![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Life Process |
An organelle is a specialized part of a cell having some specific function ; cell organ |
|
|
Cell Membrane |
All cells are bound by plasm membrane. Membranes are very thin and act as a boundary between the cell and it's environment, so maintaining the concentration of substances inside and outside the cell. |
|
|
Semi-Permeable (Membrane) |
Membranes are semi-permeable meaning that they only allow passage of only certain substances. |
|
|
Microvilli of Membrane |
The membrane may have many tiny folds known as microvilli which greatly increase the surface area which helps in absorbing nutrients. |
|
|
Phospholipid Bilayer of Membrane |
The membrane is made of a phospholipid bilayer, embedded with many different proteins. The bilayer is fluid, allowing the proteins in it to move. |
|
|
Amphipathic (Membrane) |
The phospholipid bilayer of the membrane has 'leads' of glycerol- phosphate which are hydrophilic (water loving) and tails which are hydrophobic (water hating). |
|
|
Passive Transport |
Process does not need energy (from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration). |
|
|
Active Transport |
Active transport moves substances across membrane against a concentration gradient from low to high concentration, therefore the process requires energy. |
|
|
Concentration Gradient |
The difference between the two area's concentration is called the concentration gradient. |
|
|
Diffusion |
→Refers to the movement of particles in liquid and gases resulting in net movement. →Passive transport →As a result of this random moment the molecules of a gas becomes evenly spread out. →The higher the concentration gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion. →Diffusion does not require a cell membrane. |
|
|
Factors affecting diffusion |
Temperature: Particles diffuse faster at higher temperature because they move faster.
Size: Smaller particles move faster State: Gas particles diffuse faster due to more kinetic energy |
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion |
Molecules that cross the membrane faster than is possible from their concentration gradient do so by facilitated diffusion. Special transport or carrier proteins in the membrane provide channels for the process. |
|
|
Mitochondria and transport |
Cells undergoing a lot of transport will have large amount of mitochondria and use up large amount of glucose and oxygen while producing large amount amounts of carbon dioxide and heat ( in respiration). |
|
|
Cytosis |
This is a movement of large amounts of substances into/ out of the cell by the folding of membranes. Endocytosis; transport into the cell Exocytosis; transport out of the cell |
|
|
Cell Cycle |
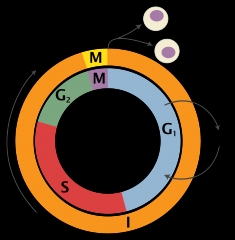
The cell cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading it's division and duplication (replication). |
|
|
DNA Replication |
1. DNA is unwound using the enzyme helices to form two separate strands.
2. Free nucleotides then follow the base pairing rule and join up with the correct bases on the strand of DNA. 3. The enzyme DNZ polymerase then joins 2 strands together giving them the double helix structure. |
|
|
Mitosis |
Cells divides by process of mitosis for growth, and to reproduce worn out or injured cells.
Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells to the parent cell so the same cell functions and processes can continue. |
|
|
Factors that affect the Rate of Mitosis |
→Stage of life- the rate of mitosis is high in organisms that are undergoing growth and repair. →Availability of nutrients- certain substances are required to build new organelles and cell components when cell replicate. →Location of cells- specific areas have higher rates of mitosis where most growth or replacement of cell is occurring. →Environmental factors- the orioles of mitosis requires enzymes. Therefore any factors that effect enzymes will also effect the rate of mitosis.
|
|
|
Enzyme |
An enzyme is a protein molecule. Each type of enzyme catalyses a particular reaction type of reaction. They can do this because the long chain of amino acids which make up the enzyme are folded into particular shape known as active site. |
|
|
Lock and Key (enzymes) |
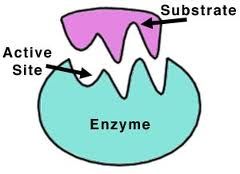
The active site allows the substrates of the reaction to fit into the enzyme. This works like lock and key. Once the substrate is in place in the active site it binds to the enzyme and the reaction then takes place rapidly. The surface of the enzyme release the product of the reaction. |
|
|
Lock and Key vs Induced |
Lock and Key →Active site is a single entity →Active site is static; precise shape →The substrate shape is affected by the enzyme Induced →Active site is made of 2 components →Active site is not static; no precise shape →The enzyme shape is affected by the substrate |
|
|
ATP |
The source of energy that keeps everything (every cell in our body) going is called ATP. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the biochemical way to store and use energy. |
|
|
Co- factors (of enzymes) |
Many enzymes need another molecule to assist in catalysis. Co-enzymes are necessary when only weak bonds form between the enzyme and substrate; the co-enzyme acts as bridge, locking the enzyme and substrate more tightly together. |
|
|
Inhibitors |
Inhibitors are substances that prevent enzymes catalyzing reactions, and so are poisons. An inhibitors can act in : →Taking over the active site of an enzyme. →Bonding to another part of an enzyme and altering the shape of the active site. |
|
|
Enzyme; optimum conditions Temperature |
Generally, the warmer the temperature the faster the enzymes catalyses a reaction (due to increased energy in particles form successful collisions). However, if the temperature becomes too high the enzymes are denatured and can no longer catalyses the reaction. |
|
|
Enzyme; optimum conditions pH |
Most enzymes optimum pH is 7, when the pH is outside of the range for an enzyme, the enzyme will denature and can no longer act as a catalyst.
|
|
|
Enzyme; optimum conditions Substrate concentration |
The rate of enzyme activity will increase as the concentration of the substation point occurs/ no more free active sites available. |
|
|
Photosynthesis Equation |
Carbondioxide + water (+sunlight energy) → Sugar glucose+Oxygen 6CO2 +6H2O→C6H12O6+6O2 |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants in which energy form. Sunlights is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into molecules needed for growth. These molecules includes sugars, enzymes and chlorophyll. Light energy is absorbed by the green chemical chlorophyll. |
|
|
Chloroplast green cell organelle |
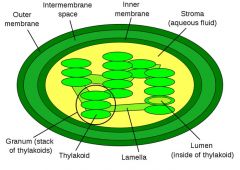
Chloroplasts are food producers of the cell. The organelles are only found in plant cells and some protists such as algae. |
|
|
Chloroplast and Photosynthesis |
The entire process of converting light energy into sugar is called the photosynthesis and it all depends on the little green chlorophyll molecules in each chloroplasts. In the process of photosynthesis, plants create sugars and release oxygen. Mitochondria works in the opposite direction. They use oxygen in the process of releasing chemical energy from sugars. |
|
|
Factors affecting photosynthesis
Size of Chloroplasts |
Larger Chloroplasts↓ Larger surface area↓ Therefore more chlorophyll↓ Therefore maximum absorption of light ↓ Therefore, maximum rate of photosynthesis |
|
|
Cytoplasmic Streaming |
To ensure that each individual chloroplast gets the maximum amount of sunlight to achieve maximum amount of photosynthesis, chloroplasts move in cell. |
|
|
Temperature factors affecting photosynthesis |
Increasing CO2 increase the rate of photosynthesis (up to an optimum temperature) when the temperature goes above the optimum, the enzymes controlling the reaction denature and can no longer catalyses the reaction. |
|
|
Light intensity factors affecting photosynthesis |
Increasing the light intensity increase the rate of photosynthesis up to a maximum. After it reaches to the maximum, further increase in light intensity have no effect on the rate of photosynthesis. |
|
|
CO2 Concentration factors affecting photosynthesis |
Increasing CO2 increases the rate of photosynthesis up to a maximum. Increasing the concentration after the maximum will have no further effect on the photosynthesis rate. |
|
|
Light wave length factors affecting photosynthesis |
Increasing rate of photosynthesis when the absorbing light is either blue or red wavelength of the electromagnetic spectrum because pigments are more active. |
|
|
Importance of Photosynthesis |
The importance of photosynthesis is what it converts solar energy into chemical energy as organic molecules. Plants are producers and therefore starting point in all food chains. Photosynthesis is plant accounts for high level (apron 20 %) of oxygen in the atmosphere. This gas is essential for the process of aerobic respiration. |
|
|
Mitochondria |
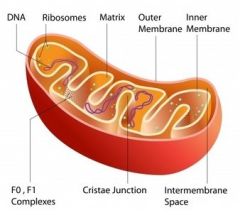
Mitochondria is commonly known as the power house of the cell as they are the site of the organelle. |
|
|
Mitochondrial Membrane Functions |
The outer membrane controls the passage of material in and out of the organelle. The inner mitochondrial membrane is compartmentalized into numerous crust, which expands it's surface area there by enhancing it's ability to produce ATP. Mitochondria forms cell that have greater demand for ATP, such as muscle cells, which contains even more cristae. |
|
|
Respiration |
Respiration is process by which the cell breaks down glucose to produce ATP and heat energy is a bi-product. |
|
|
Aerobic Respiration |
Aerobic respiration needs oxygen for the complete break down of glucose into carbon dioxide and water. Energy is release in the form of ATO and heat. |
|
|
Respiration Equation |
Glucose+Oxygen→Carbon dioxide + Water (+ATP+heat) C6H12O6+6O2→6CO2+6H2O+6H2O (+36ATP+ heat) |
|
|
Temperature factors affecting the rate of respiration |
Increasing temperature increase rate of respiration up to an optimum temperature (too high enzymes denature- human optimum temp =37 degrees) |
|
|
Body's energy demands factors affecting the rate of respiration |
Rate of respiration will increase up to a maximum as the demands from cells and tissues increases. The amount of O2 needed and amount of C2 produced increases= build up of CO2 will decrease the rate of respiration. |

