![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Difference between Acid and Base |
Answer: Acids donate protons (H⁺ ions) in a solution, while bases accept protons or donate hydroxide ions (OH⁻). |
|
|
Explain the concept of electronegativity. |
Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a covalent bond. It generally increases across a period and decreases down a group in the periodic table. |
|
|
Define the terms exothermic and endothermic reactions. |
Exothermic reactions release heat to the surroundings, resulting in a temperature increase. Endothermic reactions absorb heat from the surroundings, causing a temperature decrease. |
|
|
Explain the concept of hybridization in the context of molecular orbitals. |
Hybridization is the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals suitable for electron pairing in covalent bonds. For example, in methane (CH₄), carbon |
|
|
Define the term "equilibrium constant" (K) and explain how it relates to chemical reactions. |
The equilibrium constant (K) expresses the ratio of product concentrations to reactant concentrations at equilibrium in a chemical reaction. It provides insights into the extent of the reaction and the position of the equilibrium. |
|
|
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, and how is it used in acid-base chemistry? |
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is pH = pKa + log([A⁻]/[HA]), where [A⁻] is the concentration of the base, [HA] is the concentration of the acid, and pKa is the acid dissociation constant. It's commonly used to calculate the pH of a buffer solution. |
|
|
Oxygen in phosphate |
Oxygen (O) in the phosphate ion (PO₄²⁻) has a valence shell configuration of 2s²2p⁴. It typically forms two single bonds with phosphorus and two double bonds with the other oxygen atoms in the phosphate ion. Therefore, each oxygen atom in the phosphate ion has a total of two lone pairs and two shared pairs of electrons. |
|
|
P in phosphate |
In the phosphate ion (PO₄²⁻), phosphorus (P) is in the +5 oxidation state. Since it belongs to Group 15 of the periodic table, it typically forms three single bonds and a lone pair in the phosphate ion. Thus, in the phosphate ion, phosphorus has a valence shell configuration of 3s²3p³, with one lone pair and three shared pairs of electrons. |
|
|
Lactam |
Lactam: cyclic amide used in pharmaceuticals and polymer chemistry. |
|
|
Penicillin |
Penicillin is a group of antibiotics derived from Penicillium fungi. It's used to treat bacterial infections by inhibiting the growth of bacteria or killing them outright. Penicillin was the first antibiotic discovered and has saved countless lives since its introduction. |
|
|
Likerts scale |
5point response measurement.Strongly disagree- Strongly agree 5point response measurement.Strongly disagree- Strongly agree |
|
|
Aerotolerant organism |
Continue to use anaerobic means even in the presence of oxygen. No issues in the presence if oxygen |
|
|
Differences seen between siblings, what meiosis event accounts more? |
Independent assortment explain why the offspring may not resemble the parent. But it's crossing over and it's ability to generate unique combination that owe to the Uniqueness seen in siblings. |
|
|
Does Dna repair occurs in meiosis, when and how |
DNA repair is indeed an important aspect of meiosis, particularly during Prophase I. Homologous recombination, also known as crossing over, not only promotes genetic diversity but also serves as a mechanism for DNA repair. When homologous chromosomes pair up during Prophase I, any damaged sections of DNA on one chromosome can potentially be repaired using the corresponding undamaged sequence from the homologous chromosome. This process helps to ensure the integrity of the genetic material passed on to the next generation. DNA repair during meiosis is crucial for producing healthy gametes and maintaining the genetic health of offspring. |
|
|
Urey Miller experiment |
The Urey-Miller experiment simulated early Earth conditions, producing amino acids—the building blocks of proteins—by subjecting a mixture of gases to electrical discharges, suggesting that life's building blocks could arise spontaneously. |
|
|
What's the mechanical difference that prevents two, once same organism from mating and reproducing. |
Any physiological conditions that make two speciated animals unable to mate is a mechanical difference. |
|
|
What's the mechanical difference that prevents two, once same organism from mating and reproducing. |
Any physiological conditions that make two speciated animals unable to mate is a mechanical difference. |
|
|
What's lamrckian Fallacy |
The Lamarckian fallacy is the mistaken idea that acquired traits can be inherited, which contradicts modern genetics and evolutionary theory. |
|
|
What does Capsase's bench and tool of action |
It has Cysteine rich active site, that target Aspartate residues imof cytoplasmic protein. |
|
|
Autocrine signaling: |
Autocrine signaling: A type of cell signaling in which a cell secretes signaling molecules that bind to receptors on its own surface, leading to a response within the same cell. |
|
|
Disk diffusion test |
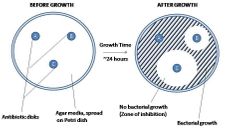
The disk diffusion test, also known as the Kirby-Bauer test, is a laboratory technique used to determine the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics. In this test, paper disks containing specific antibiotics are placed on an agar plate inoculated with the bacteria of interest. The antibiotics diffuse into the agar, creating concentration gradients. If the bacteria are susceptible to the antibiotic, a zone of inhibition will form around the disk where bacterial growth is inhibited. The size of this zone helps determine the effectiveness of the antibiotic against the bacteria. |
|
|
Targeting RBC by Tcells |
anucleate cells, like RBCs, lack MHC-1 proteins! cant be targeted by Cytotoxic CD8+ cells! |
|
|
Mnemonic for bio experiments |
* For bio experiments: **SNOWDROP**(S)outhern Blot ------- (D)NA (N)orthern Blot ------- (R)NA (O) ------ (O) (W)estern Blot -------- (P)roteinsAnd I guess the only one you manually need to know is Eastern Blot ---- Post-Translational Modifications although I've never come across a question about that.* Have No Fear Of Ice CoLd BeeR - for diatomic molecules* pH > pKa -> deprotonation | pKa > pH -> protonation | I always remember because H comes before K in the alphabet, and deprotonation comes before protonation* Red Cat!! An Ox!! Oxidation always happens at anode no matter what kind of cell; ditto with reduction happening at a cathode. Good luck everyone! |
|
|
Electrolytic cell and galvanic cell |
Youtube |
|
|
Electrolytic cell and galvanic cell |
Youtube |
|
|
does Betahydroxybutyralated histone does to gene expression |
Increases it by binding to Lysine and neutralizing the charge that decrease histone -DNA interaction |
|
|
Both muscles and liver has glycogen, which one releases more glucose to blood through glycogenolysis |
Liver Muscle don't have g6phosphatase |
|
|
Where is metal in the period table. Nonmetal. Metalloid? |
Middle and left. Right corner. Diagonal border. |
|
|
List four halogens, in downward order |
F Cl Br I At |
|
|
Names of Oxygen group |
O S Se Te Po |
|
|
Alkali metals |
H Li Na K Rb Cs Fr |
|
|
Alkaline earth metals |
Be Mg Ca Sr Ba Ra |
|
|
Nobel gases |
He Ne Ar Kr Xe Rn |
|
|
How are metal |
Atoms in sea of electronsEasily lose electrons and form positive ionsFluid valence shell.Easily slide past each other.So ductile,malleable, conductivity etc Atoms in sea of electronsEasily lose electrons and form positive ionsFluid valence shell.Easily slide past each other.So ductile,malleable, conductivity etc Atoms in sea of electronsEasily lose electrons and form positive ionsFluid valence shell.Easily slide past each other.So ductile,malleable, conductivity etc Atoms in sea of electronsEasily lose electrons and form positive ionsFluid valence shell.Easily slide past each other.So ductile,malleable, conductivity etc Atoms in sea of electronsEasily lose electrons and form positive ionsFluid valence shell.Easily slide past each other.So ductile,malleable, conductivity etc |
|
|
Is molecule and ionic compound different? |
Yes, molecules and ionic compounds are different. - A molecule is a group of atoms bonded together, either of the same element (like oxygen gas, O2) or different elements (like water, H2O). - An ionic compound is formed when ions of opposite charges attract each other and form a crystal lattice structure, such as sodium chloride (NaCl). |
|
|
nonmetal only form molecules? |
Nonmetals are commonly present in molecules due to their tendency to form covalent bonds with each other. However, nonmetals can also participate in ionic bonding with metals to form compounds such as salts. So, while nonmetals often form molecules, they can also be part of ionic compounds. |
|
|
What has low melting point , nonmetal or metal |
Nonmetal |
|
|
What are representative elements |
Section A: 1,2 ,13 to 18 Aka main group elements Section B : transition metals. |
|
|
What kind of an ion an element form? |
Representative element make ions by forming the closest noble gas.Therefore metals form cations and nonmetal anions Representative element make ions by forming the closest noble gas.Therefore metals form cations and nonmetal anions |
|
|
What ion does group11(Cu,Ag,Au) makes? And what are 5 3+ ions How about the rest |
1+ *(Cu+1/+2) 3+ => Fe,Au,Cr,Al,Bi. Rest all are 2+. |
|
|
What do elements in the same groups have in common |
Valence electrons- therefore, similar chemical properties. Same number of bonds , similar charged ions. |
|
|
Predictions of group 1, 2, 16 ,17 18,( mcat wants you to make this predictions) |
Walk through periodic table 1 : alkali metals, low density, low melting point. Easily form 1+ cation. Highly reactive. (explosive/exothermic with water to form hydroxide and Hydrogen gas. form ionic compounds with nonmetal(Nacl).reacts with hydrogen to form hydrides. Occurs only in compounds Note: unique H . Nonmetal Can form covalent bond, also ionic (hydride). Doesn't share characteristics. 2 : Alkaline earth metals. Harder,denser. Melt at higher than alkali metals. Forms 2+ cations . Mg2+. Less reactive than alkali( highest energy electron complete S shell). 14: forms 4 covalent bonds with nonmetals. All beyond 2nd period can form two additional bonds using d orbital. Only carbon forms strong π bonds to make strong double and even triple bonds. 15 : 3 covalent bonds. All beyond 2 period: two additional. Nitrogen can form 4th covalent bond by donating its lone pair of electrons to form a bond. Forms strong Pi bonds to make double and triple bond. Phosphorous can only form weak pi bonds to make double bonds. Other in 15, doesn't make double bonds. Group 16 is also called Chalcogen. Rest you find out.
|

