![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
260 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
"lipos" |
Greek word of lipids |
|
|
Lipids |
They store chemical energy and carbon atoms in the body |
|
|
Lipids |
They refer to a collection of organic molecules of varying chemical composition that are grouped together on the basis of their solubility in non polar solvents |
|
|
Phosphoglyceride (Phospholipids) Sphingolipids (Glycolipids) Steroid (Cholesterol) |
Basic components of cell membranes |
|
|
Insoluble in Polar (Water) Soluble in Non Polar Solvents and Weakly Polar Solvents |
Solubility of Lipids |
|
|
Fatty Acids, Glycerides, Non-Glycerides, Complex Lipids |
(4) Main Groups |
|
|
Energy Source |
What kind of function? When oxidized, each gram of fat releases 9 kcal of energy or more than twice the energy released by oxidation of a gram of carbohydrate |
|
|
9 kcal of energy or more than twice the energy released by oxidation of a gram of carbohydrate |
How much energy does each gram of fat releases when oxidized? |
|
|
Triglycerides |
What is the form in adipocytes of the energy storage? |
|
|
Adrenal Cortex, Testes, Ovaries |
What are the 3 steroid glands that secrete hormones? |
|
|
Hormones (Steroid Hormones) |
It is derived from cholesterol |
|
|
Carotene |
Vitamin A from plants and fruits |
|
|
Retinol |
Vitamin A from fish, dairy products and meat |
|
|
Calciferols |
Vitamin D |
|
|
Tocopherols & Tocotrienols |
Vitamin E |
|
|
Quinones |
Vitamin K |
|
|
Dietary Fat |
Serves as a carrier of the lipid-soluble vitamins |
|
|
Fats |
Shock absorber for protection |
|
|
Subcutaneous Fat |
Fat for Insulation |
|
|
6 carbons |
How many carbon does Short-Chain Fatty Acid has? |
|
|
6-10 Carbons |
How many carbon does Medium-Chain Fatty Acid has? |
|
|
More than 12 carbons |
How many carbon does Long-chain Fatty Acid has? |
|
|
Usually liquids |
Physical state of fat in plants or fish |
|
|
Oil |
It is a liquid fat |
|
|
Oil |
It contains high proportion of unsaturated fatty acids and saturated fatty acids |
|
|
Neutral Glycerides |
There are no charges (+/-) on these molecules |
|
|
Neutral Glyceride |
Primary function: Store Energy |
|
|
Neutral Glycerides, Triacylglycerol |
Excess energy-rich nutrients are converted to __ and stored as __ in fat cells |
|
|
Phosphoglyceride |
Most abundant membrane lipids |
|
|
Glycerol-3-phosphate |
Where is Phosphoglyceride derived? |
|
|
C11 & C2 |
At what carbon of glycerol-3-phosohate contains acyl groups? |
|
|
Alkenes |
What group of hydrocarbons does Unsaturated fatty acid has? |
|
|
Linear (Fully extended) |
Shape of the hydrocarbon chain of Saturated fatty acid |
|
|
Bend in carbon chain at site of C-C double bond |
"Shape" of hydrocarbon tail of Unsaturated fatty acid |
|
|
Solid |
Physical state at room temperature of Saturated Fatty Acid |
|
|
Liquid |
Physical state at room temperature of Unsaturated fatty acid |
|
|
Partially hydrogenated |
Physical state at room temperature of trans fatty acid |
|
|
Higher |
Melting point of Saturated fatty acid |
|
|
Lower |
Melting point of unsaturated fatty acid |
|
|
Essential Fatty Acid |
Fatty acid with double bonds before the 9th carbon |
|
|
Essential Fatty Acid |
Those that are needed by can't be produced by the body |
|
|
Non essential fatty acid |
Fatty acids with no double bonds before the 9th carbon |
|
|
Non essential fatty acid |
Those that are not needed but can be produced by the body |
|
|
Cannot, 9th carbon |
Your body __ form c-c double bonds before the __ |
|
|
Can, 9th carbon |
Your body __ form c-c double bonds after the __ |
|
|
Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic acid |
What are the (2) acid that can be synthesized from alpha Linoleric acid |
|
|
Eicosapentaenoic acid |
It is an acid from fish oil |
|
|
20:5 |
Formula of eicosapentaenoic acid (# of carbons : # of c-c double bonds) |
|
|
22:6 |
Formula of Docosahexaenoic acid (# of carbons : # of c-c double bonds) |
|
|
Docosahexaenoic Acid |
Primary structural component of the human brain, cerebral cortex, skin and retina |
|
|
Flaxseed, Canola (rapeseed), Soybean, Walnut, Wheat germ |
Sources of Alpha Linoleric Acid |
|
|
Corn, Safflower, Cottonseed, Sesame, Sunflower |
Sources of Linolenic Acid or Omega 6 Fatty Acid |
|
|
Esterification |
Chemical reaction of fatty acid with alcohol to form esters and water |
|
|
Esters |
Products of the dehydration of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol |
|
|
Esterification |
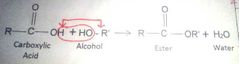
|
|
|
Acid Hydrolysis |
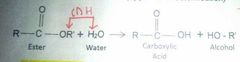
|
|
|
Acid Hydrolysis |
Producing fatty acids from esters |
|
|
Saponification |
Base-catalyzed hydrolysis of an ester |
|
|
Saponification |
The product of this reaction is an ionized salt - a soap |
|
|
Saponification |
Have a long uncharged hydrocarbon tail and a negatively charged terminus (the carboxylate terminus) that forms micelles that dissolve oil and dirt particles |
|
|
Carboxylate Terminus |
What is the negatively charged terminus in saponification? |
|
|
Uncharged |
What is the charge of the long hydrocarbon tail in saponification? |
|
|
Micelles |
An aggregate of molecules in colloidal solution as those formed by detergents |
|
|
Saponification |
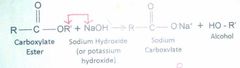
|
|
|
Soap, an ionized sallt |
Product of saponification |
|
|
Hydrogenation |
Used in food industry to convert polyunsaturated vegetable oils into saturated solid fats |
|
|
Hydrogenation |
Removal of all double bonds from a polyunsaturated fatty acid |
|
|
Partial Hydrogenation |
Carried out to add hydrogen to some, but not all, double bonds in Polyunsaturated oils |
|
|
Partial Hydrogenation |
Removal of most double bonds |
|
|
Up to 20% |
Recommended percent of total fat of Monounsaturated |
|
|
10% |
Recommended percent of total fat of Polyunsaturated |
|
|
Less than 7% |
Recommended percent of total fat of Saturated fatty acid |
|
|
Less than 3% |
Recommended percent of total fat of trans fat |
|
|
Monounsaturated and Polyunsaturated fatty acid |
Fats that are limited to lower risk of heart disease |
|
|
Saturated Fatty acid and Trans fatty acid |
Limited to increase risk of heart diseases |
|
|
1st choice: olive oil Canola oil |
Food sources of monounsaturated fatty acid (2) |
|
|
Liquid vegetable oil and fish oil |
Food sources of Polyunsaturated Fatty acid (2) |
|
|
Animal foods, coconut oil, palm oil |
Food sources of Saturated fatty acid (3) |
|
|
Shortening, margarine, crackers, cookies |
Food sources of trans fat (4) |
|
|
Trouncing Trans Fat |
Harmful articial oil that can be replaced with other ingredients |
|

|
Percentages of (8) Major food sources of Transfat |
|
|
Trans Fat |
From hydrogenated (hardened) oil found in fried foods, commercial baked goods, processed foods, margarine |
|
|
Trans fat |
Can raise harmful cholesterol and lower beneficial cholesterol |
|
|
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) |
Harmful cholesterol |
|
|
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) |
Beneficial cholesterol |
|
|
Whole milk, butter, cheese, fatty meats (beef, lamb, pork, poultry) coconut oil, palm oil, coca butter |
(7) sources of saturated fatty acid |
|
|
Saturated Fatty acid |
Main dietary cause of high blood cholesterol |
|
|
Unsaturated Fatty Acid |
Can help lower blood cholesterol if used in place of saturated fats, high in calories |
|
|
Glycerides |
Lipid esters that contain the glycerol molecule and fatty acids |
|
|
Neutral Glycerides, Phosphoglyceride |
(2) classes of glycerides |
|
|
Neutral glyceride |
Nonpolar and non-ionic glyceride |
|
|
Phosphoglyceride |
A glyceride that has a polar region, the phosphoryl group, in addition to the nonpolar fatty acid tails |
|
|
Neutral Glycerides |
Majority of the lipids stored in the body's fat cell |
|
|
Neutral Glycerides (Triacylglycerol) |
Produced after the esterification of glycerol with a fatty acid |
|
|
Monoglycerides |
Esterification at one position |
|
|
Diglyceride |
Esterification at two positions |
|
|
Triglycerides |
Esterification at 3 positions |
|
|
Triglycerides |
Most important and main storage form of lipids in man (adipocytes) |
|
|
Triaglycerol |
A glycerol added with 3 fatty acids |
|
|
Glycerophospholipids |
A glycerol with (2) fatty acids and a phosphate group. The phosphate group has an amino alcohol attached to it. |
|
|
Phosphodiester Bond |
Covalent bond in which a phosphate group joins adjacent carbon through ester linkages |
|
|
Fat |
A mixture of triglycerides containing high proportion of long-chain, saturated fatty acids |
|
|
Generally solid |
Physical state of fat in animals |
|
|
Saturated Fatty Acid |
Contains carbon to carbon single bonds |
|
|
Saturated Fatty Acid |
Each carbon atom is bonded to as many hydrogen atoms as possible |
|
|
Saturated Fatty Acid |
Each C being saturated with H |
|
|
CH3(CH2)nCOOH |
General formula of Saturated Fatty Acid |
|
|
Polar |
What is the polarity of the Hydrophilic part of the fatty acid? |
|
|
Non-Polar |
What is the polarity of the Hydrophobic part of the fatty acid? |
|
|
Decanoic, 10 carbons, Saturated fatty acid |
What is IUPAC name, number of carbons and type of fatty acid of Capric Acid |
|
|
Dodecanoic, 12 carbons, Saturated fatty acid |
What is IUPAC name, number of carbons and type of fatty acid of Lauric Acid |
|
|
Tetradecanoic Acid, 14 carbons, Saturated fatty acid |
What is IUPAC name, number of carbons and type of fatty acid of Myristic Acid? |
|
|
Hexadecanoic Acid, 16 carbons, Saturated Fatty Acid |
IUPAC name, number of carbons and type of fatty acid of Palmitic Acid |
|
|
Octadecanoic Acid, 18 carbons, Saturated Fatty Acid |
IUPAC name, number of carbons and type of fatty acid of Stearic Acid |
|
|
Eicosonic, 20 carbons, Saturated Fatty Acid |
IUPAC name, number of carbons and type of fatty acid of Arachidic Acid |
|
|
Unsaturated Fatty Acid |
Composed of atleast one carbon to carbon double bond |
|
|
Unsaturated Fatty Acid |
They are mostly in the "cis" transfiguration |
|
|
Monounsaturated Fatty Acid |
It has one carbon to carbon double bond |
|
|
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid |
It has two or more carbon to carbon double bond |
|
|
Omega 9, 1 double bond, monounsaturated, non-essential |
(1) Location of double bond (2) Number of double bond (3) Type of UFA (4) Essentiality Acid: Oleic |
|
|
Omega 6, 2 double bonds, Polyunsaturated, Essential |
(1) Location of double bond(2) Number of double bond(3) Type of UFA(4) EssentialityAcid: Linoleic |
|
|
Omega 3, 3 doouble bonds, Polyunsaturated, Essential |
(1) Location of double bond (2) Number of double bond (3) Type of UFA (4) Essentiality Acid: Alpha Linoleric |
|
|
Cis fatty acid |
Hydrogen is on the same side of the double bonds |
|
|
Cis fatty acid |
It causes a bend or "kink" that prevents the fatty acids from packing tightly, keeping them liquid at room temperature |
|
|
Cis fatty acid |
The 2 neighboring hydrogen repel each other |
|
|
Cis fatty acid |
A fatty acid that is naturally occuring |
|
|
Liquid at room temperature |
Physical state of 'cis' fatty acid |
|
|
Trans fatty acid |
Hydrogens are on the opposite site of the double bond |
|
|
Trans fatty acid |
They occur in partially hydrogenated food |
|
|
Trans fatty acid |
The (2) hydrogen are already as far apart as they can |
|
|
Omega Number |
It is identified by position of the double bond nearest to the methyl end of the carbon chain |
|
|
Omega 3 Fatty Acid |
First double bond 3 carbons away from methyl end |
|
|
Omega 6 Fatty Acid |
6 carbons away from methyl end |
|
|
Omega 9 Fatty Acid |
9 carbons away from methyl end |
|
|
Alkanes |
What group of hydrocarbon does Saturated fatty acid has? |
|
|
C3 |
At what carbon of phosphoglyceride is the phosphoryl group joined to a glycerol? |
|
|
Phosphoester Bond |
What is the bond between Phosphoryl group and glycerol at C3 of Phosphoglyceride? |
|
|
Phosphatidate |
Simplest phosphoglyceride containing a free phosphoryl group |
|
|
Phospholipids |
Group of lipids that are Phosphate esters |
|
|
Phosphoryl group |
In a phospholipid, what group is the polar head? |
|
|
Alkyl chain of fatty acid |
In a Phospholipid, what is the nonpolar tail? |
|
|
Amphipathic |
Having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic part |
|
|
Lecithin |
Other term for phosphatidylcholine |
|
|
phosphatidylcholine |
Similar to that of soap and detergent molecules |
|
|
phosphatidylcholine |
Major phospholipid in pulmonary surfactant |
|
|
Cephalin |
Other term for phosphatidylethanolamine |
|
|
phosphatidylethanolamine (cephalin) |
Similar in general structure to lecithin |
|
|
Amine group |
What group is bonded to the phosphoryl group that makes lecithin and cephalin different to each other? |
|
|
Sphingolipids |
Lipids that are not derived from glycerol |
|
|
Sphingomyelin |
Located throughout the body, but are particularly important structural lipid components of nerve cell membranes |
|
|
Sphingomyelin |
Non-Glyceride lipids in white matter |
|
|
Sphingomyelin |
Found in abundance in the myelin sheath that surrounds and insulate cells of the CNS |
|
|
Sphingomyelin |
Role is essential to proper cerebral function and nerve transmission |
|
|
Glycosphingolipids (Glycolipids) |
Are built on a ceramide backbone structure, which is a fatty acid amide derivative of sphingosine |
|
|
Ceramide |
Fatty acid amide derivative of sphingosine |
|
|
Cerebrosides, Sulfatides, Gangliosides |
(3) types of Glycosphingolipids |
|
|
Cerebrosides |
Characterized by the presence of a single monosaccharide head group |
|
|
Glucocerebrosides |
Found in the membrane of macrophages |
|
|
Glucocerebrosides |
Consists of ceramide bonded to the hexose glucose |
|
|
Galactocerebroside |
Found almost exclusively in the membrane of brain cells |
|
|
Galactocerebroside |
Consist of ceramide joined to the monosaccharide galactose |
|
|
Steroids |
Members of a large, diverse collection of lipids called the isoprenoids |
|
|
Isoprenoids |
Diverse collection of lipids |
|
|
Isoprene |
One or more 5-carbon units |
|
|
Terpene |
General term for lipids that are synthesized from isoprene units |
|
|
Terpene |
Steroid and bile salts, lipid-soluble vitamins |
|
|
Cholesterol |
Readily soluble in the Hydrophobic region of membranes |
|
|
Cholesterol |
Involved in the regulation of the fluidity of the membrane as a result of the nonpolar fused ring |
|
|
Hydroxyl group |
Polar Region of the Perhydrocyclopentanophenanthrene |
|
|
Perhydrocyclopentanophenanthrene |
Nonpolar fused ring of cholesterol |
|
|
Cholesteryl esters |
Esterified form of cholesterol |
|
|
3-O-acyl-cholest-5-en-3B-ol |
Other name for cholesteryl esters |
|
|
Cholesterol |
It is not readily catabolized by most cells, therefore, does not serve as a source of energy |
|
|
Cholic Acid, Chenodeoxycholic Acid |
Cholesterol are converted in the liver to __ and __ |
|
|
Bile Salts |
Amphipathic derivatives of cholesterol |
|
|
Bile Salts |
Absorbs cholesterol, aids in digestion, absorb important vitamins, eliminate toxins |
|
|
Cholic Acid, Chenodeoxycholic Acid |
(2) examples of bile salt |
|
|
Bile Salts |
Synthesized in the liver and stored in the gall bladder |
|
|
Emulsifying agent |
Whose polar hydroxyl groups interact with water and whose hydrophobic regions bind to lipids |
|
|
Waxes |
Derived from many different sources and have a variety of chemical compositions, depending on the source |
|
|
Waxes |
Has long hydrocarbon tails that are extremely Hydrophobic (completely insoluble in water) |
|
|
Waxes |
Aside from saturated fatty acid, Solid at room temperature |
|
|
Lanolin |
Protective coating for hair and skin (used in skin creams and ointments) |
|
|
Testosterone |
Produced by Leydig cells |
|
|
Progesterone |
Regulate condition of the inner lining of the uterus; produced by the ovaries |
|
|
Estrone |
Menopausal Hormone |
|
|
Estrogen |
Hormones responsible for menstrual cycle |
|
|
Cortisone |
Hormone in response to stress |
|
|
Cortisol |
Hormones that increase glucose |
|
|
Aldosterone |
"Mineralocorticoid" |
|
|
Aldosterone |
Hormone in charge for conservation of sodium, secretion of potassium, reabsorption of ions and water |
|
|
Cortisol |
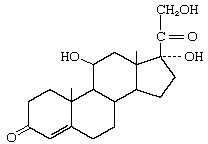
|
|
|
Corticosterone |
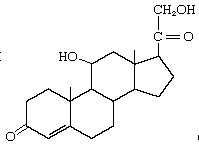
|
|
|
Aldosterone |
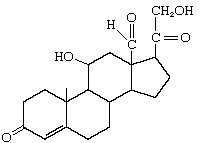
|
|
|
Progesterone |
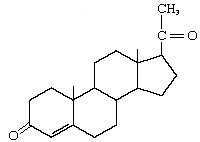
|
|
|
B-estradiol |
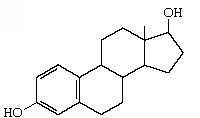
|
|
|
Testosterone |
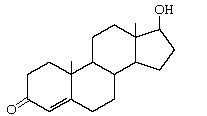
|
|
|
Complex Lipids |
Lipids that are bonded to other types of molecules |
|
|
Lipoprotein |
Consist of a core of hydrophobic lipids, surrounded by amphipathic proteins, phospholipids, and cholesterol |
|
|
Spherical, 10 to 1200 nm |
Shape and range in size of lipoprotein |
|
|
Apolipoproteins |
Lipids + Proteins = ? |
|
|
Lipoproteins |
Composed of apolipoproteins |
|
|
Apolipoproteins |
Primarily located on the surface of lipoprotein particles |
|
|
Apolipoproteins |
Help maintain the structural integrity of the lipoprotein |
|
|
Apolipoproteins |
Serve as ligands for cell receptors |
|
|
Apolipoproteins |
Activators and inhibitors of the various enzymes that modify lipoprotein particles |
|
|
Apolipoproteins |
Contain a structural motif called an amphipathic helix |
|
|
Apolipoproteins |
Protein segments arranged in coils so that the hydrophobic amino acid residues interact with lipids |
|
|
Amphipathic helix |
Ability of apolipoproteins to bind to lipids |
|
|
Apo A-I |
Major protein on HDL |
|
|
Apo A-I |
Frequently used as an index of the amount of antiatherogenic HDL present in plasma |
|
|
Apo B |
Large protein with MW 500 KD |
|
|
Apo B |
Principal protein on LDL, VLDL and Chylomicrons |
|
|
Apo B-100 |
Found on LDL and VLDL |
|
|
Apo B-100 |
Ligand for the LDL receptor |
|
|
Apo B-100 |
Critical in the uptake of LDL cells |
|
|
Apo B-48 |
Exclusively found in Chylomicrons |
|
|
Apo B-48 |
Can also be found covalently linked to apo (a) |
|
|
Apo (a) |
A plasminogen-like protein that is found in a proatherogenic lipoprotein particle |
|
|
Lipoprotein A [LP(a)] |
Proatherogenic lipoprotein particle |
|
|
Apo E |
Found in LDL, VLDL, and HDL |
|
|
Apo E |
Serves as ligand for the LDL receptor and the chylomicron remnant receptor |
|
|
Apo E2, E3, E4 |
(3) examples of apo E |
|
|
Apo E |
They affect lipoprotein metabolism because they differ in their ability to interact with the LDL receptor |
|
|
Chylomicrons |
Contain Apo B-48 |
|
|
Chylomicrons |
Account for the turbidity of postprandial plasma |
|
|
Chylomicrons |
Readily float to the top of stored plasma and form a creamy layer |
|
|
Chylomicrons |
Chylous, turbid, milky, cloudy, lipemic plasma/serum |
|
|
Chylomicrons |
Produced by the intestine, where they are packaged with absorbed dietary lipids |
|
|
Lipase |
What hydrolyzes TAG and cholesteryl esters when chylomicrons enter the circulation? |
|
|
Chylomicrons |
Are transformed into chylomicron remnant particles, which are taken up by remnant receptors in the liver |
|
|
Chylomicrons |
Deliver dietary (exogenous) lipids to hepatic and peripheral cells |
|
|
Very Low Density Lipoprotein |
Contain apo B-100, apo E, and apo C |
|
|
Very Low Density Lipoprotein |
Produced by the liver |
|
|
Very Low Density Lipoprotein |
Rich in TAG like chylomicrons |
|
|
Very Low Density Lipoprotein |
Major carriers of endogenous (hepatic derived) triglycerides |
|
|
Very Low Density Lipoprotein |
Account for most of the turbidity observed in fasting hyperlipidemic plasma specimen but do not form a top creamy layer |
|
|
Very Low Density Lipoprotein |
Transfer TAG from the liver to peripheral tissue |
|
|
Low - Density Lipoprotein |
Contains apo B-100 and apo-E |
|
|
Low - Density Lipoprotein |
More cholesterol-rich than other Apo-B containing lipoproteins |
|
|
Low - Density Lipoprotein |
Readily taken up by cells via the LDL receptor |
|
|
Low - Density Lipoprotein |
Accounts for the reason that elevated LDL levels promote atherosclerosis |
|
|
Low - Density Lipoprotein |
Significantly smaller than VLDL and Chylomicrons |
|
|
Low - Density Lipoprotein |
Can infiltrate into the extracellular space of the vessel wall, where it can be oxidized and taken up by macrophages |
|
|
Low - Density Lipoprotein |
It become filled up with intracellular lipid drops and turn into foam cells |
|
|
Low - Density Lipoprotein |
Early precursor of atherosclerotic plaques |
|
|
High - density lipoprotein |
Smallest and the most dense |
|
|
High - density lipoprotein |
Synthesized by both the liver and intestine |
|
|
High-density lipoprotein |
Can exist as either disk-shaped or as spherical-shaped particles |
|
|
Discoidal HDL |
Contains 2 molecules of apo A-I |
|
|
Discoidal HDL |
Represent newly secreted HDL |
|
|
Discoidal HDL |
Most active form in removing excess cholesterol from peripheral cells |
|
|
Discoidal HDL |
Acquire additional lipid, cholesteryl esters, and TAG from a core region between the central lipid bilayer |
|
|
Spherical HDL |
Predominant form in plasma |
|
|
Spherical HDL2 |
Larger in size and richer in lipid |
|
|
Spherical HDL2 |
More efficient in delivering lipids to the liver |
|
|
140 - 200 mg/dL |
Total Cholesterol Reference Range |
|
|
40 - 75 mg/dL |
HDL Cholesterol Reference Range |
|
|
50 -130 mg/dL |
LDL Cholesterol Reference range |
|
|
60 - 150 mg/dL |
Reference range for Triglycerides |

