![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
127 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
difference between lymphoma and leukemia
|
- lymphoma : proliferation of cells residine lymphoid tissue
leukemia : proliferation in BM / blood connection : CLL : can have features of both |
|
|
lymphoma
classification |
hodgkin lymphoma
non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
tetra B |
-B-cell
-Bi-modal (3rd - 7th decade) -Barr -virus (EBV) association -B symptomes are usual presentation |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
type of cells |
B cells
|
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
age |
bi-modal
3rd decade 7th decade |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
association |
EBV
|
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
usual presentation |
1-B symptomes
2-pruritis 3-asymptomatic enlarged LN 4-LN in chest radio |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
B symptomes |
-fever
-wt loss -night sweat |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
Lymph nodes charachteristics location / most |
- painless
-rubbery -neck / mediastinal |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
Lymph nodes progression |
starts at one location
then : progress to adjacent groups |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
Lymph nodes when they became painful |
drinking alcohol
rare presentation |
|
|
LN in mediastinam of young pt ddx
|
Hodgkin lymphoma ( most often)
then non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
Lymph nodes / mediastinal common presentation |
- chest pain
- cough - dyspnea - superior vena cava synd |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
lab findings |
WBC : elevated
lymphopenia thrombocytosis ESR : elevated |
|
|
hodgkin lymphoma
Dx |
1-biopsy LN
2-staging |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
LN biopsy charchteristics |
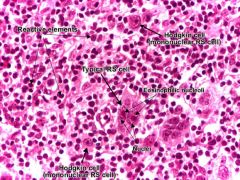
Reed-Sternberg cell
surrounded by dense inflammatory infiltrate |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
Reed-Sternberg cells other name |
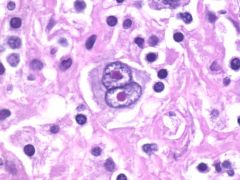
Giant "Owl's eye" cells
|
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
sub types of it |
1
|
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
most common sub type |
nodular sclerpsis
|
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
2nd most sub type |
nodular cellularity
|
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
rare varian (not classic) |
lymphocyte predominant
|
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
staging |
1-CT scan ((chest / abdomen // pelvis))
2-PET may help 3-Bone marrow in some cases |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
indication for bone marrow in staging |
1-B symptoms
2-cytopenia 3-advanced disease |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
prognosis |
majority are ((curable))
|
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
adverse prognostic factors |
-age > 45 yo
-male gender -stage 4 diseas -large mediastinal LN -abnormal CBC -WBC > 15,000 -lymphopenia -anemia -albumin < 4 g/dl |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
ttt |
stage 1+2 : chemo + radio
stage 3+4 : chemo +/- radio if bulky |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
stage 1 + 2 ttt |
chemo
followed by radio |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
stage 3+4 ttt |
full-course chemo
+/- radio if bulky disease |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
mainstay management |
chemo NOT radio
|
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
regimen |
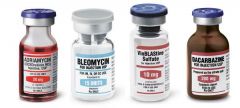
ABVD
|
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
ABVD regimen |

A : anthracyclin ( doxorubicin )
B : bleomycin V : vinblastin D : dacarbazine |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
num of cycles |
6-8 cycle
|
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
ttt complications |
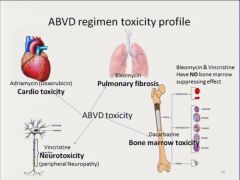
1-pulmonary toxicity / bleomycin
2-late cardiomyo : anthracyclin 3-radiation complications |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
bleomycin : pulm.toxicity |
-usually during ttt
-may asymptomatic -may present as : cough / fever // dyspnea // infiltrate |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
anthracyclin complic : |
late cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
radiation coplications |
1-risk of solid tuomors later
-breast -lung -thyroid 2-cardiac complic : atherosclerosis // constrictive + resstrictive + valve dis 3-hypothyroidism : follow |
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
ABVD complication (overall) |
increased risk of:
1- meylodysplasia 2-acute leukemia |
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
how to assess remission |
follow up scans
|
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
ttt if relapse 1st choice |
autologus stem cell trans
|
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma
staging |
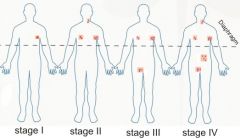
1 : one node / one extralymphatic site
2 : >1 , one side of diphragm 3 : both sides of diaphragm 4 : disseminated extralymphatics |
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
11
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
11
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
most common form |
diffuse large B cell
|
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
2nd most common |
follicular lymphoma
|
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
age |
incidence increased by age
|
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
classification |
1-low-grade ((indolent ))
2-high grade ((aggressive)) |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
indolent types |
follicular
marginal zone // MALToma CLL/SLL most skin lymphomas |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
aggressive forms |
follicular grade 3B
diffuse large B cell mediastinal large B cell periphral T-cell Mantle cell Burkitt ((((((highly aggressive))))) acute lymphoblastic lymphoma / leukemia ((((((highly aggressive))))) |
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
risk factors |
1-altered immunity
2-HIV 3-Organ trans 4-autoimmune 5-congenital immundeficiency 6-EBV // african burkitt // AIDS related 7-HTLV-1 (virus) - T-cell leukemia/lymphoma 8-hepatitis C = low grade 9-H.pylori = MALToma 10-pesticide exposure |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
and HIV |
aggressive B cell lymphoma is HIV-defining illness
|
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
EBV |
african burkitt
HIV associated |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
HTLV-1 |
Human T-lymphotropic virus 1
T-cell lymphoma / leukemia |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
hepatitis C |
low-grade B
|
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
MALToma association |
H.pylori
ttt by H.Pylori eradication radiation as 2nd line |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
presentation low-grade ((follicular)) |
LN may wax and wane for yrs
usually incidental findings |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
presentation high-grade ((diffuse large B cell)) |
firm , enlarging LN
Widespread LN +/- B symptoms |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
presentation very high grade (((burkitt / lymphoblastic)) |
usually as rapidly growing large mass
or widspread disease + markedly elevated LDH |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
DX |
1-biopsy
2-staging 3-looking for a cuase / HIV |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
staging |
1-CT (( chest / abdo// pelvis))
2-may PET 3-BM biopsy |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
spread |
hematogenous
|
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
prognosis and staging |
poorly related to stage bcz of hematogenous spread
|
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
bad prognostic in aggressive types |
- older 60
- high LDH -stage 3-4 disease - more than one extranodal site -poor performance status - low-CD4 count in AIDS related |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
ttt |
- incurable but treatable
- many options : 1-watchful waiting 2-chemotharapy 3-radio 4-rituximab |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
benefit of early aggressive ttt in asymptomatic |
NO benefit
|
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
low grade transformation |
can be to high grade
if happen treat as high grade |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
low-grade follicular survival ttt |
8-10 yrs
radiation may cure limited disease most are disseminated 40 % transform to high grade |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
high grade cure ?? |
potentially curative
|
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
high grade ttt |
chemotherapy
+/- radio |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
high grade regimens |
CHOP
rituximab- CHOP ((if B cell) |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
high grade CHOP |
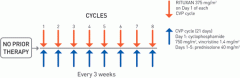
C : cyclophosphamide-alkylating agent
H : Hydroxydaunorubicin ( doxorubicin or Adriamycin) O : Oncovin (vincristine) P : prednisolon |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
high grade main complication during ttt |
tumor lysis
|
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
high grade CNS |
leptomeningeal infiltrate rather than mass
Dx : LP ttt : intrathecal chemo +/- radio |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
CNS disease risk factors |
1-HIV
2- extranodal dis / BM/sinuses/testicles 3-High LDH 4-Burkitt / lymphoblastic |
|
|
non-Hodgkin lymphoma
high grade ttt of relapse |
autol.stem cell
|
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia prevelance |
most common leukemia in US
|
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia age |
65 yo
|
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia gender |
male predominance
|
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell type |
B CELLS origine
|
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia main cause of death |
infection
|
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia manifistation |
maixed Leukemia / lymphoma\
1-asymptomatic 2-lymphocytosis : 25 % , up to 100,000 may asymptomatic 3-lymohadenopathy 4-spleenomegaly 5-anemia 6-thrombocytpenia 7-B symptoms 8-hypogammaglobulinemia 9-autoimmune / anemia/plt |
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia main cause of increased risk of infection |
hypogammaglobulinemia
|
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia diagnosis |
1-CBC
2-Bone marrow 3-staging / LN/Spleen /liver |
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia CBC findings |
lymphocytosis : at least 5ooo circulating B cells
|
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia blood film |
small mature lymphocytes
smudge cells |
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia BM |
lymphocytosis
commonly > 30 % |
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia staging |
low
intermediate high |
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia low |
stage 0
............................. lymphocytosis only (blood / BM) |
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia intermediate |
stage 1+2
....................................... lymphocytosis + LN lymphocytosis + liver/or/spleen |
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia high |
stage 3+4
............................... lymphocytosis + anemia (<11) lymphocytosis + plt < 100,000 |
|
|
what is SLL
|
Small lymphocytic lymphoma
....................................................... same disease as CLL but more lymphadenopathy than leukemia |
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia prognosis |
incurable
median survival ( 4-20 yrs) |
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia adverse features |
1-rapid lymphocyte doubling time
2-advanced stage at diagnosis 3-cytogenetics : 11 + 17 deletion .....bad 13 deletion ..........good 4-immunoglobulin gene muatation (IgVH mutation .......bad) |
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia Richter syndrome |
transformation of CLL to aggressive lymphoma
|
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia Richter syndrome % |
5 %
|
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia Richter syndrome prognosis |
diffucult to ttt
|
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia Richter syndrome when to suspect |
1-worsening B symptoms
2-rapid growth in one or more LN |
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia |
- observe if early or asymptomatic
-ttt if indication -IVIG if frequent infection |
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia indication for ttt |
1-bulky LN / Spleen / liver
2-B symptoms 3-BM failure / anemia / low plt 4-autoimmune failing therapy (anemia / low plt) 5-rapidly progressive or richter transf |
|
|
CLL
chronic lymphocytic leukemia medication used |
-- fludarabine
--rituximab // almetuzomab --chlorambucil --cyclophosphamide bendamutin |
|
|
Hairy cell leukemia
what |
rare B-cell leukemia
|
|
|
Hairy cell leukemia
median age |
55 yo
|
|
|
Hairy cell leukemia
gender |
male predominance
|
|
|
Hairy cell leukemia
course |
indolrnt but progressive
|
|
|
Hairy cell leukemia
manifistation |
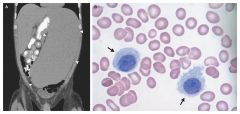
--- pancytopenia
---massive spleenomegaly ---dry tap |
|
|
Hairy cell leukemia
charectaristic feature |

dry tap despite hypercellular marrow
|
|
|
Hairy cell leukemia
Dx |
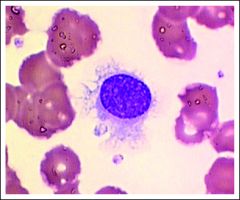
-peripheral smear : small - medium lymphocytes
with hairy projections |
|
|
Hairy cell leukemia
ttt |
--purine analouges :
1-Cladribine 2- pentostatin --results in complete remmission |
|
|
Mnemonic to some it all up:
I like to think of hairy cells as trapped in their own world. They are TRAP stain positive. They are trapped in the red pulp. They are trapped in the bone marrow and that’s why you get a dry tap. They trapped everywhere else, therefore, they don’t show up in the lymph nodes and that’s why the clinical finding of lymphadenopathy is absent. |
1
|

