![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where does sporogony occur |
Mosquitoes |
|
|
Differentiate schizogony and sporogony |
schizogony occurs in man whle sporogony occurs in mosquitoes / other insect vectors |
|
|
occurs every 36 hrs |
multiple infections |
|
|
to what cells does schizogony occur |
hepatic, RBC |
|
|
symptoms of malaria (2) |
fever and chills |
|
|
how do you diagnose malaria |
blood smear |
|
|
stain used in thick smear |
rowmanowsky stain |
|
|
if mosquitoes are the _______ host then man is the _________ host |
definitive, intermediate since sexual maturation of the parasite occurs in the mosquio: definitive |
|
|
female gametocyte |
macrogametocyte |
|
|
type of schizogony in liver cells |
primary exo-erythrocytic schizogony |
|
|
define recrudescence |
increase surviving population of erythrocytic plasmodia |
|
|
liver delayed schizogony of hypnozoites |
true relapse/ recrudescence |
|
|
what are hypnozoites ? |
dormant cells in the liver |
|
|
if the definitve host is the FEMALE anopheles mosquito then it is also the ____ vector |
biological |
|
|
what is schizogony |
asexual rep of sporozoans in the human host |
|
|
what are the factors reaponsible for te spread of malaria |
1. source (carrier) 2. anopheles vector 3. susceptible person |
|
|
other signs and symptoms |
1. anemia 2. fever 3. spleenomegaly |
|
|
when does splenomegaly occur? |
2nd week |
|
|
15-60 mins |
cold |
|
|
sweating |
2-3 hrs |
|
|
types of anemia thay can be acquired |
microcytic and normocytic |
|
|
methods of transmission (4) |
1. mosquitoes 2 transfusion 3. congenital 4. syringes ( drug addicts ) |
|
|
you would have difficult in detecting because of: |
1. blood films after anti- malarial drugs 2. apyrexial period of falciparum 3. 2-3 days of primary infection |
|
|
warning signs |
1. parasetimia-more than 10% multiple rings in rbc |
|
|
2 types of smear used |
thick and thin smear |
|
|
stain in thin smear |
giemsa |
|
|
angle in thin smear |
narrow |
|
|
angle of thick smear |
wide |
|
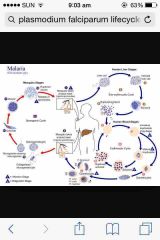
sabta daw bi list everything you know bout this drawing |
Paper |
|
|
type of malaria in malariae |
Quarten |
|
|
type of malaria in falciparum |
subterian, tropical , pernicious malaria |
|
|
type of malaria in vivax |
benign |
|
|
geographic distribution of: 1. falciparum 2. vivax 3. malariae 4. ovale |
1. tropical and sub tropical regions 2. temperate zones 3. widespread: RARE 4. lowest incidence and is the TMRAREST |
|
|
type of dots found bet the 3'r malaria groups |
1. schaudin's dots 2. maurer 3. ziemann |
|
|
life span of the 4 |
0.5-1, 1-3, over 20 yrs, 1-3 years |
|
|
stippling shape of falciparum |
star |
|
|
stippling shape of vivax |
round |
|
|
stippling color or malariae |
pink |
|
|
name and color of flxiparum stipplings |
violet/ red, maurer's dots |
|
|
collection time for lab diagnosis of malaria |
peak of fever |
|
|
factors for contributing difficulty in detecting the disease |
1. anti-malarial drugs 2. apyrexial period of falciparum malaria 3. collected 2-3 days in cases o primary infection |
|
|
vector for trophozoite induced malaria |
mechanical ( transfusion, communal sharps, congenital) |
|
|
differentiate incubation period of sporozoite induced and trophozoite induced |
sporozoite- long ; troph - short |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE : relapses may not occur in trophozoite induced malaria |
true |
|
|
effect of schizogontocidal drugs on sporozoite induced malaria |
no radical cure |
|
|
differentiate thick and thin smears, give at least (5) differences |
1. narrow: thin; wide : thick 2. giemsa: thick; wright: bulky thick stains |
|
|
give the 3 possible stains for diagnosis of malaria |
1. wright 2. giemsa 3. romanowsky |
|
|
Moist cool conditions |
12 days |
|
|
Mode o transmission of histolytica (6) |
1. injestion 2. polluted water 3. droppings of cockroaches and flies 4. human excreta in eggie gardens 5. std 6. asylums and mental hospitals |
|
|
diseases produced of: vivax, ovale, malariae, falciparum |
1. benign tertian malaria 2. ovale 3. quartan malaria 4. subtertian malaria |
|
|
diseases produced of: vivax, ovale, malariae, falciparum |
1. benign tertian malaria 2. ovale 3. quartan malaria 4. subtertian malaria |
|
|
common in temperate zones, common in tropical regions |
vivax, temperate: falciparum, tropical |
|
|
diseases produced of: vivax, ovale, malariae, falciparum |
1. benign tertian malaria 2. ovale 3. quartan malaria 4. subtertian malaria |
|
|
common in temperate zones, common in tropical regions |
vivax, temperate: falciparum, tropical |
|
|
rarest type of malaria |
vivax |
|
|
diseases produced of: vivax, ovale, malariae, falciparum |
1. benign tertian malaria 2. ovale 3. quartan malaria 4. subtertian malaria |
|
|
common in temperate zones, common in tropical regions |
vivax, temperate: falciparum, tropical |
|
|
rarest type of malaria |
vivax |
|
|
used to study relationship of parasite to the invaded RBC |
thin film |
|
|
diseases produced of: vivax, ovale, malariae, falciparum |
1. benign tertian malaria 2. ovale 3. quartan malaria 4. subtertian malaria |
|
|
common in temperate zones, common in tropical regions |
vivax, temperate: falciparum, tropical |
|
|
rarest type of malaria |
vivax |
|
|
used to study relationship of parasite to the invaded RBC |
thin film |
|
|
RBCS are hemolyzed |
thick smears |
|
|
diseases produced of: vivax, ovale, malariae, falciparum |
1. benign tertian malaria 2. ovale 3. quartan malaria 4. subtertian malaria |
|
|
pale blue cytoplasm; chromatin mass in the center |
microgametocyte |
|
|
deep blue cytoplasm chromatin mass periphery |
macrogametocyte |
|
|
best place to examine on a slide |
Near tail |
|
|
ample time for thick smear |
4-5 minutes |
|
|
angle for thin smear |
45 degree |
|
|
angle for thick smear |
none L.O.L |
|
|
stain for thin and thick |
wright and giemsa |
|
|
more sensitive and diagnostic type of smear |
thick smear |
|
|
200 leukocytes, 10 or more what do you do? |
record no. of parasites |
|
|
200 leukocytes, 9 or less |
continue till 500 leukocytes then record no. of parasites |
|
|
common in temperate zones, common in tropical regions |
vivax, temperate: falciparum, tropical |
|
|
formula for computation |
(no. of parasites * 8000/ no of leukocytes) / no. of leukocytes |
|
|
% RBC INFECTED formula |
[no of infected/ total no. of rbc ]* 100 |
|
|
Histidine rich protein II is specific for what parasites? |
plasmodium falciparum |
|
|
minimum requirement of RBC in thin smears |
500 |
|
|
distinguish between falciparum and non- falciparum |
plasmodium LDH |
|
|
combined detection of HRP II with an undetermined "panmalarial antigen" |
DiamedOptiMal IT |
|
|
rarest type of malaria |
vivax |
|
|
used to study relationship of parasite to the invaded RBC |
thin film |
|
|
RBCS are hemolyzed |
thick smears |
|
|
appearance of rbc in vivax ovale malariae and falciparum |
vivax enlarged and ovale, not that much enlarged. malariae and falciparum are normal |
|
|
type of rbs ingested by vivax, ovale, malariae and falciparum |
vivax and ovale- young rbc malariae- mature falciparum- everything |
|
|
no secondary exoerythro schizogony thus no re lapse |
falciparum and malariae |
|
|
duration of exoerythrocyticschizpgony for falciparum, vivax, ovale and malariae |
36-48= falciparum 48- vivax, ovale 72- malariae |
|
|
no. of merozoites of the ff: vivax, ovale, malariae, falciparum |
1. 16 2. 8 3. 8 4. 16 |

