![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Laws of reflection |
-Angle of incidence, angle of reflection, normal and point of incidence all lie on the same planes -angle of incidence=angle of reflection |
|
|
Characteristics of image |
Virtual-cannot be captured on screen Upright Same size Object dist=image dist Laterally inverted |
|
|
Laws of refraction |
-Incident ray, refracted ray and the incident all lie on the same plane -ratio of sine angle of incident is equal to sine angle of refraction is a constant. Sini/sinr =constant |
|
|
Refractive index |
n=c/v n is refractive index c is speed of light in vacuum v is speed of light in medium |
|
|
Snell's law |
n1sini=n2sinr n1-refractive index of incident medium n2-refractive index of refraction medium Frm less dense medium to more dense medium. Light ray bend toward normal Frm more dense medium to less dense medium. Light ray bend away frm normal. Speed of light in vacuum=3×10^8 m/s |
|
|
Conditions for total internal reflection |
1. Light ray frm optically denser medium to less dense 2.angle of incidence must be more than critical angle |
|
|
Critical angle |
When angle of refraction=90° Calculate by using n1sini=n2sin90 When angle i less than angle c - refraction Angle i =angle c - 90° Angle i more than angle c - total int reflection |
|
|
Optical fibres |
Transmit data Core must have higher refractive index Cladding have lower refractive index Minimise data loss through total int reflection |
|
|
Features of lenses |
Optical center- mid point of lens Principal axis- horizontal plane cutting through the optical center Focal point- point which all rays parallel to the principal axis converge after refraction Focal length- dist between optical center and focal point |
|
|
Predictable rays |
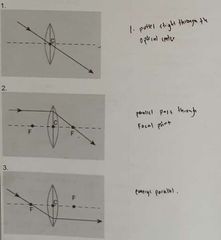
|
|
|
Position of ray and image |
Infinity- real, diminished,inverted , telescope Between 2f and infinity- real, inverted, diminished, camera eye 2f- inverted, same size, real, photocopy Between 2f and f- real,inverted, magnified, visualiser F- real and virtual, magnified, spot light Less than f- virtual, magnified, upright , magnifying glass |

