![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Front (Term) Money |
Back (Definition) Any commodity or token that is generally acceptable as a means of payment. |
|
|
Front (Term) Money serves 3 functions: |
Back (Definition) -Medium of exchange -Unit of account -Store of value |
|
|
Front (Term) Medium of Exchange |
Back (Definition) Any object that is generally accepted in exchange for goods and services. |
|
|
Unit of Account |
An agreed measure for stating the prices of goods and services. |
|
|
Store of Value |
It can be held and exchanged later for goods and services. |
|
|
Money consists of: |
-Currency -Deposits at banks and other depository institutes |
|
|
Currency |
The notes and coins held by individuals and businesses. |
|
|
Deposits |
Also counted as money because the owners of the deposits can use them to make payments. |
|
|
Measures of Money |
M1: Currency held by individuals and businesses plus chequable deposits owned by individuals and businesses M2: Consists of M1 and all other deposits. |
|
|
M1 & M2 |
M1: Is money as chequable deposits and currency are a means of payment. M2: Is money as they can be easily converted into a means of payment. |
|
|
What is money? |
-Deposits are money but cheques are not -Credit cards are not money |
|
|
Depository Institute |
Private firm that takes deposits from households and firms and makes loans to other households and firms. -Chartered banks, credit unions & causes populaires, trust and mortgage loan company |
|
|
Chartered Bank |
Private firm to receive deposits and make loans. |
|
|
Chartered Bank |
Private firm to receive deposits and make loans. |
|
|
Credit Unions & Caisses Populaires |
Cooperative organization that receives deposits from and makes loans to its members. |
|
|
Trust & Mortgage Loan Companies |
Privately owned depository that receives deposits, makes loans and acts as a trustee for pension funds and estates. |
|
|
Trust & Mortgage Loan Companies |
Privately owned depository that receives deposits, makes loans and acts as a trustee for pension funds and estates. |
|
|
What depository institutions do: |
-Cheque clearing -Account management -Credit cards -Internet banking -Most is from depositors used to make loans and buy securities to earn higher interest rate than that paid to depositors |
|
|
Reserves |
Notes & coins in a depository's vaults or its account at the Bank of Canada. |
|
|
Reserves |
Notes & coins in a depository's vaults or its account at the Bank of Canada. |
|
|
Liquid Assets |
Government of Canada treasury bills and commercial bills. |
|
|
Reserves |
Notes & coins in a depository's vaults or its account at the Bank of Canada. |
|
|
Liquid Assets |
Government of Canada treasury bills and commercial bills. |
|
|
Securities |
Government of Canada bonds and other bonds such as mortgage-backed securities. |
|
|
Reserves |
Notes & coins in a depository's vaults or its account at the Bank of Canada. |
|
|
Liquid Assets |
Government of Canada treasury bills and commercial bills. |
|
|
Securities |
Government of Canada bonds and other bonds such as mortgage-backed securities. |
|
|
Loans |
Commitments of funds for an agreed-upon period of time. |
|
|
Depository Institutions: |
-Create liquidity -Pool risk -Lower cost of borrowing -Lower cost of monitoring borrowers |
|
|
Bank of Canada |
Canada's central bank that is: -The banker to banks and government -Lender of last resort -Sole issuer of bank notes |
|
|
BOC Assets & Liabilties |
Asset: -Government securities -Loans to depository institutes Liabilities: -Bank of Canada notes -Depository institution deposits |
|
|
Open Market Operation |
BOC conducts and open market operation, which is the purchase or sale of government securities by the BOC in the open market. |
|
|
Limiting Factors in Quantity of Loans |
-Monetary base -Desired reserves -Currency drain ratio |
|
|
Monetary Base |
Size of the base limits the total quantity of money a banking system can create. |
|
|
Desired Reserves Ratio |
Reserves a bank plans to hold. Ratio of reserves to deposits the bank plans to hold. |
|
|
Currency Drain Ratio |
Leakage of bank reserves into currency. The ratio of currency to deposits. |
|
|
Excess Reserves |
Bank's actual reserves exceed its desired reserves, causing an excess. |
|
|
Money Multiplier |
Ratio of the change in the quantity of money to the change in monetary base. |
|
|
Influences on Money Holding |
-The price level -The nominal interest rate -Real GDP -Financial innovation |
|
|
Demand for Money |
Relationship between the quantity of real money demanded and the nominal interest rate when all other influences on the amount people wish to hold remain the same. |
|
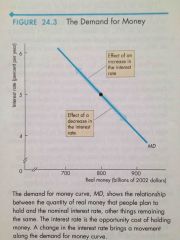
Front (Term) Demand for Money |
Back (Definition) Interest Rate: -Increase-Up along curve -Decrease-Down along curve |
|
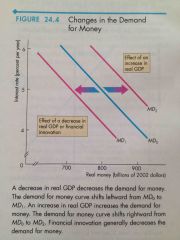
Front (Term) Changes in Money Demanded |
Back (Definition) -Increase-Shift right -Decrease-Shift left |
|
|
Short Run & Change in Money Supply |
If there is a surplus of money and people hold more than quantity demanded they enter loan able funds market and buy bonds. If it decreases they sell bonds. |
|
|
Long-Run Equilibrium |
The price level will rise by the same percentage as the rise in the quantity of money. |
|
|
Quantity Theory of Money |
Proposition that in the long-run, an increase in the quantity of money brings an equal percentage increase in the price level. |
|
|
Quantity Theory of Money |
Proposition that in the long-run, an increase in the quantity of money brings an equal percentage increase in the price level. |
|
|
Velocity of Circulation |
Average number of times a dollar of money is used annually to buy the goods and services that make up GDP. |
|
|
Inflation Rate |
=Money Growth Rate - Real GDP Growth Rate |

