![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Characteristics of living things
|
Reproduce
Feed Respire Grow Excrete Move Sensitive Made of cells |
|
|
Habitat
|
A place where an organism lives
|
|
|
Population
|
A population is a group of organisms of the same species living in the same please have the same thing and able to breed with one another
|
|
|
Community
|
A community is all the organisms of all the different species living in the same habitat
|
|
|
Ecosystem
|
The living organisms in the pond, the water in it, the stones and the mud at the bottom, make up an ecosystem.
|
|
|
Niche
|
The way in which an organism lives it's life - the way it fits into the ecosystem.
|
|
|
Species
|
Group of similar organisms which are able to interbreed
|
|
|
All organisms
|
Prokaryote, protoctists, fungi, plants, animals
|
|
|
Primary producers
|
Plants are the only source of energy for all living organisms thus plants are the primary producers of food in any ecosystem
|
|
|
Herbivores
|
Animals that feed on plants
Example, sheep, cattle, slugs and caterpillars |
|
|
Carnivores
|
Animals that eat other animals
|
|
|
Predators
|
Carnivores that kills animals that they eat
|
|
|
Omnivores
|
Animals whose diet consists of both animals and plants. Humans are omnivores
|
|
|
Pollinators
|
Hummingbirds that carry pollen from one plant to another
|
|
|
Parasites
|
Parasites are organisms that live in or on another species called the host which they get the food out of
|
|
|
Food chain
|
The sequence by which energy in the form of food, passes from plant to animals and then to other animals
|
|
|
Trophic level
|
This indicates the number of stages in a food chain between the feeder and the sun
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Plants the first trophic level these are the primary producers. Primary producers are always at the first trophic level. Herbivores are at the second trophic level. Carnivores are at the third trophic level.
|
|
|
Symbiosis
|
Two different species living together intimately.
|
|
|
Parasitism
|
This is where one partner benefits from the Association and the other suffers.
|
|
|
Commensalism
|
This is where one partner benefits and the other partner usually does not gain from the relationship but does not suffer.
|
|
|
Mutualism
|
This is where both organisms gain from the association. Neither can live without each other.
|
|
|
Epiphyte
|
This is where the roots of a plant do not enter the soil. For example plants growing on another one.
|
|
|
Nitrogen fixing
|
This is where a bacterium is able to use nitrogen gas from the air spaces in the soil, and combine it with other substances to make ammonium ions and other compounds
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Decomposers feed on waste material from animals and plants, and on their dead bodies.
|
|
|
Role of Decomposers
|
Decomposers helps to release substances from dead organisms to be used again by living ones. The two substances released is Carbon and Nitrogen.
|
|
|
Carbon
|
Carbon is an essential part of carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
|
|
|
Carbon cycle
|
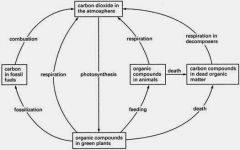
|
|
|
Nitrogen
|
Living things need nitrogen to make proteins. Nitrogen molecules are inert, which means that they will not readily react with other substances.
|
|
|
Nitrogen cycle
|
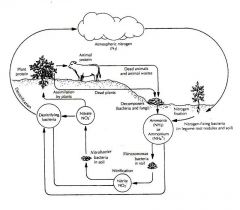
|
|
|
Nitrogen fixation
|
This is when nitrogen gas changes into a more reactive form.
|
|
|
How nitrogen fixation occurs
|
Lightning - Nitrogen gas combines with oxygen in the air, forming nitrogen oxides, which dissolves in rain and washed into the soil forming nitrates.
Artificial Fertilizers - Nitrogen and hydrogen is reacted in an industrial chemical process forming ammonia. The ammonia is used to make ammonium compounds and nitrates and then sold as fertilizers. Nitrogen - fixing bacteria - This uses nitrogen gas from the air spaces in the soil and combine it with other substances to make ammonia. |
|
|
The water cycle
|
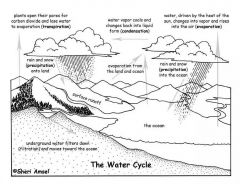
|

