![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
96 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
atom
|
Basic unit of all matter
|
|
|
|
Protons
|
Positively charged particles in the nucleus
|
|
|
|
Neutron
|
Neutral particles in the nucleus
|
|
|
|
Electron cloud
|
Large area of mostly empty space around nucleus, more than 99% of atoms value and less than 1% of atoms mass
|
|
|
|
Electrons
|
Charged particles in electron cloud
|
|
|
|
Periodic table of elements
|
An element is a piece of matter made of only one kind of atom all are neutral
|
|
|
|
Atomic number
|
The number at the top of the box the number of protons in an atom-- identifies to which element an atom belongs- the number of electrons
|
|
|
|
Mass number
|
The sum of protons and neutrons in an atom (always a whole number)
|
|
|
|
isotopes
|
Atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers
|
|
|
|
Isotopes
|
Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
|
|
|
|
Electron configuration
|
Electrons are held in the energy levels first energy level to second energy level 8
|
|
|
|
Valence electrons
|
Electrons in the outermost energy level --how the periodic table is arranged
|
|
|
|
Octet rule
|
Rule of eight, 8 valence electrons and is a stable configuration of electrons exception to valence electrons in the first energy level is stable-- helium
|
|
|
|
Ionic bonding
|
Electrons are transferred from one atom to another in order to satisfy the octet rule
|
|
|
|
Ions
|
Atom with a charge of positive or negative
|
|
|
|
Cation
|
Is a positively charged ion
|
|
|
|
Anion
|
A negatively charged ion
|
|
|
|
Compounds
|
Ionic bonding creates charged components that can be pulled apart by water or solvent
|
|
|
|
Electrolyte
|
Are ions
|
|
|
|
Covalent bonding
|
Electrons shared between atoms in order to satisfy the octet rule
|
|
|
|
Diatomic molecules
|
Two atoms of the same element bonded together
|
|
|
|
Structural formula
|
series of - for single, double, or triple covalent bonds
|
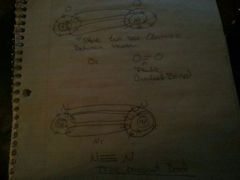
|
|
|
Elements commonly used by the body
|
Carbon nitrogen phosphorus oxygen hydrogen
|
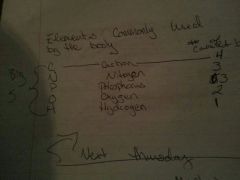
|
|
|
Property of water
|
is an excellent solvent makes the solution of many substances
|
|
|
|
Property of water to brake compounds
|
Thanks I own it compounds into individual ions do the water's polarity
|
|
|
|
Acids
|
Anytime there is more hydrogen ions in the solution it is a
|
|
|
|
Bases
|
Anytime there are fewer hyrdrogen then hydroxide ions in solution is
|
|
|
|
Neutrals
|
Anytime hydrogen and hydroxide ions in solution are equal
|
|
|
|
Acid
|
Molecules that I hadn't hydrogen ions to make a solution acidic
|
|
|
|
Base
|
Molecule that adds Oh - to a solution or remove hydrogen from the solution and does makes a solution more basic or alkaline
|
|
|
|
PH scale
|
Scale 0 acid ,7.0 is neutral, and 14 is basic or alkaline
|
|
|
|
Alkalosis
|
PH above 7.45
|
|
|
|
Acidosis
|
PH below 7.35
|
|
|
|
Buffers
|
Regulate pH weak acids and bases
|
|
|
|
Acid
|
If the pH of the body rises and becomes too basic then buffers act as
|
|
|
|
Bases
|
If the pH of the body falls and becomes too acidic then buffers act as bases and these buffers remove hydrogen ions from the solution
|
|
|
|
Polymer
|
Long-chain molecule made up of repeating units
|
|
|
|
Monomer
|
Repeating unit of a polymer
|
|
|
|
Carbohydrate
|
Sugar starts glycogen cellulose
|
|
|
|
Monosaccharides
|
Simple ring structures example glucose
|

|
|
|
Isomers
|
Have same chemical formula but different structural formula examples glactose and fructose
|
|
|
|
Disaccharides
|
Two monosaccharides join together using dehydration synthesis reaction
|
|
|
|
Disaccharide example
|
Maltose equal to glucose sucrose equal one glucose and one fructose lactose equals 1 glucose and 1 galactose
|
|
|
|
polysaccharides
|
Many monosaccharides joined together using the hydration synthesis reactions example starch is a polymer of glucose used by plants to store energy
|
|
|
|
Glycogen
|
Polymer of glucose used by humans to store energy liver skeletal muscle
|
|
|
|
Cellulose
|
Polymer of glucose used by plants as a structual molecule cell wall adds fiber
|
|
|
|
Dehydration synthesis
|
reaction used to build macromolecules of the body or remove a molecule harder in order to join molecules together
|
|
|
|
Hydrolysis
|
Reaction used to break molecules apart atom molecule of water to break molecules apart
|
|
|
|
Lipids
|
Fats oils and waxes macromolecules insoluble in water much less oxygen than carbohydrates
|
|
|
|
Fatty acids
|
fatty acids contain a carboxyl group at one end and a hydrocarbon chain can be either saturated or unsaturated saturated fatty acid accentuated with hydrogen all single covalent bonds between carbon atoms each carbon can hold 2 hydrogen
|
|
|
|
Unsaturated fatty acids
|
Fewer H atoms one or more double covalent bonds between carbon atoms
|
|
|
|
Glycerides
|
Consist of a molecule of glycerol and fatty acids 3 fatty acids make triglyceride or fat
|
|
|
|
Steroids
|
All have the same for ring structures example cholesterol used to make other steroids used in cell membrane hormones adrenal glands gonads ovaries testes
|
|
|
|
Phospholipids
|
Phosphate head hydrophilic and water loving fatty acid tails hydrophobic water fearing repels water is a polar molecule
|
|
|
|
Micelle
|
Ball of phospholipids normally used in digestive system has a bilayer make up cell membranes
|
|
|
|
Bilayer
|
Make up cell membranes will be important in cell transport
|
|
|
|
Proteins
|
Fundamental two bodies function and structure made up of amino acids 20 different amino acids and are polymers
|
|
|
|
Amino acids
|
1 all have the same basic structure to all contain carboxyl group an amino group 3 join together using dehydration synthesis reaction always the carbon carboxyl group joins to the nitrogen amino acid group carbon to nitrogen bond is a peptide
|
|
|
|
Primary structure
|
Sequence of amino acids
|
|
|
|
Secondary structure
|
Small scale bending folding coiling of the polypeptide chain certain amino acids are all attracted to each other
|
|
|
|
Tertiary structure
|
Large-scale bending folding coiling of the polypeptide chain give a protein its unique 3d dimensional shape 3d shape is called conformation if a protein loses its conformation it loses its function
|
|
|
|
Quaternary structure
|
Different polypeptide chains combined into a single protein different chains are called subunits example hemoglobin protein located in red blood cells
|
|
|
|
Some proteins
|
Ascetic groups not amino acid molecule built into protein example hemoglobin contains molecules of scheme contains Fe or iron protein is important in everything the body does and builds
|
|
|
|
The nature of protein
|
Protein that loses its shape or conformation and no longer functions
|
|
|
|
Agents of protein denature
|
High temperature pH shifts ionic shift
|
|
|
|
Nucleic acids
|
DNA and RNA polymers of nucleotide phosphate group monosaccharides nitrogen base
|
|
|
|
RNA
|
Is a single strand of nucleotides uses the sugar fibrose different base then DNA
|
|
|
|
DNA
|
Is a double strand of nucleotide bases bond to each other rival nucleic acid deoxyribose nucleic acid
|
|
|
|
DNA and RNA 5 different bases
|
cytosine guanine Adinene thiamine uracil. complimentary bases---only combine in certain combinations
|
|
|
|
Cell membrane
|
Made up of a phospholipid bilayer to Rows hydrophilic hydrophobic
|
|
|
|
Peripheral proteins antigens
|
Do not spend the width of the membrane or marker molecules
|
|
|
|
Receptors
|
Allow the cell to respond to the presence of specific molecules example hormones
|
|
|
|
Integral protein
|
Span the width of the membrane
|
|
|
|
Channel proteins
|
Small opening gated can open or close charged positive or negative
|
|
|
|
Carrier proteins
|
Changes confirmation to transport molecules across the membrane
|
|
|
|
Ion pumps
|
Carry ions across membranes
|
|
|
|
Diffusion
|
The movement of particles from areas of high concentration to areas of lower concentration high to low concentration gradient diffusion results from natural molecular motion
|
|
|
|
No net diffusion
|
Both sides are equal
|
|
|
|
4 factors that influence rate of diffusion
|
1--Temperature if temperature increases rate of diffusion increases if temperature decreases the rate of diffusion decreases temperature affects molecular motion --2--size of particles --3-concentration gradient and --4 -distance
|
|
|
|
Lipid solubility and diffusion
|
Ability for something to dissolve in fat lipid soluble molecules can freely dissolve the most substances dissolve in each other example lipid molecules fatty acids steroids and gases
|
|
|
|
Diffusion across the membrane size of molecules and channels
|
Open channels are so small only small molecules can diffuse through example h2o
|
|
|
|
Diffusion across the membrane charges on the particles and channels
|
Need an office only charge channel to move things through important for ions
|
|
|
|
Osmosis
|
Diffusion of water across a cell membrane
|
|
|
|
Isotonic solution
|
Equal volume concentration of a solution is equal to the solid concentration of a cell no net movement or diffusion
|
|
|
|
Hypertonic solution
|
Higher solu concentration outside the cell than inside the cell anything about 0.9 morsel you means less water water higher in cell water diffuses out of cell cell shrivels
|
|
|
|
Hypotonic solution
|
Lower solute concentration than in the solution inside a cell cell swells cell can explode water higher outside side when water diffuses into cell
|
|
|
|
Diffusion and osmosis
|
Require no cellular energy
|
|
|
|
Filtration
|
Movement of water and saw you to cross-sell barriers results from high hydrostatic pressure examples capillaries and blood pressure provide hydrostatic pressure
|
|
|
|
Facilitated diffusion
|
Use carrier proteins to move large non lipid molecules across the membrane carrier proteins change confirmation to move molecules across the membrane
|
|
|
|
Characteristics of facilitated diffusion
|
Move along concentration gradient high to low to specific carriers move specific molecules example glucose carrier proteins 3 often require signal molecules to bind to a receptor before the carrier changes its shape example glucose insulin is a signal molecule for glucose carriers
|
|
|
|
Rate of facilitated diffusion depends on
|
A the number of carriers NB abundance of signal molecules does not require energy is a type of diffusion
|
|
|
|
Active processes--- active transport
|
Requires cellular energy active transport ion pumps move ions against a concentration gradient low-to-high example sodium potassium pump in nueron
|
|
|
|
Endocytosis
|
So brings in large quantities of material involves changes in cell membrane
|
|
|
|
Pinocytosis
|
Fluid brought into cell
|
|
|
|
Phagocytosis
|
Cell brings in large cellular material phagocytes example white blood cells lysosomes digest cellular material
|
|
|
|
Exocytosis
|
cell secretes large quantities of material involves Golgi apparatus and secretory vesicles involves changes in the cell membrane ie.. gland cells
|
|

