![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
What condition might lead to peeing on your shoes?
|
Hypospadia
(abnormal opening of the urethra along the ventral aspect of penis |
|
|
What conditions are commonly associated with Cryptorchidism (undescended testicles)?
|
Epispadias Hypospadias Sterility and testicular cancer
|
|
|
What condition is an abnormal lesion on the dorsal surface of the penis?
|
Epispadia
|
|
|
What is an inflammation of glans penis, which can be generalized, localized, viral induced, fungal infection, bacteria, or INFECTION?
|
Balanitis
|
|
|
What is an inflammation of the glans penis and prepuce (foreskin)?
|
Balanoposthitis
(this does not occur in circumcised men) |
|
|
What is the inability to easily retract the prepuce over the glans penis that can lead to inflammation and infection and is treated with circumcision?
|
Phimosis
|
|
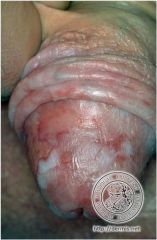
What is this dysplasia that runs throughout all of the layers of the squamous surface covering, presents as a grayish white solitary, plaque-like lesion of the shaft due to increased keritosis and acanthosis (analogous to leukoplakia in the oral cavity) and may progress to SCC?
|
Bowen Disease
|
|
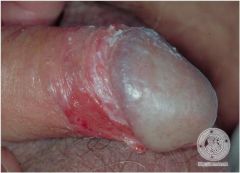
What neoplasm presents as erythematous patches on the glans penis (analogous to erythroplakia in the mouth) More Likely To Become Invasive than Bowen's Disease?
|
Erythroplasia of Queyrat
|
|
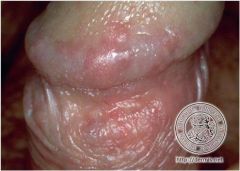
What presents as little lumps/bumps that develop, reddish brown papules, HPV lesions of the shaft
|
Bowenoid Papulosis
|
|
|
What type is the most common type of carcinoma of the penis?
|
SCC of the glans or Prepuce
-accounts for 0.25% of cancers in men -pts are most often uncircumsized w/poor hygiene & HPV 16&18+ -treated by penectomy |
|
|
What is a rare condition where there is no formation of the scrotum, so the testicles do not descend?
|
Agenesis of the Scrotum
|
|
|
*What is an accumilation of SEROUS fluid within the tunica vaginalis causing scrotal enlargement?
|
Hydrocele
|
|
|
*What is an accumilation of BLOOD within the tunica vaginalis causing scrotal enlargement?
|
Hematocele
|
|
|
*What is an accumilation of LYMPH fluid within the tunica vaginalis causing scrotal enlargement?
|
Chylocele
|
|
|
*What is swelling of the spermatic cord veins causing scrotal enlargement?
|
Varicocele
|
|
|
*What is the dilated efferent ductile of epididymus causing scrotal enlargement?
|
Spermatocele
|
|
|
*What is the risk of testicular cancer in patients who have Cryptorchidism?
|
4x more likely to develop testicular cancer
|
|
|
When should the testicals descend in a normal male?
|
one year old
|
|
|
What type of testicular inflammation is caused by UTI, STD: Chlamydia, Gonorrhea; System: Tuberculosis?
|
Epididymitis
|
|
|
What type of Testicular Inflammation is caused by UTI, mumps, tuberculosis, Mumps?
|
Orchitis
|
|
|
What type of neoplasms account 95% of testicular neoplasms?
|
Malignant neoplasms
|
|
|
What age ranges are testicular cancers most prevalent?
|
Malignant Seminoma
|
|
|
What testicular cancer always makes hCG?
|
Choriocarcinoma
(note: a man with stage III choriocarcinoma is unlikely to survive) |
|
|
T/F
Spermatocytic seminomas are the same thing as seminomas. |
False they have nothing to do with seminomas
|
|
|
What are three of the most frequent malignant testicular neoplasms?
|
1) Seminoma
2) Embryonal carcinoma 3) Choricarcinoma |
|
|
What is stage I of testicular neoplasms?
|
Primary tumor confined to the testes
|
|
|
What is stage II of testicular neoplasms?
|
Metastasis confined to retroperitoneal nodes below level of diaphragm
|
|
|
What is stage III of testicular neoplasms?
|
Metastasis beyond retroperitoneal lymph nodes
|
|
|
What does the prognosis of testicular neoplasms depend upon?
|
The stage and Histologic type
i.e. stage II and Non-seminoma |
|
|
T/F
There is a very high chance for cure of seminomas. |
True
|
|
|
What type of testicular neoplasm has the worse prognosis?
|
Stage III Non-seminoma
|
|
|
What is the general prognosis for testicular cancer?
|
Very good (96% survival rate)
|
|
|
What are two different Tumor markers secreted by Germ-cell Neoplasms?
|
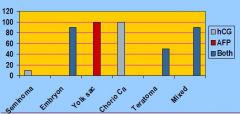
hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin)
AFP (Alpha-fetoprotein) |
|
|
Only 10% of Seminomas make any markers. If you are going to find anything it will be ______.
|
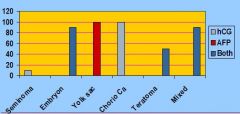
hCG
|
|
|
What protein serves as a marker in liver cancer and testicular cancer?
|
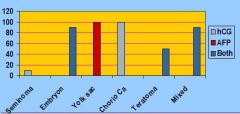
AFP (Alpha-fetoprotein)
|
|
|
Which tumors ALWAYs make AFP?
|
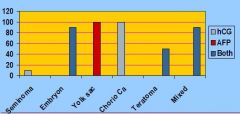
Yolk Sac Tumors
|
|
|
Which tumors ALWAYs make hCG?
|
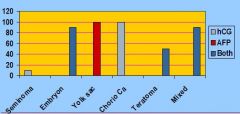
Choriocarcinomas
|
|
|
T/F
Seminomas may have a good prognosis and an intermediate prognosis, but never have a poor prognosis. |
True
HCG and LDH can be at any level but there is NO poor prognosis of SEMINOMAS |
|
|
What levels do we want our chemical markers at when assessing testicular prognosis of GOOD?
|
GOOD MARKERS
AFP<1,000 hCG<5,000 LDH<1.5 |
|
|
What are the three tumor markers secreted by germ cell neoplasms?
|
hCG
AFP LDH (lactic acid dehydrogenase) |
|
|
What is the prognosis of a patient with No non-lung spread with AFP=1,000-10,000; hCG=5,000-50,000; and LDH=1.5-10 for Non-seminomas?
|
Intermediate prognosis
|
|
|
What is the most common cancer in men?
|
Prostate Cancer
|
|
What is the main consequence of having a problem with your prostate gland?
|
Constricts flow through the urethra, leading to:
-difficulty emptying the bladder -pressure on kidneys -ascending bacterial infections causing pyelonephritis |
|
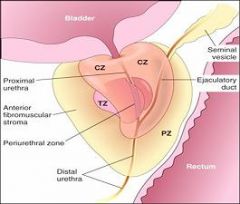
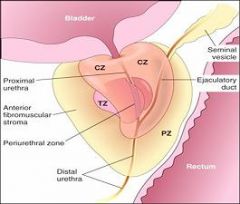
Where does prostate hyperplasia usually occur?
|
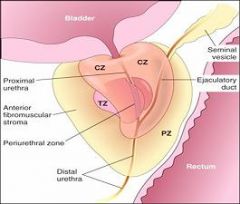
Prostate hyperplasia usually occurs in the central and transitional zones
|
|
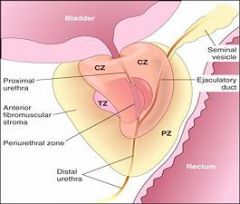
Where does prostate cancer usually form?
|
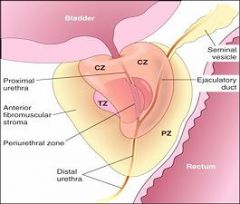
The Peripheral Zone
|
|
|
What neoplasm is swollen, red, and always welcome at Dr. Hirsch's house?
|

MONKEY BUTT
(wow I am tired of studying) |
|
|
What is caused by cell replication of epithelial and stromal elements following DHT concentration?
|
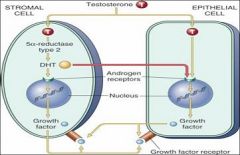
Nodular Hyperplasia
|
|
|
Which cell generates Dihydroxytestosterone in nodular hyperplasia?
|
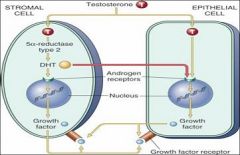
The Stromal Cell
|
|
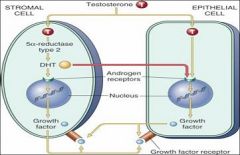
T/F
Nodular hyperplasia alone causes increased risk of cancer to the prostate |
False
It is not the nodular hyperplasia by itself. It is the nodular hyperplasia + inflammatory atrophy that leads to increased risk of prostate cancer |
|
|
What leads to increased risk of prostate cancer, involving DHT?
|
Nodular Hyperplasia & Inflammatory Atrophy
|
|
|
Where does prostate cancer usually occur?
|
In the periphery of the gland (not in the central peri-urethral zone)
|
|
|
T/F
PSA is a NORMAL expressed protein from prostate cells |
True
|
|
|
What could an elevation of PSA indicate?
|
1) Prostatitis
2) Nodular hyperplasia 3) Prostate Cancer |
|
|
T/F
PSA >4.0ng/L alone is a good indicator of prostate cancer |
False Elevated PSA + another test is necessary
|
|
|
What are some methods of determining prostate cancer?
|
1) Transrectal Ultrasonography
2) Needle Biopsy 3) Digital Rectal Examination |
|
|
What is a good indicator of whether or not prostate cancer has metastasized?
|
Elevation of Acid Phosphatase Levels
(*only found when prostate cancer has extended beyond the capsule or has metastasized*) |

