![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Amino Acids provide metabolic energy of ____ kcal / g.
|
4 kcal/g
|
|
|
|
The general structure of an amino acid is the charged "zwitterion" form. Describe that structure.
|
Alpha carbon with an amino group, a carboxyl, R group and H.
|
|
|
|
The structure of a general amino acid is called... and looks like...
|
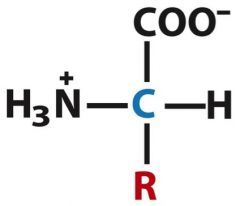
zwitterion
|
|
|
|
Naturally occurring amino acids are almost exclusively [what stereoisomer]?
|
L-stereoisomer
|
|
|
|
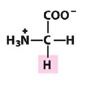
Gly
Glycine |
Nonpolar, alipathic R group
|
|
|
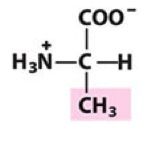
Ala
Alanine |
Nonpolar, alipathic R group
|
|
|
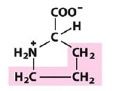
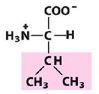
Pro
Proline |
Nonpolar, alipathic R group
|
|
|
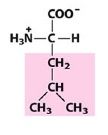
Val
Valine |
Nonpolar, alipathic R group
|
|
|
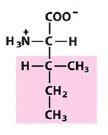
Leu
Leucine |
Nonpolar, alipathic R group
|
|
|
Ile
Isoleucine |
Nonpolar, alipathic R group
|
|
|
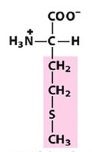
Met
Methionine |
Nonpolar, alipathic R group
|
|
|
___ amino acids have an α-amino group; _____ is the exception with an α-imino group.
|
19 ; proline is the only one with an α-imino group.
|
|
|
|
Which amino acid is actually an imino acid?
|
Proline - it is the only one that is an imino acid because it has a secondary imine in its structure.
|
|
|
|
Which amino acid has an isopropyl group attached to the α-carbon?
|
Valine
|
|
|
|
Starting with Leucine, how do you get to isoleucine, structurally?
|
Moving a methyl group form the gamma position to the beta position produces isoleucine.
|
|
|
|
Which is the only Nonpolar, alipathic R group with sulfur?
|
Met
Methionine |
|
|
|
List all the nonpolar, alipathic R groups.
|
Glycine, Alanine, Proline, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine.
|
|
|
|
List all the polar, alipathic R groups.
|
Serine, Threonine, Cysteine, Asparagine, Glutamine.
|
|
|
|
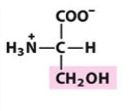
___ is like Alanine with a hydroxyl group at the beta-carbon.
|
Ser
Serine |
|
|
|
Ser
Serine |
Polar, uncharged R group
|
|
|
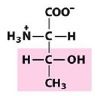
Thr
Threonine |
Polar, uncharged R group
|
|
|
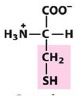
Cys
Cystine |
Polar, uncharged R group
|
|
|
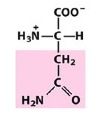
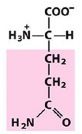
Asn
Asparagine |
Polar, uncharged R group
|
|
|
Gln
Glutamine |
Polar, uncharged R group
|
|
|
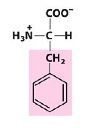
Phe
F Phenylalanine |
Aromatic R Groups
|
|
|
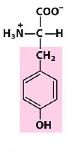
Tyr
Tyrosine |
Aromatic R group
|
|
|
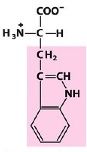
Trp
Tryptophan |
Aromatic R Group
|
|
|
A hydroxylated phenylalanine yields which amino acid?
|
Tyr
Tyrosine |
|
|
|
Which amino acid serves as a precursor to serotonin in the brain?
|
Trp
Tryptophan |
|
|
|
When the enzyme that hydroxylates phenylalanine to tyrosine is not present and a buildup of phenylalanine happens, what illness can occur?
|
Phenylketonuria
|
|
|
|
What two amino acids are used to detect and measure proteins?
|
Trp, Tyr @ 280nm
Tryptophan , Tyrosine |
|
|
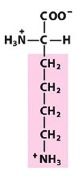
|
Lys
Lysine |
Positively charged R group
(basic) |
|
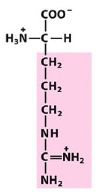
|
Arg
Arginine |
Positively charged R group
(basic) |
|
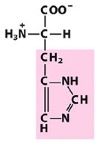
|
His
Histidine |
Positively charged R group
(generally basic but can be weakly acidic depending on the environment) |
|
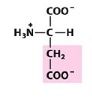
|
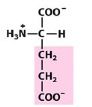
Asp
Aspartate |
Negatively charged R group
(acidic) |
|
|
Glu
Glutamate |
Negatively charged R group
(acidic) |
|
|
______ is a dimer of cysteine with a _________ linkage between the two monomers.
|
Cystine ; disulfide
|
|
|
|
List the amino acids that are essential (must be provided by diet).
|
PVT TIM HALL
Phe, Val, Thr, Trp, Ile, Met, His, Arg, Lys, Leu |
|
|
|
Name the amino acids that contain sulfur.
|
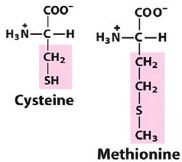
|
|
|
|
True or False: There are some amino acids that occur in proteins but which are not included in the genetic code.
|
True. These are synthesized by post-translational modification of precursor amino acids already incorporated into the proteins. Examples are...
[press "h" on your keyboard for the third side] |
1. Hydroxyproline - Found in collagen. Formation requires vitamin C. [Vitamin C deficiency causes scurvy, a disease of connective tissue.]
2. γ-Carboxyglutamate - Formation requires vitamin K. Occurs in blood-clotting protein, prothrombin. [The anticoagulant drug, Coumadin (Dicoumarol) is a vitamin K antagonist.] 3. Selenocysteine - Plays a role in proteins involved in antioxidative mechanisms. [Selenium is an essential micronutrient but toxic in higher concentrations.] |
|
|
Amino acids are incorporated into proteins by forming _____ bonds with each other.
|
Peptide bond , via a dehydration reaction.
|
|
|
|
Amino acid residues joined together are considered a protein if...
|
its molecular weight (MW) is greater than or equal to 10,000.
|
|
|
|
A peptide is named from which terminus to which terminus?
|
Amino terminus to carboxyl terminus.
|
|
|
|
True or False: Peptide bonds characteristically have a trans configuration that has a double bond character.
|
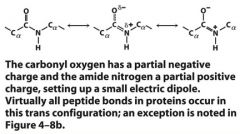
|
Due to resonance forms, the peptide bond has a signif degree of double bond character. This prevents rotation around the C-N bond, resulting in a rigid, planar structure. With a few important exceptions, peptide bonds are formed in the trans config.
|
|
|
Which amino acids are considered basic due to the basic side chains?
(Carries positive charge at neutral pH.) |
His, Lys, Arg
Histidine, Lysine, Arginine |
|

