![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the structures in the lower genital tract?
|
Vulva
Vagina Cervix |
|
|
What are the pathologic conditions that can affect the vulva?
|
Lichen sclerosus
Squamous carcinoma |
|
|
What's the most common malignancy of the vagina?
|
Metastatic carcinoma
Extension of carcinoma from the uterus or the vulva. |
|
|
What's the cause of SCC in the vulva in younger patients? Older?
|
Younger: HPV
Older Not HPV |
|
|
What is leukoplakia?
|
White plaques
|
|
|
What are the vulvar dermatoses?
|
Lichen sclerosus
Squamous hyperplasia |
|
|
What are the atypical lesions of the vulva?
|
VIN1
VIN 2-3 Paget's disease |
|
|
What's another name for lichen sclerosis?
|
Atrophic vulvitis
|
|
|
Who gets lichen sclerosis?
|
Postmenopausal women
|
|
|
What are the complications from Lichen sclerosis?
|
Atrophy
Fibrosis Scarring Associated with SCC |
|
|
WHat happens to the skin in LIchen sclerosis?
|
Thinning of the epidermis: parchment!
|
|
|
What's the cause of lichen sclerosis?
|
AI
|
|
|
What's the triad in Lichen sclerosus?
|
Epidermal thinning
Collagenized upper dermis Lichenoid lymphocytic imfiltrate |
|
|
What are the findings in lichen simplex chronicus?
|
Acanthosis
Hyperkeratosis |
|
|
What is the presentation of extramammary pagets?
|
Puritic, red, crust, sharply demarcated area on the labia majora
|
|
|
Who gets extramammary pagets?
|
Elderly women
|
|
|
What's the treatmnet for extramammary pagets?
|
Wide local excision
|
|
|
What is a congenital vaginal neoplasm?
|
Sarcoma botryoides
Grape-cluster appearance |
|
|
Who gets clear cell adenocarcinoma?
|
People who have an exposure to intrauterine DBS
|
|
|
Where is clear cell adenocarcinoma found?
|
Vagina
Cervix |
|
|
What HPV is associated with SCC of the vagina?
|
HPV16
|
|
|
Who gets infected wtih HPV?
|
Young, sexually active women
|
|
|
What is the structure of the HPV virus?
|
Non-enveloped
dsDNA virus |
|
|
What are the oncogenic HPV viruses?1
|
16
18 |
|
|
What are the non-oncogenic HPV strains?
|
6
11 |
|
|
What kind of cervical carcinoma is associated with HPV 18?
|
Endocervical adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
What kind of cervical carcinoma is associated with HPV 16?
|
SCC
|
|
|
What conditions are associated with HPV 6 and 11?
|
External genital warts
|
|
|
What is required for the development of cervical cancer?
|
HPV infection
|
|
|
What are risk factors for the development of cervical cancer?
|
Smoking
# of sexual partners Age of first intercourse Immune compromised |
|
|
What is the natural history of an HPV infection?
|
Great majority are cleared: 80%
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of the clearance of HPV?
|
Cell-mediated immune response is developed
Development of TYPE SPECIFIC antibodies (if you have Abs against 16, 18 can still get you!) |
|
|
How long does it take to progress from a wart to a carcinoma in situ with HPV?
|
10 years
|
|
|
How long does it take to progress from CIS to carcinoma in HPV?
|
10 years
|
|
|
What are the low grade HPV infections?
|
INfection
Condyloma Mild dysplasia Grade 1 neoplasia |
|
|
What are the high grade HPV infections?
|
Modreate dysplasia
Severe dysplasia |
|
|
What's the characteristic histological feature of a condylomata?
|
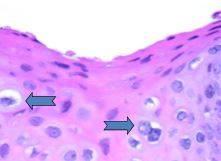
Koilocyte:
Nuclear enlargement with halo around it |
|
|
Why are young women more susceptible to HPV?
|
Virus needs to get to the basal layer to cause cancer.
In young women, the transformation zone (where there's a short distance to the basal layer) is wider, where a lot of damage and repair occurs |
|
|
What is the transformation zone?
|
Place where there's squamo-columnar junctions
This expands at puberty from the os, then goes back at menopause. |
|
|
Why is there such a cycle of damage and repair at the transormation zone in women going through puberty?
|
1. Increased estradiol
2. Increased glycogen storage 3. Increased bacteria 4. More acidic pH 5. Columnar cells can't take the pH, so they transform to squamous This happens every cycle: it's easy for HPV to get to the basal cell layer, where it wants to get to. |
|
|
How does HPV cause problems in the cell?
|
Integrates its own DNA into the host, which then can cause problems with cell cycle regulation
|
|
|
What genes in HPV are responsible for causing dysplasi?
|
E6
E7 |
|
|
What is the action of the gene E6 from HPV?
|
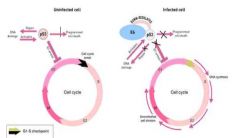
Transformation
Targets the degradation of the p53 tumor suppressor |
|
|
What is the action of the gene E7 from HPV?
|
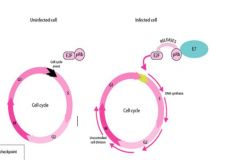
Transformation
Binds to the RB protein, a tumor promotor |
|
|
What makes something CIN3?
|
If there's full thickness dysplasia
|

