![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Give examples of nucleotides that are components of
a) intracellular communication b) intercellular communication |
a) intracellular: cellular messengers like cAMP, which is involved in activation o glycogenolysis
b) intercellular: ATP released by certain nerve terminalsthat act on postsynaptic receptors |
|
|
There are 2 types of pathways leading to nucleotide biosynthesis. What are they?
|
1. De novo synthesis. Need Ribose 5-phosphate, certain amino acids, CO2, NH3
2. Salvage pathways. Nucleosides and free bases are "recycled". |
|
|
What are the four ingredients needed for De novo nucleotide biosynthesis?
|
i. Ribose 5-phosphate
ii. certain amino acids iii. CO2 (directly in the form of bicarbonate) iv. NH3 (technically ammonium released from glutamine) |
|
|
In the De novo synthesis of purines, the first reaction yields....
|
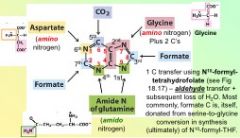
N #9 . It is the Amide N of glutamine.
|
|
|
In De novo synthesis of purines, the second reaction yields...
|
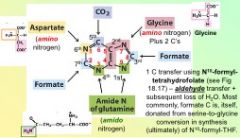
glycine (amino nitrogen plus 2 carbons)
|
|
|
In De novo synthesis of purines, the third reaction yields...
|
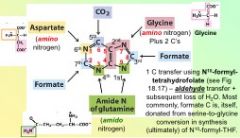
a carbon from Formate. 1 C transfer using N10-formyl-tetrahydrofolate.
|
|
|
In De novo synthesis of purines, the fourth reaction yields...
|
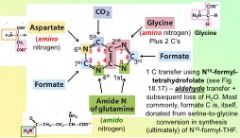
N #3 is another amide from glutamine
|
|
|
In De novo synthesis of purines, the fifth reaction yields...
|
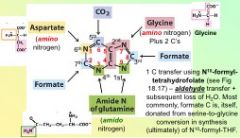
a carbon from bicarbonate
|
|
|
In De novo synthesis of purines, the sixth reaction yields...
|
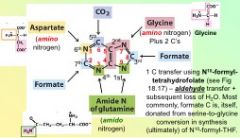
an amino nitrogen from aspartate
|
|
|
In De novo synthesis of purines, the seventh reaction yields...
|
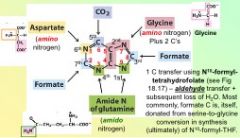
a carbon from formate
|
|
|
_______ is a substrate which plays a role in de novo biosynthesis in both purines and pyrimidines.
|
PRPP
5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate |
|
|
How do we make 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP)? (What is the equation that yields it?)
|
Ribose 5-Pi + ATP -> 5-PRPP + AMP Enzyme: Ribose phosphate pyrophosphokinase (highly allosterically regulated)
|
|
|
PRPP is derived from Ribose 5-Pi + ATP. Where does the Ribose 5-Pi come from?
|
Oxidation of Glucose-6-phosphate in the pentose phosphate pathway, which is highly active in cells that need to make antioxidants, cells that are involved in making a lot of fat and in cells that are involved in hyperplastic growth.
|
|
|
PRPP is made from....
|
Ribose 5-phosphate which is made from Glucose 6-phosphate.
|
|
|
What is the committed step in purine de novo synthesis?
|
The 1st step when the amide from glutamine becomes the N #9. Once we've made 5-Phospho-beta-D-ribosylamine.
|
|
|
PRPP -- (first 1step committed rxn) --> 5-phospho-beta-D-ribosylamine ----(many rxns)---> _________ -----> adenylate (AMP) or guanylate (GMP)
|
inosinate
note: that AMP synthesis requires GTP and GMP synthesis requires ATP |
|
|
In purine de novo synthesis, from the insoniate internediate, AMP sysnthesis requires ______ and GMP synthesis requires ______.
|
AMP synthesis requires GTP ; GMP synthesis requires ATP.
|
|
|
The conversion of GMP and AMP to triphosphates to be used in biosynthesis is carried out by...
|
1) base-specific nucleoside monophosphate kinases (ex. AMP -> ADP)
2) Ubiquitous nucleside diphosphate kinase (ex. ADP -> ATP) mono to di is A BASE SPECIFIC kinase while di to tri is a ubiquitous one!! |
|
|
What is purine's nucleotide synthesis control mechanisms?
|
There are three mentioned. First level: feedback inhibition of the first committed step (PRPP to 5-phosphoribosyylamine) by AMP, GMP, IMP. Second level: short feedback loops of AMP regulating AMP, GMP regulating GMP. Third level: "balancing" b/c to make AMP need GTP and to make GMP need ATP.
|
|
|
The de novo biosynthesis of pyrimidines differs from that of the purines in that...
|
the base is created initially and then it is attached to PRPP later whereas in purine de novo biosynthesis starts upon the substrate PRPP. With pyrimidines, the formation of carbamoyl phosphate is first.
|
|
|
The formation of _________ is the FIRST STEP in de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis. What is the reaction that yields this first step?
|
Formation of carbamoyl phosphate.
Glu + CO2 + ATP -----> carbamoyl phosphate |

