -> Vas deferens -> Seminal glands -> Prostate -> Urethra -> External urethral orifice |

