![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
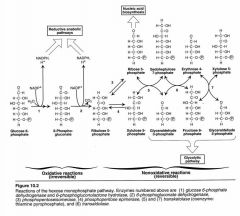
What is the purpose of PPP? X 3.
|
1.) Produce NADPH for pathways
2.) Produce NADPH for glutathione (GSH) regeneration 3.) Produce pentoses for nucleic acid synthesis |
|
|
What does glucose become in the PPP and what enzyme is used?
|
Glucose 6 Phosphate with the help of hexokinase/glucokinase.
|
|
|
When are NADPH's made?
|
1.) When converting G6P to 6-Phosphogluconolactone.
2.) When converting 6-Phosphogluconate to Ribulose 5 Phosphate |
|
|
NADPH is a competitive inhibitor of what?
|
Glucose 6 Phosphate Dehydrogenase
|
|
|
When is CO2 made?
|
When converting from 6-Phosphogluconate to Ribulose 5 Phosphate
|
|
|
1.) G6PDH
2.) 6 Phosphogluconate DH 3.) Isomerase 4.) Epimerase 5.) Transketolase 6.) Transaldolase 7.) Transketolase |
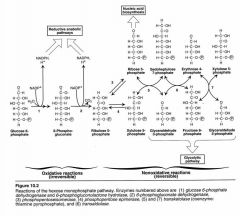
Enzymes
|
|
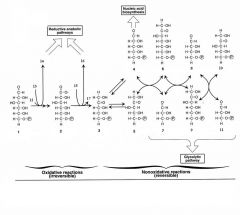
N2K
|
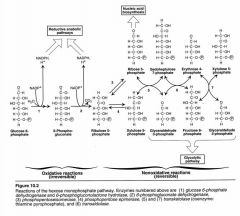
Answers
|
|
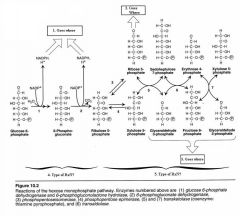
Questions
|
Answers
|
|
|
Structure of glutathione
|
1.) Glycine
2.) Cysteine 3.) Glutamate |
|
|
In erythrocytes, NADPH is generated only by?
|
G6PDH
|
|
|
How does glutathione peroxidase help with detox?
|
Glutathione peroxidase will react with reduced glutathione (GSH) to convert hydrogen peroxide to water.
|
|
|
How is NADPH involved in the detox reaction?
|
NADPH will reduce the oxidized GS-SG into reduced GSH for the reaction to occur again.
|
|
|
G6PDH has as a side effect, a resistance to what disease?
|
Malaria (P. Falciparum)
|
|
|
What is the purpose of microsomal cyt P-450?
|
To hydroxylate non-polar drugs or xenobiotics to better excrete them.
|
|
|
How does NADPH help microsomal cyt P-450 monooxygenase?
|
NADPH will reduce cyt P-450 reductase which will activate it to reduce cyt P-450 which will activate it to hydroxylate non polar drugs.
|
|
|
Locations of carbohydrate metabolism.
|
1.) Salivary alpha amylase in mouth.
2.) Pancreatic alpha amylase in small intestine. 3.) Final digestion occurs in jejunem where mucosal cell membrane-bound enzymes work. |
|
|
What stops salivary amylase from continuing to break down carbohydrates?
|
The strong acidity of the stomach.
|
|
|
What is lactate deficiency?
|
The inability to cleave a disaccharide such as lactose.
|
|
|
What is the result with lactate deficiency?
|
Lactate will be used by the intestinal bacteria creating CO2, 2 carbon metabolite, 3 carbon metabolite, and H2.
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of lactate deficiency?
|
Bloating, diarrhea, and dehydration.
|
|
|
What does NAD+ accept, from what, and what does it use it for?
|
Accepts electron pair from oxidized intermediates for ENERGY PRODUCTION (catabolism)
|
|
|
What does NADP+ accept, from what, and what does it use it for?
|
Accepts electron pair from oxidized intermediates for BIOSYNTHESIS (anabolism)
|
|
|
What does transketolase require?
|
Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
|
|
|
When you lack transketolase activity, what diseases manifest? X 2
|
Beri - Beri (thiamine deficiency)
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome |

