![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
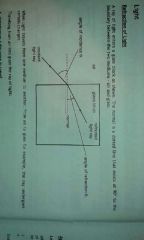
Draw a diagram of when a Ray of light enters a glass block |
|
|
|
|
What are the changes of when the ray of light travels from air into glass |
•experiences a decrease in speed •experiences a decrease in wavelength •refracts (bends) toward the normal if it enters the glass box at an sloping angle •experiences no change in frequency |
4 points |
|
|
What are the changes of when the rays of light travels from glass into air |
•experiences an increase in speed •experiences an increase in wavelength •refracts (bends) away from the normal if it leaves the glass box at an sloping angle •experiences no change in frequency |
4 points |
|
|
What is the normal? |
The normal is a dotted line which is perpendicular to the boundary between different mediums at the point at which the ray meets the boundary. |
|
|
|
What is the incidence ray |
The incidence ray is the ray that approaches the boundary between different medium. |
|
|
|
What is the reflected ray? |
The reflected ray is the ray that is reflected at the boundary and which moves away from it. |
|
|
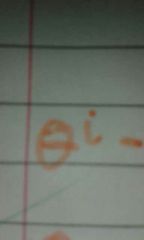
What is |
Angle measured from the normal to the incidence ray. |
|
|
|
Draw a diagram of reflection |
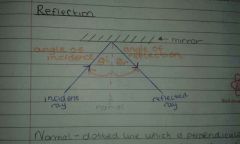
|
|
|
|
What happens when light enters a glass object at an oblique angle? |
When light enters a glass object at an oblique angle, its path will change (unless it passes at an angle of incidence of 0° (i.e along the normal) in which case it does not change direction) |
|
|
|
What is refraction? |
Refraction is the effect whereby a wave changes direction when it crosses a boundary between 2 different medium as it experiences a change in speed. |
|
|
|
What is a lense? |
A lense is an object that refracts light. |
|
|
|
What are the main lenses |
•Converging (convex) •diverging (concave) |
|
|
|
What are covex lenses and draw it |
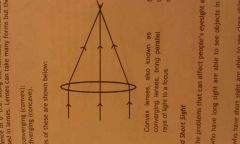
Convex lenses, also known d converging lenses, bring parallel rays of light to a focus. |
|
|
|
What are concave lenses and draw them |
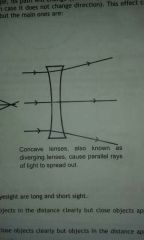
Concave lenses, also known as diverging lenses, cause parallel rays of light to spread out. |
|
|
|
what happens with people who have long sight |
People who have long sight are able to see objects in the distance clearly but close objects appear blurred. |
|
|
|
What happens to people who have short sight |
People who have short sight are able to see close objects clearly but objects in the distance appear blurred. |
|
|
|
What happens when rays of light from a nearby object enter the eye of someone with long sight and what can be done to fix it (draw it also) |

When rays of light from a nearby object enter the eyes of someone with long sight the rays come to a focus behind the retina. To enable them to focus the rays onto the retina, a convex(converging lenses) is placed in front of the eye. |
|
|
|
What happens when rays of light from a distance object enter the eye of someone with short sight and what can be done to fix it (and draw it) |
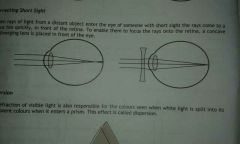
When rays of light from a distance object enter the eye of someone with short sight the rays come to a focus quickly, in front if the retina. To enable them to focus the rays onto the retina, a concave(diverging lenses) is placed in front of the eye. |
|
|
|
What is dispersion? |
Dispersion is when the refraction of visible light is responsible for the colours seen when white light is split into its component colours when it enters a prism. |
|
|
|
Draw what happens when white line passes through a prism and the colours produced |

|
|
|
|
What is the critical angle? |
The critical angle for a medium is •the angle of incidence that produces an angle of refraction of 90° •maxium angle of incidence at which refraction occurs •Minimum angle of incidence at which total internal reflection occurs. |
|
|
|
When do Total internal reflection occurs? |
Total internal reflection occurs when the incidence angle is greater than the reflected angle, resulting in the ray being reflected back into the medium at the boundary at an angle equal to the incidence angle. |
|
|
|
Draw and label when total internal reflection is utilised in optical fibres. |

|
|
|
|
What is the principle of reversibility of a ray path? |
The principle of reversibility states that light will follow exactly the same path if its direction of travel is reversed. |
|

