![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What composes the Ventral Striatum?
|
Nucleus Accumbens
|
|
|
What composes the striatum?
|
Caudate nucleus
Putamen |
|
|
What composes the Lentiform Nucleus?
|
Putamen
Globus Pallidus |
|
|
What composes the Corpus striatum?
|
Caudate nucleus
Putamen Globus Pallidus |
|
|
What arteries supply the corpus striatum?
|
Medial and Lateral Striate Arteries
|
|
|
What arteries supply the subthalamus?
|
Posteromedial arteries
|
|
|
What arteries supply the substantia nigra?
|
Posteromedial arteries
Posterolateral arteries Anterior Choroidal arteries |
|
|
In the motor system, basal ganglia, what is the dopaminergic center?
|
Substantia Nigra
|
|
|
In the limbic system, basal ganglia, what is the dopaminergic center?
|
Ventral Tegmental center
|
|
|
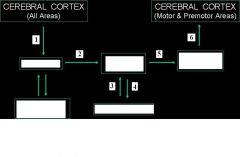
Describe the projections of the motor system pathway.
|
Substantia Nigra
to Striatum to Globus Pallidus to Dorsal Thalamus to Motor/Premotor Cortex |
|
|
Describe the projections of the limbic system pathway.
|
Ventral Tegmental Area
to Ventral Striatum to Dorsal Thalamus to Frontal, Limbic Cortex |
|
|
What causes Parkinsonism?
|
Depletion of dopamine
from Substantia Nigra to Striatum |
|
|
What causes Schizophrenia?
|
Increase in dopamine
from Ventral Tegmental Nucleus to Ventral Striatum OR Decrease in Dopamine from Ventral Tegmental Nucleus to Frontal, Limbic Cortex |
|
|
What are the basal ganglia components of the motor system?
|
Caudate nucleus
Putamen Globus Pallidus |
|
|
What are the basal ganglia components of the limbic system?
|
Nucleus Accumbens
Amygdala |
|
|
What are the functions of the motor system?
|
Planning, Facilitation, Initiation, and Suppresion of Movement
|
|
|
What are the functions of the limbic system?
|
Mood, motivation, and behavior
|
|
|
All areas of the cerebral cortex project to where?
|
Striatum
|
|
|
In subcortical areas of the motor pathway what are the components of the two feedback circuits?
|
1. Striatum and Substantia Nigra
2. Subthalamus and Globus Pallidus |
|
|
What is the connection between the substantia nigra and the striatum called?
|
Nigrostriatal
|
|
|
What is the connection between the Raphe nucleus and the striatum called?
|
Raphestriatal
|
|
|
The lateral globus pallidus projects where?
|
To subthalamus
|
|
|
The medial globus pallidus projects where?
|
To Dorsal Thalamus
|
|
|
The subthalamus will project to where?
|
Medial globus pallidus
|
|
|
Corticostriatal neurons:
- NT - excitatory or inhibitory? |
Glutamate
Always excitatory |
|
|
Describe the neuron connection of the DIRECT pathway from the striatum to the dorsal thalamus.
- NT - excitatory or inhibitory. |
1. Striatum to Medial Globus Pallidus via GABA (inhibitory) neurons.
2. Medial Globus Pallidus to Dorsal Thalamus via GABA (inhibitory) neurons |
|
|
Describe the neuron connection of the INDIRECT pathway from the striatum to the dorsal thalamus.
- NT - excitatory or inhibitory. |
1. Striatum to Lateral Globus Pallidus via GABA (inhibitory) neurons.
2. Lateral Globus Pallidus to Subthalamus via GABA (inhibitory) neurons 3. Subthalamus to Medial Globus Pallidus via Glutaminergic (excitatory) neurons. 4. Medial Globus Pallidus to Dorsal Thalamus (VA/VL) via GABA (inhibitory) neurons. |
|
|
Dopaminergic neurons come from where and project into where?
|
From Substantia Nigra
to Striatum's direct and indirect pathway |
|
|
Are dopaminergic neurons excitatory or inhibitory?
|
Excitatory to the direct pathway
Inhibitory to the indirect pathway |
|
|
What type of NT does interneurons in the basal ganglia use?
|
Acetylcholine, thus cholinergic receptors
|
|
|
Neurons from the Raphe nucleus to the striatum use what NT?
|
Serotonin
|
|
|
Describe the basal ganglia pathway to LMN.
|
There is none
|
|
|
Basal ganglia connect to the cerebral cortex on which side?
|
ipsilaterally
|
|
|
During movement, describe the feedback circuits of basal ganglia neurons.
|
Fire continually
|
|
|
Describe the basal ganglia neuron activity in feedforward circuits.
|
Fire prior to UMN
|
|
|
Suppression of movement is mediated by what components of the basal ganglia?
|
Striatum
Subthalamus |
|
|
Facilitation of movement is mediated by what components of the basal ganglia?
|
Striatum
Substantia Nigra (dopamine) |
|
|
Describe the input from the areas of the cerebral cortex to the striatum.
- NT - involves what? |
Glutaminergic (excitatory)
Planning and initiation of movement |
|
|
Describe the output from the dorsal thalamus to the motor cortex.
- NT - involves what? |
Glutaminergic (excitatory)
Movement (changes threshold of UMN) |
|
|
Describe the output from the medial globus pallidus to the dorsal thalamus.
- NT - involves what? |
GABA (inhibitory)
Inhibits movement, but tonically active 20% of neurons decrease activity to allow movement 80% of neurons increase activity to inhibit competing movements |
|
|
Describe the interneurons of the striatum.
- NT - involves what |
Acetylcholine
Modulate and suppress dopamine activity |
|
|
Describe the Striatal output pathway.
- NTs - Involves what? |
Direct Pathway
- GABA and Substance P - Facilitates movement Indirect Pathway - GABA and Enkephalin - Suppresses movement |
|
|
Describe the activity of the Substantia Nigra
- NT - Involves what? |
Dopamine
Excites direct pathway of striatum Inhibits indirect pathway of striatum |
|
|
List the similarities between Basal Ganglia circuits and the Cerebellar circuits.
|
1. Both have NO direct connections with LMN
2. Both receive fibers from Widespread areas of Cortex 3. Both converge on Motor Cortex (frontal lobe) via Dorsal thalamus 4. Both function as Feedforward systems 5. Both function as Feeback systems 6. Both work in concert to control same UMN 7. GABA inhibition is prevalent in both. |
|
Who is the most handsome man?
|

Young S. Noh
Hell yeah!!!! |

