![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
refraction |
- bending of light through different transparent media - fast in gas > liquid > solid |
|
|
when light travels from denser medium to less dense medium |
- speed increases - ray bends away from normal |
|
|
when light travels from less dense medium to denser medium |
- speed decreases - ray bends towards normal |
|
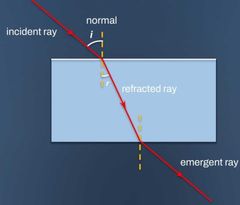
|
incident ray does not touch boundary refracted ray does not touch boundary |
|
|
refractive index |
- no units - n > 1 - RI increase = SOL decrease n = vacuum/air ÷ medium |
|
|
snell's law |
n1sin@1=n2sin@2 light follows same path if reverse used to find angle of incidence/refraction |
|
|
critical angle |
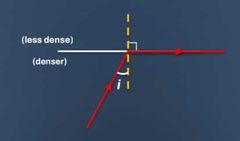
angle of incidence such that angle of refraction is 90 use to determine total internal reflection |
|
|
total internal reflection |
- complete reflection of a light ray inside an optically denser medium at its boundary with an optically less dense medium - light ray must travel from a denser medium to a less dense medium - i > c |
|
|
lenses |
parallel light rays converge/diverge after passing through lenses due to refraction |
|
|
principal axis |
horizontal line passing through optical lens center |
|
|
optical center |
midpoint between surfaces on lens on its principal axis (not where light ray is refracted) |
|
|
focal point |
point at which all light rays parallel to the principal axis converge after refraction by the lens behind optical center |
|
|
focal length |
distance between optical center to focal point |
|
|
ray diagrams |
rays always follow one of 3 characteristics: 1) passes through the optical center 2) is parallel to principal axis then refracts to pass through the focal point after the optical center 3) passes through the focal point before the optical center then is parallel to principal axis |
|
|
object >2F |
image is inverted, real, diminished eg: camera & eye |
|
|
object = 2F |
image is inverted, real, same size eg: photocopier |
|
|
F < object < 2F |
image is inverted, real, magnified eg: projector, photograph enlarger |
|
|
object = F |
image is upright, virtual, magnified eg: spotlight (producing parallel beam of light) |
|
|
object < F |
image formed is upright, virtual, magnified eg: magnifying glass |
|
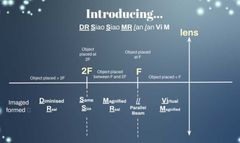
|
object > 2F : diminished, real object @ 2F : same size F < object < 2F : magnified, real object @ F : // object < F : virtual, magnified |

