![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Financial Institutions & Markets |
-Finance and money -Physical capital and financial capital |
|
|
Finance |
Activity of providing the funds that finance expenditures on capital. |
|
|
Money |
What we use to pay for goods and services and factors of production to make financial transactions. |
|
|
Financial Capital |
The funds that firms use to buy physical capital. |
|
|
Gross Investment |
The total amount spent on new capital. |
|
|
Gross Investment |
The total amount spent on new capital. |
|
|
Net Investment |
The change in the value of capital. |
|
|
Wealth |
The value of all the things that people own. |
|
|
Saving |
The amount of income that is not paid in taxes or spent on consumption goods and services. |
|
|
Saving |
The amount of income that is not paid in taxes or spent on consumption goods and services. |
|
|
Wealth & Saving |
Wealth increases wen the market value of assets rises (called capital gains) and decreases when the market value of assets falls (called capital losses). |
|
|
Mortgage |
A legal contract that gives ownership of a home to the lender in the event that the borrower fails to meet the agreed loan payments (repayments and interest). |
|
|
Bond |
A promise to make specified payments on specified dates. |
|
|
Bond Market |
Bonds issued by firms and governments are traded in this market. |
|
|
Mortgage-Backed Security |
Entitles the holder to the income from a package of mortgages. |
|
|
Stock |
Certificate of ownership and claim to the firm's profits. |
|
|
Stock |
Certificate of ownership and claim to the firm's profits. |
|
|
Stock Market |
Financial market in which shares of stocks of corporations are traded. |
|
|
Financial Institution |
A firm that operates on both sides of the markets for financial capital. |
|
|
Canadian Financial Institutions |
-Commercial banks -Trust and loan companies -Credit unions and caisses populaires -Pension funds -Insurance companies |
|
|
Net Worth |
The market value of what a financial institution has lent minus the market value of whah it has borrowed. |
|
|
Illiquid |
A firm is illiquid if it has made long-term loans with borrowed funds and is faced with a sudden demand to repay more of what it has borrowed than its available cash. |
|
|
Insolvent |
If net worth is negative, the institution is insolvent and must go out of business. |
|
|
Financial Assets |
Stocks, bonds, short-term securities and loans. |
|
|
Interest Rate |
On a financial asset the interest rate received is expressed as a percentage of the price of the asset. If the asset price rises, the interest raw falls. If the asset or falls, the interest rate rises. |
|
|
Loanable Funds Market |
The aggregate of all the individual financial markets. |
|
|
Net Taxes |
Taxes pad to the governments minus the cash transfers received from governments. |
|
|
Investment is Funded By: |
-Household saving -Government budget surplus -Borrowing from the rest of the world |
|
|
I=S+(T-G)+(M-X) |
Investment is financed by household saving, S, the government budget surplus, (T-G), and borrowing from the rest of the world, (X-M). |
|
|
National Saving |
The sum of private saving (S) and government saving (T-G). |
|
|
Nominal Interest Rate |
Number of dollars that a borrower pays and a lender receives in interest in a year expressed as a percentage of the number of dollars borrowed and lent. |
|
|
Real Interest Rate |
Nominal interest rate adjusted to remove the effects of inflation on the buying power of money. |
|
|
Financial Flows |
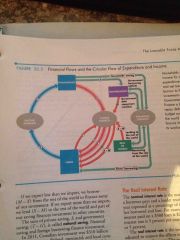
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Quantity of Loanable Funds Demanded |

The total quantity of funds demanded to finance investment, the government budget deficit, and international investment or lending during a given period. |
|
|
Investment is determined by: |
-The real interest rate -Expected profit |
|
|
Demand for Loanable Fundsl |
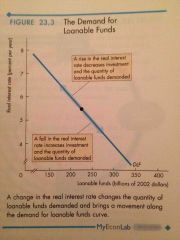
Relationship between the quantity of Loanable funds demanded and the real interest rate, when all other influences on borrowing plans remain the same. |
|
|
Quantity of Loanable Funds Demanded |

The total quantity of funds demanded to finance investment, the government budget deficit, and international investment or lending during a given period. |
|
|
Default Risk |
Risk that a loan will not be repaid. |
|
|
Demand for Loanable Fundsl |
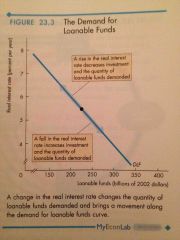
Relationship between the quantity of Loanable funds demanded and the real interest rate, when all other influences on borrowing plans remain the same. |
|
|
Increase in Demand |
If profits that firms expect to earn increase, they increase their planned investment and increase their demand for loanable funds to finance that investment. |
|
|
Increase in Supply |
If one of the influences on saving plans changes and increases saving, the supply of loanable funds increases. |
|
|
Long Run Growth of Demand & Supply |
Both demand and supply fluctuate in the long run and they tend to increase over time, at a similar pace. |
|
|
Supply of Loanable Funds |
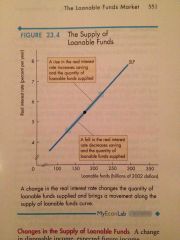
Relationship between the quantity of loanable funds supplied and the real interest rate when all other influences on lending plans remain the same. |
|
|
Demand for Loanable Fundsl |
Relationship between the quantity of Loanable funds demanded and the real interest rate, when all other influences on borrowing plans remain the same. |
|
|
Changes in Demand for Loanable Funds |
The greater the expected profit from new capital, the greater is the amount of investment an the heater the demand for Loanable funds. |
|
|
Quantity of Loanable Funds Supplied |
Total funds available from private saving, the government budget surplus, and international borrowing during a given period. |
|
|
Decision to save/spend is influenced by: |
-The real interest rate -Disposable income -Expected future income -Wealth -Default risk |
|
|
Equilibrium in the Loanable Funds Market |
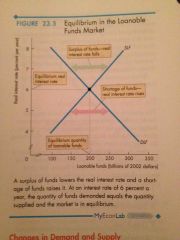
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Increase in Demand |
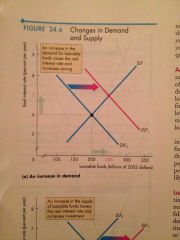
If profits that firms expect to earn increase, they increase their planned investment and increase their demand for loanable funds to finance that investment. |
|
|
Expected Future Income |
The higher the future expected income, the smaller is its savings today. |
|
|
Wealth |
The higher the wealth, the smaller is the household's saving. |
|
|
Government Budget Surplus |
Increases the supply of loanable funds. The real interest rate falls, which decreases household saving and decreases the quantity of private funds supplied. |
|
|
Government Budget Deficit |
Increases the demand for loanable funds. Real interest rate rises, increases household saving and increases the quantity of private funds supplied. |
|
|
Crowding-Out Effect |
Is the tendency for a government budget defect to raise the real interest rate and decrease investment. |
|
|
International Capital Mobility |
Because lenders are free to seek the highest real interest rate and borrowers are free to seek the lowest real interest rate, the loanable funds market is a single, integrated, global market. |
|
|
International Borrowing & Lending |
A country's loanable funds market connects with the global market through net exports. -Negative and the world supplied funds to them -Positive and the ou try is a supplier of funds to the rest of the world |
|
|
Demand & Supply in the Global & National Markets |
Determined the world equilibrium real interest rate. |
|
|
Global Market |
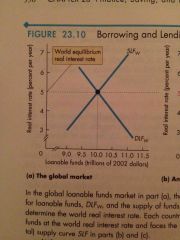
Back (Definition) |
|
|
International Lender |
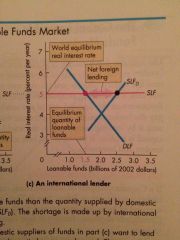
|
|
|
International Borrower |
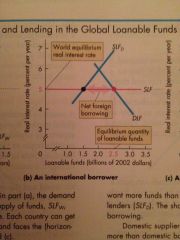
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Changes in Demand & Supply |
Change in the demand or supply in the global loanable funds market changes the real interest rate in the way shown. The effect of the change depends on the size of the country. |

